The National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC) in the United States announced a new report on February 16, revealing that the sea ice extent in Antarctica has decreased to just 1.91 million square kilometers.
This is the lowest level recorded since data collection began in 1979. According to NSIDC, Antarctica will soon enter its melting season in just a few weeks, and the sea ice extent is expected to decline even further before reaching its annual minimum.
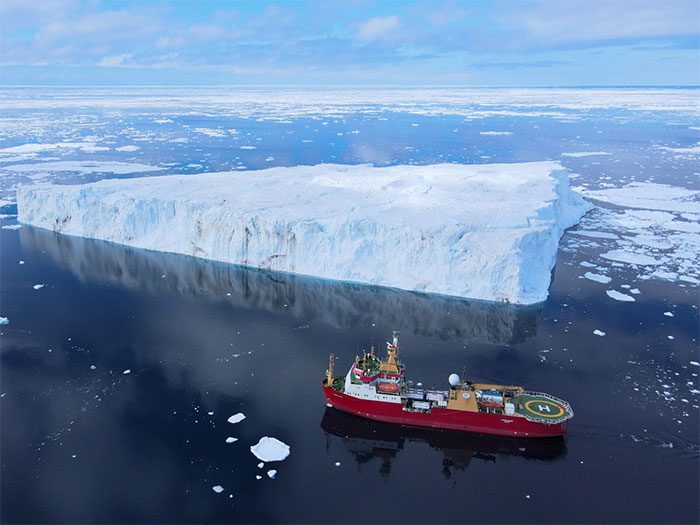

The Italian icebreaker Laura Bassi carrying scientists conducting research in Antarctica.
The melting sea ice in Antarctica does not have a direct impact on current sea levels since the ice is already floating on the ocean. However, this sea ice surrounds the massive ice shelves of Antarctica.
<pTherefore, according to NSIDC, the disappearance of sea ice exposes these ice shelves to wave action and warmer temperatures, threatening to accelerate their melting and potentially raise sea levels if global temperatures continue to rise in the coming centuries.
Moreover, the melting of sea ice also contributes to accelerating global warming. White sea ice reflects up to 90% of solar energy back into space. When it is replaced by dark, open water, the ocean will absorb a corresponding amount of heat.
Not only Antarctica but also the Arctic is drawing significant attention in the fight against climate change. American billionaire George Soros expressed support on February 16 for the idea of using solar geoengineering technology to protect Arctic ice from melting.
This is seen as a last-resort solution to combat global warming as it involves altering the physical properties of the Earth’s atmosphere to reflect more sunlight back into space or increase the amount of solar radiation that can escape.
According to one proposal, artificial white clouds would be used to enhance the solar energy reflectivity of the ice in the Arctic.