On November 25, according to a statement from the Central Party Office, the Central Executive Committee of the Party has agreed to restart the Ninh Thuan Nuclear Power Project and continue research on the nuclear power program in Vietnam.
This initiative aims to ensure national energy security, meet socio-economic development goals, enhance scientific and technological capabilities, and promote sustainable development in the country.
Nuclear power is a long-established energy technology used by many developed countries to address urgent energy issues.
However, nuclear energy has some drawbacks and requires special attention to improve safety in its exploitation, usage, and international cooperation.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Nuclear Power
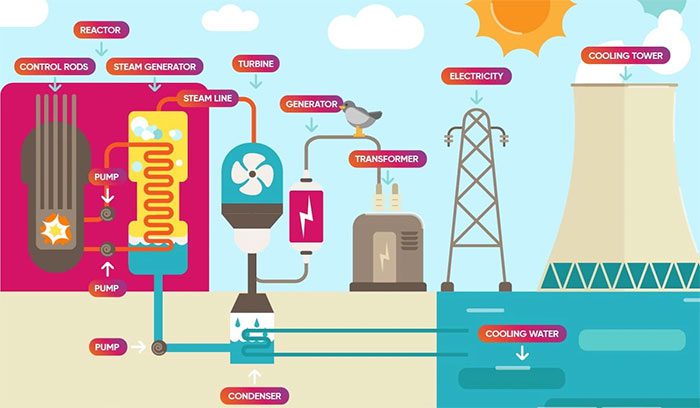
Basic model of a nuclear power plant (Photo: Aydemperakende).
Essentially, nuclear energy is the “leverage” generated by nuclear reactors through the release of their energy to produce heat. This heat is then used in steam turbines to generate electricity in power plants.
Compared to coal, gas, and other forms of power generation, nuclear power provides the lowest greenhouse gas emissions.
According to the Nuclear Energy Institute (NEI), nuclear fission produces more clean energy than any other energy source and is responsible for producing 62% of the total non-emitting electricity in the United States.
Another advantage of nuclear power is that once operational, the electricity generated by nuclear power plants is much cheaper than that produced by coal, gas, or any other fossil fuel plants.
Most of the costs are upfront (construction costs), and maintenance of the plants does not require excessive effort.
This factor, combined with the relatively long lifespan of nuclear power plants (approximately 40-60 years), creates favorable conditions for countries to implement nuclear power models.

Nuclear power technology is considered quite environmentally friendly (Photo: Getty).
Unlike other renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar energy, which depend on weather conditions, nuclear energy does not have such limitations. On the contrary, this model is not affected by climatic factors and still produces stable energy output even in times of disaster.
The biggest drawback of nuclear power is the very high initial construction costs, which can take 5-10 years.
Additionally, there is the risk of accidents. Chernobyl (Soviet Union), Three Mile Island (USA), and Fukushima Daiichi (Japan) are nuclear disasters that no country wants to experience.
However, accidents can still occur. In all the major nuclear incidents mentioned, human error or natural disasters led to the collapse of power plants.
Radioactive waste and its environmental impact is another crucial point to consider when discussing nuclear power.
Although the amount of radioactive waste generated during electricity production is small, it is considered hazardous. Therefore, waste must be stored safely to prevent environmental contamination.
How Developed Countries Apply Nuclear Power
Nuclear power plants have been built in 31 countries worldwide. Among them, two-thirds of the nuclear reactors are located in China, India, and Russia.

The USA is the largest producer of nuclear power in the world.
However, the USA is the largest producer of nuclear power globally, accounting for about 30% of the world’s nuclear power generation, according to data from World-nuclear.org.
In 2022, the nuclear reactors in the USA produced 772 TWh, representing 18% of the total electricity output.
Almost all of the USA’s nuclear power generation capacity comes from reactors built between 1967 and 1990, with no new construction projects initiated since 1977.
The reason for this is that the gas production source is considered more economically attractive, along with increased safety concerns following the Three Mile Island nuclear power plant accident in 1979.
Although new construction has nearly halted for over 30 years, the USA’s dependence on nuclear energy has been increasing each year.
Specifically, in 1980, nuclear power plants in the USA produced 251 TWh of electricity, accounting for 11% of the country’s total electricity output. By 2019, that output had risen to 809 TWh, representing over 30% of the total electricity generated from nuclear power worldwide.
China, the second-largest nuclear power producer, has a different approach, as the drive to develop nuclear energy is increasing due to air pollution from coal-fired power plants.
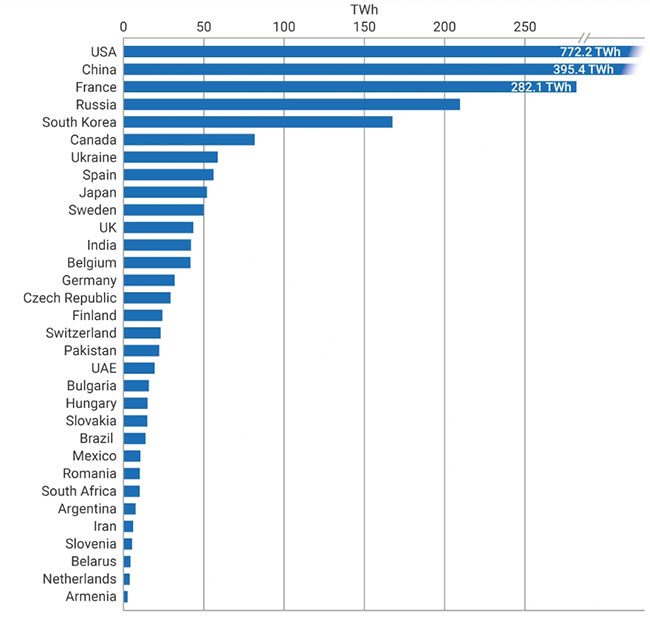
Nuclear power generation by country in 2023 (Source: World Nuclear Association, IAEA PRIS).
China aims to “go global” by exporting nuclear technology, leveraging its significant advantages in the nuclear supply chain and closed-loop systems.
According to World-nuclear.org, China has largely become self-sufficient in designing and building reactors but still maximizes the use of Western technology, combining improvements in the process.
Currently, there are 30 reactors under construction in China, and it is expected that the country will surpass the USA in nuclear power generation in the near future.
France, ranked third in nuclear power generation, has the advantage of being the largest net exporter of electricity in the world due to very low electricity production costs, earning over 3 billion euros annually from this.
Currently, France produces about 70% of its electricity from nuclear energy thanks to a long-term policy focused on energy security, while actively developing nuclear technology.
Reactors, especially fuel products and services, are significant export items for France.
In February 2022, France announced plans to build 6 new reactors and is considering building 8 more reactors.
In an interview, Mr. Tran Chi Thanh, Director of the Vietnam Atomic Energy Institute, stated that the global trend is returning to nuclear power to combat climate change and balance CO2 emissions.
“The current trend in many countries is to combine nuclear power with renewable energy. Nuclear power serves as a solid foundation for developing renewable energy because the electricity system needs a stable source of power to ensure reliable operation,” the expert analyzed.
Dr. Ngo Duc Lam, former Deputy Director of the Institute of Energy (Ministry of Industry and Trade), mentioned that many countries, including Russia, have begun transitioning from large-scale nuclear power to smaller-scale, lower-cost nuclear energy.
The favorable conditions of small modular reactor nuclear energy include low costs, short construction times, making it suitable for most countries, and meeting electricity supply demands promptly.