Artificial Intelligence (AI) is not a new concept. The renowned inventor Adolph Whitman introduced AI-supported robotics over 100 years ago.
The German scientist Adolph Whitman was a visionary in the field of AI and robotics. His most famous invention that broke the boundaries of robotics was Occultus, developed in 1909. It was one of the first types of robots capable of understanding human language. It could move autonomously, respond to commands, and interact with people in a comprehensible manner.
Technological Marvel
At the time of its creation, Occultus garnered widespread attention from the invention community due to its unparalleled capabilities compared to other robots of its era. Whitman enabled this robot to walk, move, talk, sing, whistle, and even laugh. With its appearance resembling that of a bearded man, Occultus was so human-like that it was indistinguishable from a distance of one meter.
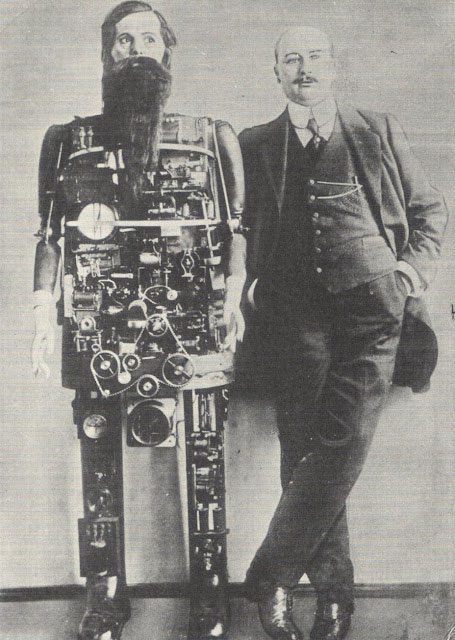
A rare photo of the Occultus robot and its creator Adolph Whitman. (Image: History of Yesterday).
It was composed of numerous gears and intricate machinery. The chest contained several turntables, but the way these mechanisms were controlled remains a secret of the inventor. It is said that wireless signals were the magic behind Occultus. Each part of the robot was operated by a small electric motor.
More importantly, Occultus was equipped with a range of sensors and motors that allowed it to move easily. Two cameras installed in its body enabled the robot to detect surrounding objects as well as recognize faces. Additionally, it had four infrared proximity sensors located at each corner of its body to prevent collisions with objects or people while navigating through tight spaces.
Occultus also possessed an AI tool that allowed it to analyze speech and make decisions based on that speech. This enabled Occultus to respond appropriately to human commands and recognize simple gestures such as waving or pointing.
Safety was a crucial factor when Adolph Whitman designed Occultus. He incorporated proximity sensors to detect if anything or anyone approached the robot too closely and automatically shut down all motors until the threat was no longer present. Furthermore, these sensors also helped Occultus learn simple tasks without the risk of injury or damage from collisions.
Beyond being a technological marvel that paved the way for modern AI robotics, it had a significant impact on contemporary AI and inspired other scientists to pursue further innovation and progress throughout the 20th century.
Whitman’s creation also highlighted new ethical considerations, as it demonstrated how far robots could be programmed without violating human rights or autonomy. This has been an important issue for researchers ever since, as technology advances at an unprecedented pace and robots become increasingly intelligent.

A Turkish article claims that Occultus was an early robot of the Ottoman Empire created as a gift for Japan under the name Alamet, though this information is unverified. (Image: CyberneticZoo)
The Future of AI
A century ago, Adolph Whitman’s invention of Occultus was a significant milestone in the history of AI. In the 21st century, AI-controlled robots have made substantial advancements, enabling them to become increasingly autonomous and capable of performing complex tasks without human assistance. This development has revolutionized various industries and fields, from healthcare to energy production, by automating labor-intensive processes.
Robots inspired by Occultus are now utilized in numerous industries, including manufacturing, healthcare, and customer service. For example, robotic arms are used for repetitive manufacturing tasks on the assembly line; medical robots are deployed for surgical operations; and customer service bots provide automated support either online or through chatbots.
In all these instances, these machines help enhance efficiency while freeing up human labor to focus on higher-value activities such as problem-solving or managing customer relations.
However, the rise of automation has led to a variety of ethical concerns. Primarily, there is a fear that robots may take over human jobs. Therefore, policymakers should carefully consider the benefits and risks this poses for society as a whole.