The Tasmanian devil may have an incredibly cute face, but it is quite fierce when it comes to mating. After mating, the male can even lose its life.
The Tasmanian devil’s scientific name is Dasyurus. This creature is like the “hybrid child” of a cat and a mouse, with brown or black fur adorned with white spots, a pink nose, and strong teeth.
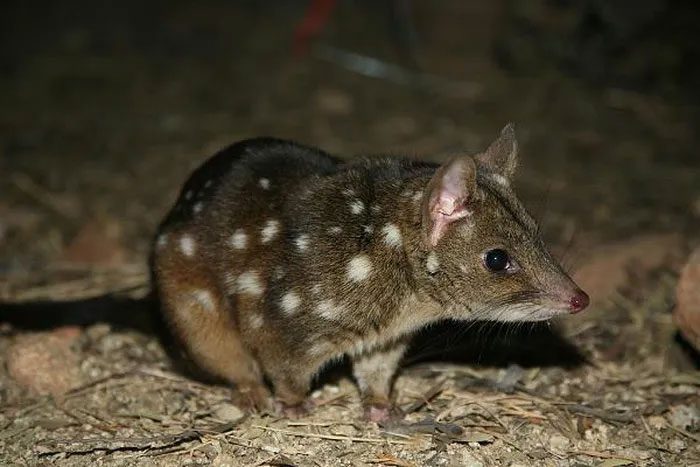

Tasmanian devil.
The Tasmanian devil is native to Australia and Papua New Guinea. Its diet mainly consists of insects and other small animals, fruits, and nuts… It is a carnivorous marsupial. Therefore, it is not as approachable as many other small animals due to its very sharp teeth and readiness to attack anyone who comes near.
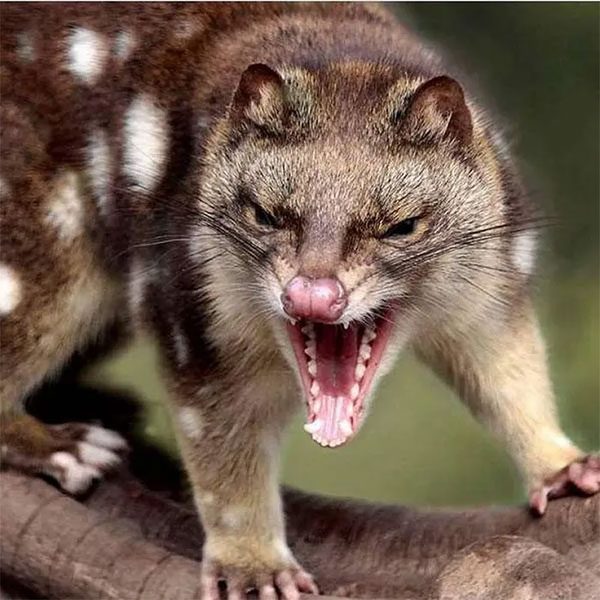

This animal exhibits quite aggressive behavior during mating.
The Tasmanian devil is a nocturnal creature. It prefers to hide in its “den,” which can be a self-dug burrow, in trees, or in termite mounds. This animal displays quite aggressive behavior during mating. Each mating session lasts an average of several hours but can extend up to a day. This is because males do not release a lot of sperm at one time, so they must ejaculate multiple times to ensure that sperm can fertilize the eggs.
After selecting a mate, Tasmanian devils will mate approximately five times. However, if the male does not satisfy the female during mating, the female is always ready to seek out a better mate.
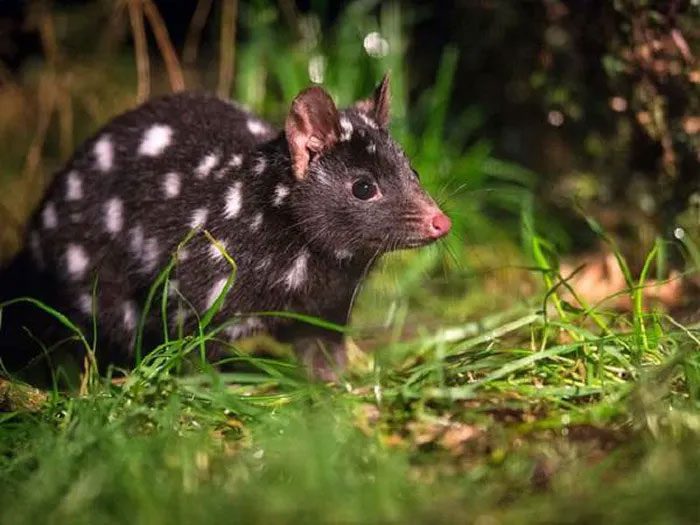

The Tasmanian devil prefers to hide in its “den,” which can be a self-dug burrow, in trees, or in termite mounds.
Therefore, under the stimulation of the female Tasmanian devil, the male will extend the mating duration to pass on its wonderful genes. However, male Tasmanian devils often exhaust themselves to death in their frantic pursuit to mate as often as possible.
Throughout the mating season, male Tasmanian devils expend a significant amount of testosterone (the sexual hormone) and must fight with other males, spending very little time eating and sleeping.
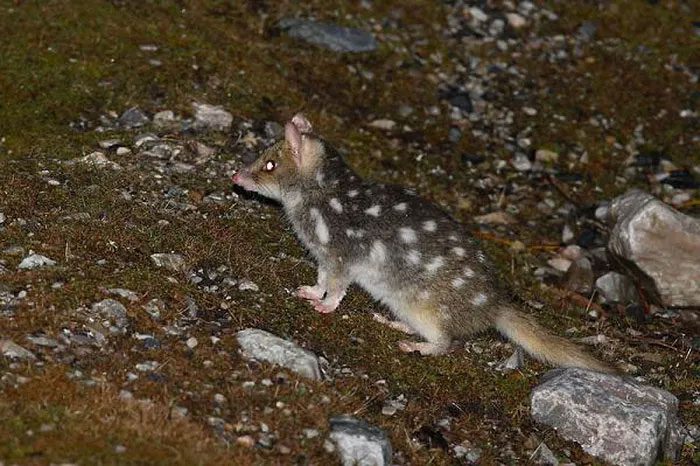

Males produce far more sperm than females produce eggs.
So why is the act of mating in nature “in the hands” of the females? The choice of mating in nature has one purpose: to reproduce a new generation.
Males produce far more sperm than females produce eggs. Moreover, during reproduction, the male’s only role is to mate; it has no involvement in providing for their offspring. The female, on the other hand, is responsible not only for mating but also for carrying and giving birth, as well as nurturing the young. Therefore, males will not let go of any female they can mate with.