The Grizzly Bear: An Impressive Creature Captivating Humans for Centuries The enormous size and strength of grizzly bears make them one of the most formidable predators in North America.
The Largest Grizzly Bear Ever Captured
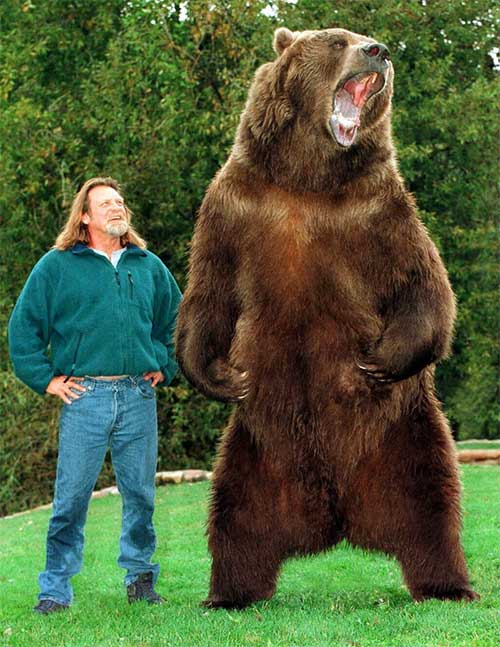
The largest recorded North American grizzly bear weighed more than a moose, which is an astonishing feat since moose are among the largest terrestrial animals in North America.
The largest recorded North American grizzly bear was captured in Alaska. The male bear was killed by a hunter named Larry Fitzgerald, who was hunting with a guide in the Alaskan wilderness.
The bear weighed approximately 1,600 pounds (730 kg) and stood over 10 feet (3 meters) tall when on its hind legs. This bear was estimated to be around 15 years old and was considered a problematic bear by local authorities due to its involvement in several human-bear conflicts in the area.
The skull of this North American grizzly bear was also measured, revealing a size of 27 inches, making it the largest grizzly bear skull ever recorded.
While the size of these bears is impressive, it is worth noting that the hunting of North American grizzly bears is widely debated among individuals. Many believe that these animals should be protected and allowed to live freely in their natural habitats.
This is particularly important because North American grizzly bears play a crucial role as a keystone species in several ecosystems, helping to maintain the balance of these systems. Consequently, many areas have established “North American Grizzly Bear Recovery Zones” and are taking steps to minimize conflicts between humans and bears.
It is essential to protect these massive creatures so they can thrive in their natural environments, playing a vital role in maintaining the health and diversity of our ecosystems.
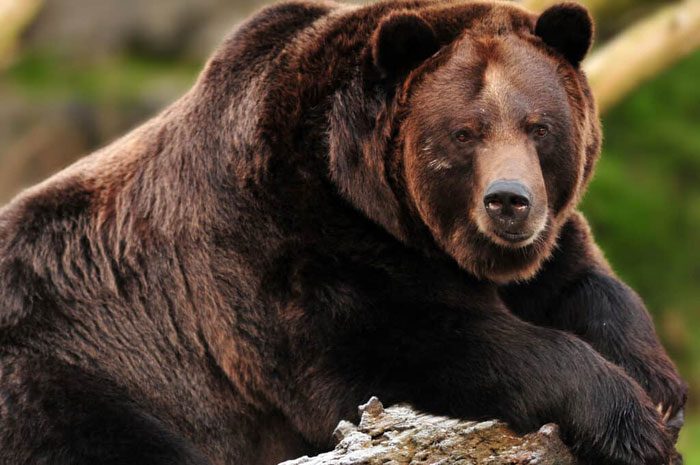

The largest recorded North American grizzly bear was captured in Alaska.
Average Size of a North American Grizzly Bear
An average North American grizzly bear stands about 7 feet (2.1 meters) tall and can weigh up to 860 pounds (400 kg). Females are typically smaller, averaging around 6 feet (1.8 meters) tall and weighing between 250-350 pounds (113 – 160 kg). However, there are exceptions, such as the giant bear previously mentioned.
Average Size of a Moose
Moose come in various subspecies, with sizes differing based on age, nutrition, and geographic location. Therefore, their weights also vary depending on the moose subspecies.
Moose are typically among the largest terrestrial animals globally, weighing on average between 875-1,600 pounds (from 400 to over 700 kg). They can stand anywhere from 6-7 feet (averaging around 2 meters) to over 10 feet (3 meters). Notably, some adult male moose can reach about 2.4 meters from hoof to shoulder.
These impressive animals truly amaze, and witnessing them in the wild is an unforgettable experience.

