Scientists have successfully hacked the genetic code of cells to give proteins new powers. If applied, this method could cure many diseases. Humanity even dreams of the possibility of being as strong as superheroes.
The dream of immortality and superhuman health has always been a hope for mankind. This can be seen in the superhero characters of American science fiction films.
These are individuals with intelligence, strength, superpowers, and a resilient body always ready to protect humanity, safeguarding the Earth from domination and destruction by ruthless underground forces.
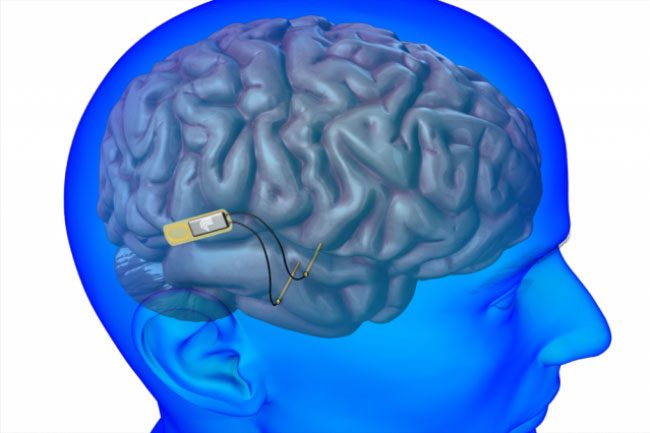
Inserting electronic chips into the human body is no longer unusual – (Photo: AFP).
Moreover, after completing their rescue missions, these superheroes return to normal life as mere students, also eating, studying, loving, feeling joy and anger like ordinary people.
Transforming into a superhero is not just a fanciful dream of children; it has a real scientific basis.
Transforming Humans into Superheroes
Many scientists have devoted their passion and resources to projects like this, and the current pioneer is the world’s richest technology billionaire Elon Musk.
In addition to his ambitious space projects, he is also leading in the field of artificial intelligence (AI). Recently, on May 25, his startup Neuralink received approval from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to test a device developed by the company for implantation into the human brain.
According to information provided by Elon Musk, this device has the ability to decode human brain activity and connect the brain to computers.
Musk has also stated that this implant could potentially cure diseases such as obesity, autism, depression, and schizophrenia, in addition to allowing web browsing through thought and interaction without physical contact.
During a presentation, Neuralink showed the audience footage of monkeys playing basic video games and moving a cursor on a screen using the Neuralink device.
If the implantation is successful in humans, this event will officially usher in an era of true cyborgs.
In fact, the term “cyborg” first emerged in the 1960s as a contraction of the words “cybernetic” and “organism”. Today, it refers to beings that exist in both biological (human) and artificial (machine) forms.
If this can be achieved, the boundary between humans and computers will gradually blur, allowing humans to think faster and work with vast amounts of computer data, while computers will enhance the weaknesses and deficiencies of human biology, making it stronger and healthier.
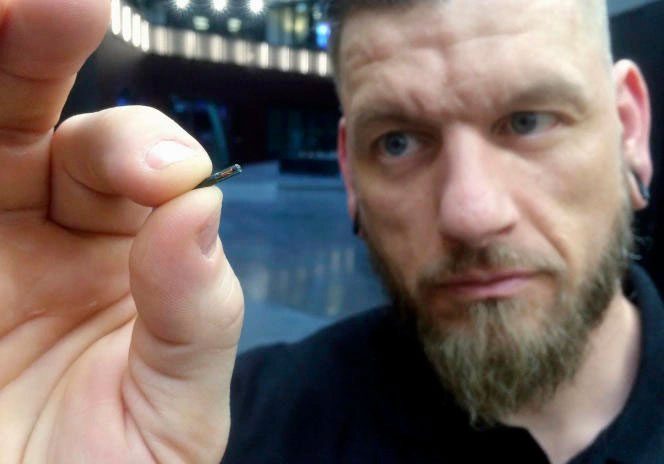

Chips are becoming smaller, contributing to human life support – (Photo: AFP).
Scientists are even aiming for humanity’s deepest desire for immortality by transferring their life essence into a soulless machine.
This means that in the future, when the connection between the brain and computer systems is perfected, we could copy our entire memories and personalities and store them in cloud computing systems.
