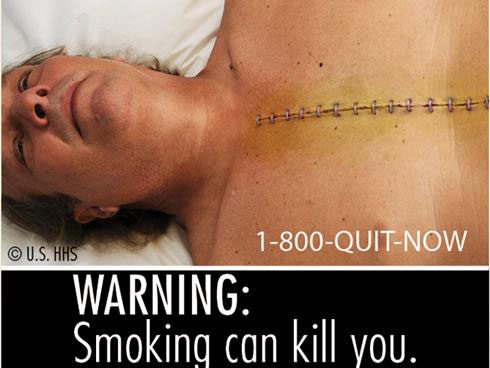
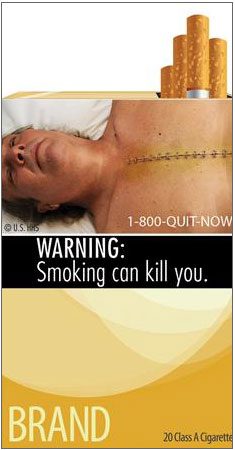
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has released 9 illustrative images to warn about the dangers of tobacco, aimed at preventing children from smoking and encouraging adults to quit.
These 9 illustrations were selected from a pool of 36 images after reviewing relevant scientific literature, analyzing the results from 18,000 research participants, and gathering over 1,700 opinions from various focus groups.
These warning illustrations represent the most significant change in tobacco packaging in the past 25 years and will have an impact on all aspects from packaging to advertising. The regulation mandating that all tobacco packages and advertisements must include health warning images will soon be implemented before September 2012.
 Health and Human Services Secretary Kathleen Sebelius stated: “These warning labels provide a straightforward, realistic, and powerful depiction of the health risks associated with tobacco. They are intended to encourage smokers to quit and prevent children from starting to smoke.“
Health and Human Services Secretary Kathleen Sebelius stated: “These warning labels provide a straightforward, realistic, and powerful depiction of the health risks associated with tobacco. They are intended to encourage smokers to quit and prevent children from starting to smoke.“
In the United States, tobacco use is the leading cause of preventable deaths. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reports that nearly 443,000 people die each year from smoking-related diseases, with healthcare costs and lost productivity due to smoking amounting to $200 billion annually.
Additionally, a study published on June 22 in the Journal of the American Medical Association by the Harvard School of Public Health (HSPH) and the University of California revealed that men with prostate cancer who smoke are 61% more likely to experience disease recurrence and mortality compared to non-smokers.
In the U.S., prostate cancer is the most commonly diagnosed cancer and the second leading cause of cancer deaths among men. This serves as another reason to encourage people to refrain from using tobacco.
The regulation requiring tobacco health warnings was proposed in November 2010 in accordance with the Tobacco Control Act aimed at reducing smoking in households. This legislation received widespread bipartisan support in Congress and was signed into law by President Barack Obama on June 22, 2009.