Their weight also varies depending on the moose subspecies.
Reasons Grizzly Bears Can Reach Giant Sizes
The largest recorded North American grizzly bear is an incredible feat when considering the natural size and strength of these animals. So, what causes them to grow to such sizes?
Reason 1: Genetics
Genetics is one of the primary reasons this North American grizzly bear grew larger than average. Grizzly bears have existed for thousands of years, allowing ample time for them to evolve and adapt to their environment.
Over time, bears with larger body sizes have been more successful in hunting, mating, and surviving in the wild. As a result, these larger bears have passed their genes onto their offspring, creating a population of larger bears.

North American grizzly bears have existed for thousands of years, allowing ample time for evolution.
Scientists have discovered that specific genes, such as those related to metabolism and growth hormones, influence the size of bears. These genes produce growth hormones that help develop muscle and bone tissues in bears.
The diploid genotype of North American grizzly bears comprises 37 pairs of chromosomes and an average distance of 688 base pairs between heterozygous positions in this combination. It is essential to consider other factors, such as diet and hibernation patterns, when determining the size of North American grizzly bears.
Reason 2: Diet
The diet of bears is a critical factor explaining why North American grizzly bears are so enormous. Grizzly bears are omnivores, meaning they consume both plant and animal matter. Their diverse diet includes everything from berries and nuts to fish, small mammals, and even larger prey.

Grizzly bears are omnivores, meaning they eat both plants and animals.
North American grizzly bears often eat salmon and other fish in areas rich in aquatic life. These fish are high in protein and fat, essential nutrients for bears. Protein aids in building and repairing muscle tissues, while fat provides the necessary energy to survive in the wild.
In areas where larger prey, such as moose, are available, North American grizzly bears will also consume them. By eating these larger prey, grizzly bears can gain weight and grow larger than those that only consume berries and nuts. These animals also offer a high protein and fat content, making them a crucial part of the North American grizzly bear’s diet.
However, North American grizzly bears do not always have access to these large prey, especially in food-scarce areas. In such situations, bears must rely on other food sources, such as berries, nuts, and small mammals. While these foods are not as rich in protein and fat as larger prey, they still provide sufficient nutrients for bears to survive and grow.
The amount of food also plays a role in the physical development of North American grizzly bears. Bears with access to abundant food sources can consume more calories and nutrients, allowing them to grow larger than those limited in food access.
Reason 3: Habitat
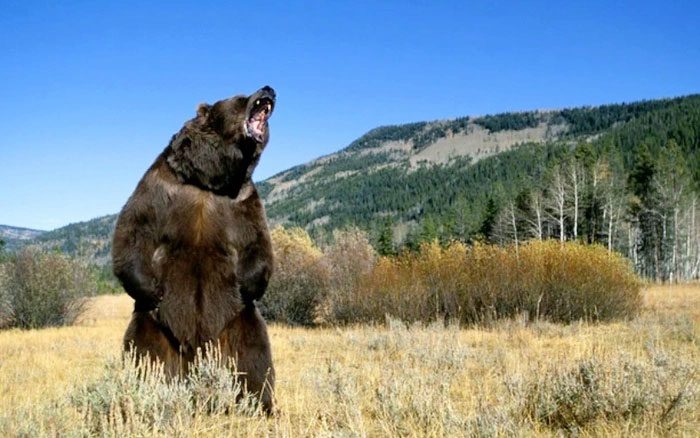

Each habitat can influence the size and development of North American grizzly bears.
North American grizzly bears are found in various habitats, including forests, mountains, and tundras. Each of these habitats provides different resources and challenges, which can affect the size and development of grizzly bears.
Grizzly bears can gain more weight and grow significantly more in areas with abundant food and a milder climate than in harsher environments. For example, bears living along the coastal areas of Alaska may have access to more fish and other food sources than those living inland. Coastal bears tend to be larger than those living inland.
Habitat also plays a vital role in the physical development of North American grizzly bears. Bears living in areas with steep terrain and rugged landscapes tend to be more muscular than those in flat areas. This is because bears in these areas must exert more effort to climb and navigate their environment, building muscle and enhancing their strength.
Another factor that can affect the size and growth rate of bears is the bear population density. In areas with high bear densities, there may be more competition for food and resources. This can make it difficult for bears to obtain the necessary nutrients to grow and develop. Conversely, areas with lower bear densities may provide more resources for each bear, allowing them to grow larger.