Food can become contaminated with bacteria from water sources, waste, soil, or during the human processes of production and transportation.
| Article by Dr. Pharm. Pham Duc Hung (who interned at Harvard University, USA; PhD graduate from KU Leuven, Belgium) and Dr. Nguyen Thi Thanh Van (specializing in Biotechnology, working at Uppsala University, Sweden) on common microorganisms that can cause food poisoning. |
Groups of Microorganisms Causing Food Poisoning
In addition to Clostridium botulinum, many other types of microorganisms can also cause food poisoning, including: Clostridium, Salmonella, Campylobacter, Listeria, Bacillus cereus, E. coli, Staphylococcus, and Shigella.
Listeria is a very dangerous food poisoning agent, with a mortality rate of 20-30% among cases. This group of bacteria is widely present in the environment and can be isolated from soil, fruits, vegetables, milk, and unpasteurized dairy products. The incubation period ranges from 7 to 70 days, and the illness can last for several weeks.
Salmonella is widely found in nature, primarily in the intestines of humans and animals. It is often found in poultry meat and eggs, as well as in unpasteurized milk and cheese. The incubation period is 12-72 hours, and symptoms can last from 4 to 7 days.
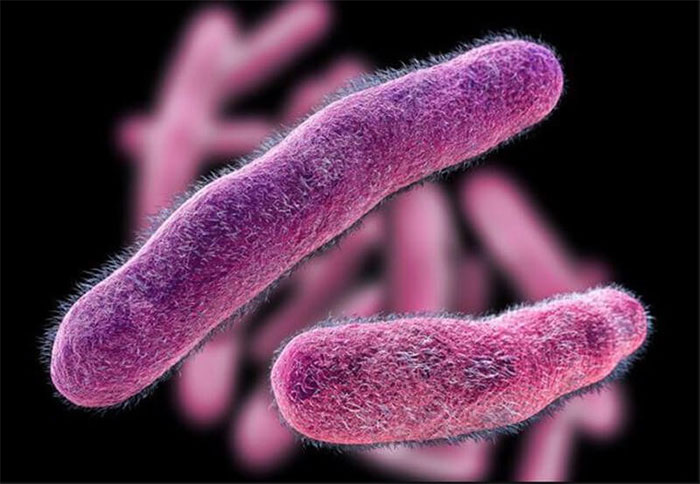
Salmonella is commonly found in poultry meat and eggs. (Photo: Innovationtoronto).
Campylobacter is one of the most common bacteria causing stomach pain. It typically resides in the intestines of livestock and poultry, and is often found in raw meat, unpasteurized milk, and contaminated water. The incubation period is 2 to 5 days, with the illness lasting 7-10 days.
In some severe cases, patients may develop Guillain-Barré syndrome (GB), which causes weakness and can lead to paralysis of the muscles within 2-4 weeks after infection. This syndrome can last for weeks to years. It is estimated that approximately 40% of GB cases in the USA are caused by Campylobacter.
Bacillus cereus is also one of the common causes of stomach pain worldwide. This bacterium can form heat-resistant spores, allowing it to be found in both raw and cooked foods. The incubation period is very short, occurring within a few hours, and infected individuals may recover on their own.
E. coli is a very common bacterium found in the intestines of humans and animals. The main sources of infection are feces, untreated water, and raw foods. The incubation period is 3 to 4 days, with symptoms lasting up to 10 days. Most patients will recover within 6 to 8 days.
Staphylococcus primarily resides on hosts in humans and animals. The bacteria can thrive on food and release toxins. Foods that are easily contaminated include meat, eggs, milk, and dairy products. While cooking can kill the bacteria, their toxins may still remain in the food.
Food contaminated with Staphylococcus toxins does not spoil or have an unpleasant odor, making it difficult to detect. Symptoms can appear from 30 minutes to 8 hours after consuming contaminated food.
Shigella is the most common bacterium causing diarrhea. Foods that are easily contaminated include fresh fruits and vegetables, as well as raw milk. Symptoms can appear 1 to 2 days after consuming contaminated food and can last for 5-7 days.
How to Prevent Food Poisoning
People should limit the consumption of high-risk foods that are not pasteurized, such as milk or fruit juices, raw seafood, and undercooked meats.
For fresh fruits and vegetables, you should wash them under running water before cooking, packaging, or eating. Leftover or unused food should be stored in the refrigerator.
Keep raw foods separate from cooked foods to avoid cross-contamination. If using the same cutting board for raw meat and cooked foods, it is essential to wash the board with warm water and soap between uses. We should thaw food in the refrigerator or microwave.
Finally, don’t forget to wash your hands. Wash your hands with soap and water for at least 20 seconds, especially after using the restroom and before cooking.


















































