Cabbage is a common vegetable that thrives in winter. However, it is also a nutritious vegetable that is used for eating, healing, and beauty…
Table of Contents: Benefits of Cabbage
- Helps Form Red Blood Cells
- Prevents Cancer
- Good for Cardiovascular Health
- Boosts Immunity
- Aids in Weight Loss
- Detoxifies the Body
- Good for the Brain
- Good for the Eyes
- Anti-Inflammatory
- Bone Health
- Helps with Headaches
- Promotes Digestive Health
- Good for Pregnant Women
- Despite Many Benefits, Cabbage Is Not Recommended for the Following People:
- How to Best Consume Cabbage?
The nutritional content and vitamin levels in cabbage are 4.5 times higher than carrots and 3.6 times higher than potatoes. Additionally, vitamins A and P in cabbage work together to strengthen blood vessel walls. Cabbage also contains anti-cancer compounds such as sulforaphane, phenethyl isothiocyanate, and indole-3-carbinol. However, there are many other benefits of cabbage that we may not be aware of:
Helps Form Red Blood Cells
Iron is an essential component that promotes the formation of red blood cells, thus preventing symptoms of anemia. Consuming cabbage along with orange or grapefruit juice can optimize iron absorption from cabbage.
Prevents Cancer
Cabbage and other cruciferous vegetables contain compounds that can combat cancer cells in the body. They stimulate enzymes to inhibit tumor growth. Research in China has also shown that women who consume certain amounts of vegetables such as cabbage and broccoli have a reduced risk of breast cancer symptoms.

Cabbage has a higher vitamin content than many other vegetables.
This leafy vegetable contains a group of compounds known as glucosinolates, which are sulfur-containing compounds. They break down in the body to form bioactive compounds such as isothiocyanates, indoles, nitriles, and thiocyanates that have anti-cancer effects.
Studies have found that indoles and isothiocyanates can inhibit the growth of various cancers, including bladder, colon, breast, liver, lung, and stomach cancers.
Research has shown that cabbage contains sulforaphane, a sulfur-containing compound capable of inhibiting a dangerous enzyme called histone deacetylase (HDAC), which is responsible for cancer cell growth.
Another study indicated that red cabbage possesses a strong antioxidant known as anthocyanin (a compound that gives color to fruits and vegetables), which has been shown to slow the proliferation of cancer cells.
Good for Cardiovascular Health
What other effects does cabbage have? Cabbage is high in potassium, which is beneficial for cardiovascular health and helps maintain healthy blood circulation while preventing blockages in the blood vessels to the heart. Potassium is also effective at reducing symptoms of hypertension. The high potassium content in cabbage makes it one of the recommended foods for managing high blood pressure.
Boosts Immunity
Not only fruits like oranges, grapes, or apples are rich in vitamin C, but cabbage also contains a significant amount of this vitamin, which helps strengthen the immune system. Vitamin C is also excellent for skin health.
Aids in Weight Loss
Cabbage is among the top vegetables recommended for those looking to lose weight naturally and healthily. It contains many vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients. You can consume large amounts of cabbage since it is high in fiber and low in calories, which will not contribute to weight gain.
Detoxifies the Body
Thanks to its high vitamin C and sulfur content, cabbage can help eliminate toxins (free radicals). Free radicals are one of the main causes of arthritis, skin diseases, rheumatism, and gout.
Good for the Brain

