Cerebral Circulation Disorder (CCD) is a common condition among the elderly. It is caused by dysfunction of the brain due to the compression, blockage, or narrowing of blood vessels that supply the brain, resulting in inadequate blood flow to nourish the brain.
What are the symptoms of CCD?
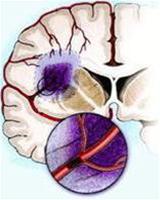 |
| Location of cerebral blood vessel blockage (Image: TTO) |
In acute cases of CCD, common symptoms include dizziness, light-headedness, nausea, vomiting, and a heavy head when changing positions. These symptoms often occur around midnight or early morning.
Many patients express their fear of these symptoms as they can easily be mistaken for a stroke, especially in individuals with hypertension. However, an episode of CCD does not cause weakness or paralysis of the limbs, face, or mouth. In addition to the typical symptoms during an acute episode, patients may also experience decreased concentration, reduced cognitive ability, slow comprehension, reluctance to engage in reasoning, and forgetfulness.
What causes CCD?
As mentioned earlier, CCD is caused by a lack of adequate blood flow to nourish the brain, which requires blood rich in nutrients, especially oxygen. This phenomenon may occur due to the aging process of cerebral blood vessels or vascular sclerosis (atherosclerosis of the brain).
Atherosclerosis is a condition that has long been recognized by medical professionals, characterized by thickening and hardening of the vessel walls and arteries (arteriosclerosis), with many atherosclerotic plaques that reduce blood flow and hinder circulation to the brain, leading to CCD.
The causes of atherosclerosis have been attributed to the deposition of fats, with cholesterol playing a central role. Cholesterol is primarily produced by liver tissue and is metabolized into HDL (High-Density Lipoprotein) and exists as LDL-C. Excessive amounts of this substance can lead to the formation of atherosclerotic plaques in the arteries (often referred to as “bad cholesterol”).
Scientific studies have shown that atherosclerosis and its complications are leading causes of mortality among the elderly.
How can CCD be prevented?
To effectively prevent CCD, elderly individuals should limit or avoid animal fats, alcohol, and egg yolks (as alcohol severely impacts liver function). Smoking, whether cigarettes or other tobacco products, should be absolutely avoided. Furthermore, the use of vegetable oils should also be moderated.
Elderly individuals should engage in regular daily exercise, following appropriate and gentle routines. Those with hypertension should be particularly cautious of potential strokes. Therefore, individuals at risk of CCD should undergo regular health check-ups at well-equipped medical facilities to receive appropriate monitoring, treatment, and scientific health advice from healthcare professionals.
Principles of CCD treatment
First and foremost, when experiencing an acute episode of CCD or transient ischemic attack, patients should be taken to a hospital immediately for timely examination and treatment. Treatment may involve the use of antiplatelet medications and drugs to enhance oxygen delivery to the brain. If there are accompanying conditions such as hypertension or diabetes, they need to be monitored and treated in conjunction.