When the biological body dies, the next step would be to transfer all copied data into a human-shaped “super robot”, equipped with some upgraded “android” operating system, allowing us to continue “living” immortally with our digitized intelligence and personality, becoming a true cyborg.
James Lovelock – a renowned British scientist and novelist, the father of the Gaia theory (Earth as a living superorganism that continuously self-regulates) – has predicted that the first cyborg will appear no later than 2050.
Becoming the richest person in the world proves that Elon Musk is not a “madman” investing in fanciful and unproductive ventures.
The Neuralink project must be the result of the culmination of numerous successful biotechnological experiments by renowned scientists, combined with groundbreaking developments in information technology that create ultra-small chips capable of integrating and functioning within the human brain.
Indeed, looking at the broader picture, scientists have made rapid and remarkable progress in the field of biotechnology, laying the groundwork for Musk’s confident undertaking of this project.
Hacking Cells and DNA to Cure Diseases
In a study published in the journal Nature Biotechnology in 2017, scientists hacked a cell and reprogrammed it like a conventional computer.
In simple terms, cells function like tiny computers, capable of receiving and issuing information.
For example, if we consume a lot of candy, the blood sugar level rises, prompting pancreatic cells to receive this information and then release insulin to lower the blood sugar level.
Similarly, scientists have found ways to intervene and modify DNA algorithms, and can command a specific segment of DNA to emit light, for instance.
Biologist Wilson Wong from Boston University (USA), the lead researcher on this project, stated that they could use these glowing cell parts to diagnose diseases by activating them with a specific protein related to certain diseases.
If the cells glow after being mixed with a patient’s blood, it indicates that the blood test subject has that disease. This will be a much cheaper diagnostic method compared to current blood testing methods.
Recently, on June 20, the journal Nature reported that Peter Schultz and his colleagues at the University of California, Berkeley (USA) successfully hacked the genetic code of cells to endow proteins with new powers. If applied, this method could cure many diseases.
In another study, Swiss scientists amazed the world by successfully testing a flexible electronic tissue made from silicon and platinum electrodes to reconnect damaged nerves during spinal grafts.
The Da Vinci channel also reported that British scientists developed a hearing device implanted in the ear connected to the brain’s nerves, allowing deaf individuals to hear. Similarly, they developed a camera linked to a computer, which analyzes colors and transmits them to a device implanted in the visual cortex, stimulating nerve cells in the visual cortex to help the blind see.
A notable success in biotechnology was the creation of the sheep Dolly by Ian Wilmut, Keith Campbell, and their colleagues at the Roslin Institute in Edinburgh, Scotland through cloning. This sparked a debate on whether cloning should be applied to humans.
Bioethical Issues and the Future of Humanity
Humans often feel excited about groundbreaking scientific advancements aimed at helping humanity live healthier, longer, and happier lives.
However, the darker side of it, if imagined, could lead humanity to a terrifying future, presenting many challenges for today’s generation.
The first issue is defining what it means to be HUMAN. Human identity will change completely if people are connected to computers.
Will humans control computers, or will they be trapped in a vast cloud of data that suppresses their minds, forcing them to decide and act according to the predetermined dataset? There will be no freedom, creativity, and a loving heart that no computer can measure or replace.

The Matrix is a science fiction film featuring humans cloned as robots.
And if humans become “immortal” cyborgs, could we clone thousands of such “cyborgs” to serve as tools for war?
Similarly, regarding cloning, theoretically, they could clone as many identical humans as desired.
At that point, humans could no longer be regarded as unique individuals with fundamental rights as defined by the United Nations Charter, but would instead become mere lifeless data files.
The second issue is related to social governance. Who will maintain social order when all of humanity is connected through computer networks? Who governs the computer networks? If a malicious actor hacks the computer network, shuts it down, or even cuts off the power, what will happen to humanity? A single click from a bad actor could lead to catastrophic consequences for everyone.
It’s important to remember that in 2017, experts from the University of Washington (USA) published a remarkable study. For the first time in the world, they used gene encoding molecules to attack and seize control of a computer.
Therefore, lawmakers and governments around the world must exercise extreme caution regarding research that directly intervenes with human beings, as a catastrophic scenario, even extinction for humanity, could very well occur.