The Vertiia eVTOL aircraft features 8 rotors, accommodates 5 passengers, has a maximum speed of 300 km/h, and is expected to serve medical purposes.
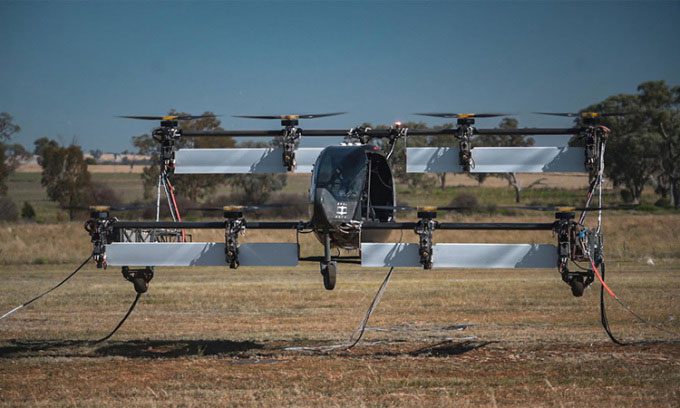

The Vertiia aircraft prototype performing tethered flight testing in February 2023. (Photo: AMSL Aero)
Australian company AMSL Aero conducted the first tethered flight test of its Vertiia prototype, as reported by Interesting Engineering on February 21. Vertiia is an electric vertical takeoff and landing (eVTOL) aircraft, aimed at becoming a safe mode of transport to alleviate traffic congestion.
The new aircraft model stands out with its compact design thanks to a box-wing structure. “The combination of structural design and unique aerodynamics allows the aircraft to travel farther while consuming less energy,” according to AMSL Aero.
Vertiia is equipped with 8 rotors and can carry up to 5 passengers. The aircraft can travel at a maximum speed of 300 km/h and has a range of 250 km on battery power before requiring a recharge. Its operational range can increase to 1,000 km when using hydrogen fuel.
Vertiia employs distributed electric propulsion technology (propulsion provided by multiple rotors), which allows it to land safely even if one or more rotors fail. “A small eVTOL aircraft can provide a level of safety similar to that found in large passenger aircraft,” said Andrew Moore, co-founder of AMSL Aero.
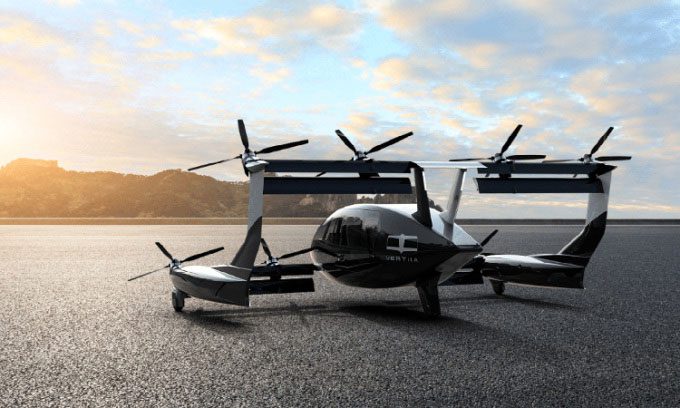

Design of the Vertiia vertical takeoff and landing aircraft. (Photo: AMSL Aero)
AMSL Aero anticipates that the aircraft will be used for medical purposes, transporting patients, especially in remote areas, to hospitals. Additionally, the company is considering other applications such as cargo transport, rescue operations, and passenger transport.
“Air taxis are also a potential application. Many people in Sydney, Melbourne, and Brisbane will want to significantly reduce their commute time by flying directly from home to work,” Moore added. AMSL Aero plans to start delivering the Vertiia aircraft to customers in 2026.