Virgin Galactic Successfully Completes Fifth Crewed Flight to Suborbital Space Ahead of Commercial Operations Next Month.
The Eve aircraft successfully took off from the runway. (Video: Virgin Galactic)
The mission on May 25, named Unity 25, marks Virgin Galactic’s first flight to suborbital space since July 2021, following the company’s historic flight carrying billionaire Richard Branson, the founder of the Virgin Group, along with other passengers.
Virgin Galactic employs an air-launch system to transport passengers and research equipment to suborbital space. Currently, this system includes two operational vehicles: a spaceplane with a capacity for 2 pilots and 6 passengers named VSS Unity, paired with the carrier aircraft VMS Eve. Unity takes off from the runway, being carried aloft beneath the wing of Eve. Upon reaching an altitude of 15,000 meters, Eve releases Unity, allowing the vehicle to ignite its rocket motor and continue into suborbital space.
Passengers aboard Unity will experience several minutes of weightlessness and view Earth against the black backdrop of space before returning to the runway. Unity has completed five such flights. The latest mission began at 11:15 PM on May 24, Hanoi time, when Eve took off from Spaceport America in New Mexico. Unity was attached to a pylon situated between the two fuselages of the carrier aircraft.
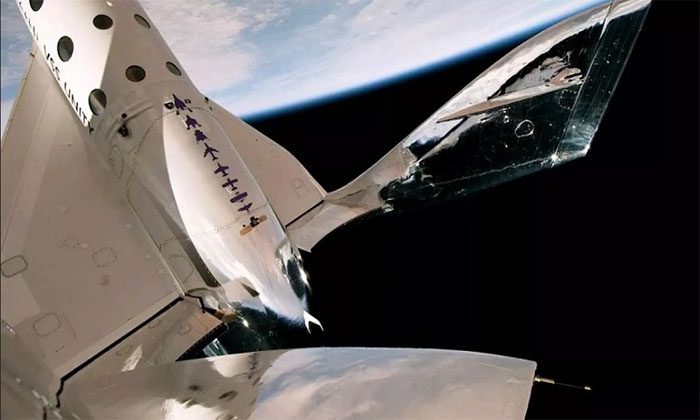

After separation, Unity reached a maximum speed of Mach 2.94 (3,630 km/h) and a peak altitude of 87.2 km.
A total of 8 individuals participated in the flight, all of whom were Virgin Galactic employees. Jameel Janjua and Nicola Pecile piloted VMS Eve, while Mike Masucci and C.J. Sturckow operated VSS Unity. The cabin of the spacecraft included Beth Moses, the astronaut training director (wife of Mike Moses), astronaut trainer Luke Mays, mission specialist Christopher Huie, and Jamila Gilbert. Unity 25 marks Beth Moses’ third spaceflight.
After separation, Unity achieved a maximum speed of Mach 2.94 (3,630 km/h) and a peak altitude of 87.2 km, according to a Virgin Galactic representative. This altitude is considered sufficient for spaceflight according to NASA and the U.S. Air Force. However, space is officially recognized as beginning at an altitude of 100 km. Unity returned to Earth at 12:37 AM on May 26, landing at Spaceport America. Eve landed shortly after, concluding the Unity 25 mission.
After the flight in July 2021, Virgin Galactic grounded both Eve and Unity for maintenance and upgrades. For example, Virgin Galactic replaced Eve’s pylon. Such changes have made the Eve-Unity system more robust and durable. The company aims to conduct monthly flights with Eve and Unity after commencing commercial operations. However, they have even higher long-term goals, including building a fleet of spaceplanes capable of launching weekly, projected to commence operations in 2026.
Virgin Galactic faces significant competition in the suborbital space tourism industry from Jeff Bezos’ Blue Origin. Blue Origin’s New Shepard rocket and capsule system has conducted six crewed space missions but has been grounded since September 2022 after a vehicle malfunction during a crewless research mission.