Cabbage or cruciferous vegetables are rich sources of vitamin K.
Cabbage and other cruciferous vegetables provide a wealth of vitamin K and anthocyanin, which can support mental health and brain focus. These nutrients may also help prevent nerve damage, reducing the risk of Alzheimer’s disease and dementia. Thus, cabbage is very beneficial for your brain health.
Good for the Eyes
Cabbage is a rich source of beta-carotene. Most people, especially the elderly, who regularly consume cabbage can help prevent macular degeneration and improve eye health, as well as prevent cataracts. Beta-carotene has been shown in some studies to reduce the risk of prostate cancer.
Anti-Inflammatory
Cabbage has anti-inflammatory properties and is a major source of glutamine. Glutamine is a powerful anti-inflammatory substance, so consuming cabbage can reduce the effects of conditions such as inflammation, irritation, allergies, joint pain, fever, and skin disorders.
Bone Health
Cabbage contains minerals such as calcium, magnesium, and potassium. These minerals are known for their ability to maintain bone health.
Helps with Headaches
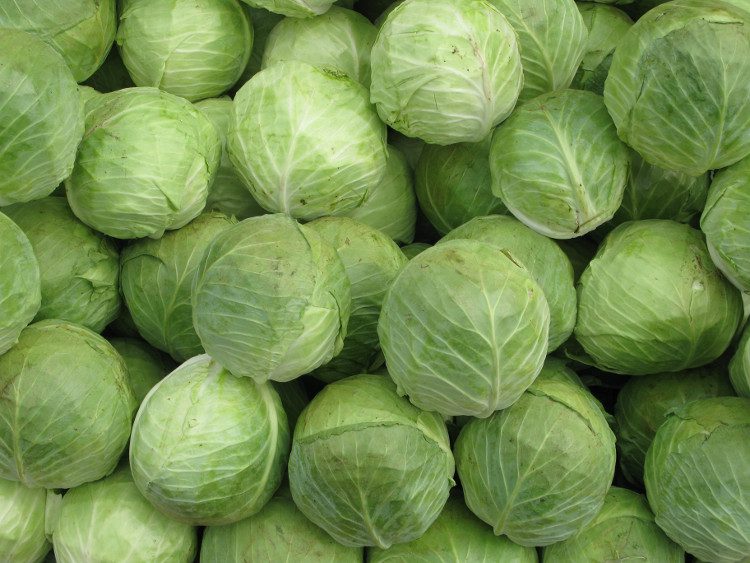

Crushing cabbage leaves and placing them on the forehead can also relieve headaches.
Using cabbage leaves as a warm compress can help alleviate headaches. Moreover, crushing cabbage leaves and placing them on the forehead can also provide relief. For chronic headaches, consuming cabbage juice (25-50ml) may help eliminate headache pain.
Promotes Digestive Health
Like other vegetables, cabbage helps with bowel movements due to its high fiber content.
Good for Pregnant Women
Folic acid is crucial for fetal development; therefore, consuming cabbage can help meet the nutritional needs for folic acid in pregnant women.
Despite Many Benefits, Cabbage Is Not Recommended for the Following People:
People with Thyroid Issues or Goiter
Cabbage contains small amounts of goitrin, which can exacerbate goiter and thyroid enlargement. Therefore, it should only be consumed in moderation, cut into leaves, soaked, and finely chopped before cooking to allow goitrogen to break down.
People with Kidney Problems
Research indicates that cabbage contains a considerable amount of oxalic acid. Overconsumption of cabbage may lead to oxalic acid combining with nutrients such as potassium, magnesium, iron, and calcium, forming oxalate salts, which can deposit in the kidneys and increase the risk of kidney stones.
Thus, patients with severe kidney failure or those on dialysis should absolutely avoid cabbage.
For healthy individuals, it is advisable to chop and cook cabbage thoroughly to minimize oxalic acid levels.
Fermented cabbage. (Photo: Vietnam+).
People with Stomach Issues
Eating raw cabbage can cause bloating, especially for those with stomach pain. Therefore, it should not be consumed raw; if eaten, it should be cooked.
People with Cold Body Constitution
According to traditional medicine, cabbage is considered a cooling food; thus, individuals with a cold body constitution who often feel cold in their hands and feet, or have abdominal coldness after eating cold foods, should limit their cabbage intake. If they still wish to consume cabbage, adding a piece of fresh ginger during cooking can help neutralize the coolness of cabbage.
Allergy Sufferers
Individuals who are currently experiencing allergies should avoid consuming large amounts of cabbage, especially fermented cabbage, as it can exacerbate allergic reactions or lead to subconjunctival hemorrhaging. The reason for this is the histamine content in fermented cabbage, which can cause itching, congestion, tearing, and runny nose.
Individuals on Anticoagulant Medications
Cabbage contains vitamin K, a substance known to promote blood clotting. Therefore, individuals taking anticoagulant medications such as warfarin should limit or avoid eating cabbage.
Cabbage may also interact with other medications, including oxazepam (Serax) and diabetes medications.
How to Best Consume Cabbage?
Nutritional experts recommend that healthy individuals eat cabbage 3-4 times a week to reap the benefits of this vegetable. Although cabbage is rich in nutrients, relying solely on it can limit the intake of other essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants in your diet.
It is important to aim for a diverse diet that includes a variety of colorful vegetables and fruits to ensure you receive a complete range of nutrients. Remember, a balanced and diverse diet is the foundation of good health.