Experts have successfully reconstructed the face of a high-status woman from the mysterious Nabataean civilization based on skeletal remains found in a tomb.
For the first time in history, a team of archaeologists, forensic scientists, and model makers at the Royal Commission for AlUla (RCU) recreated the face of a Nabataean woman who lived over 2,000 years ago, as reported by Ancient Origins on February 7.
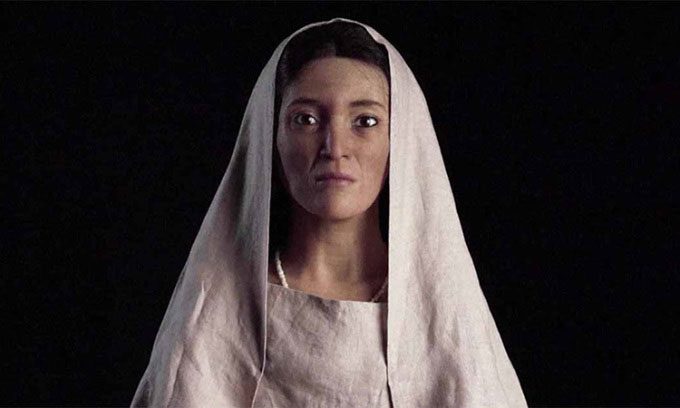

The face of the wealthy woman named Hinat. (Photo: RCU).
The woman is referred to as Hinat, who rests in a tomb on the outskirts of Hegra, Saudi Arabia. The tomb is well-preserved and contains the remains of approximately 80 individuals, some of whom are likely relatives.
Hinat’s remains are more intact than most of the other skeletons in the tomb. As a result, she was chosen for the facial reconstruction project in 2019. Experts believe that Hinat was a wealthy Nabataean woman of high social status, living in the 1st century BCE.
The reconstruction process involved many archaeologists, anthropologists, forensic specialists, and a 3D sculptor. In September 2019, this team gathered in London to discuss Hinat’s appearance and attire. They also created a character profile with information about her clothing, hair, and jewelry.
By July 2020, the experts completed the 3D reconstruction. They then crafted a silicone bust of Hinat, adding makeup, earrings, and individual strands of hair. Following this, they dressed the bust in a handmade linen garment, similar to the textiles found in tombs at Hegra.
This is the first time experts have reconstructed the face of a Nabataean woman using this method, providing a valuable opportunity to depict the appearance of the Nabataean people. “One of the challenges in archaeological studies of the Nabataeans is the lack of imagery. They are not frequently depicted in their own artworks. Throughout decades of work at Nabataean archaeological sites, we have also not uncovered many remains,” said Dr. Christopher A. Tuttle, an expert on the Nabataeans.
The reconstruction of Hinat’s face is a significant achievement that sheds light on the lives of the enigmatic Nabataean civilization. It also exemplifies how technology and artificial intelligence (AI) are transforming the fields of archaeology and history.