The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) has defined the boundaries between the five oceans of the world, despite not achieving complete consensus among nations.
There are five oceans on Earth, all interconnected, forming a continuous body of water. Previously, there were only four oceans: the Atlantic Ocean, the Pacific Ocean, the Indian Ocean, and the Arctic Ocean. In 2000, the International Hydrographic Organization decided to add a new ocean surrounding the least populated continent, Antarctica, based on evidence that this body of water has a distinct ecosystem and unique impacts on the global climate. The Southern Ocean became the fifth ocean on Earth and ranks fourth in size, according to Amusing Planet. Similar to national borders, the boundaries of the five oceans are clearly defined by the International Hydrographic Organization, although not everyone agrees with these boundaries.
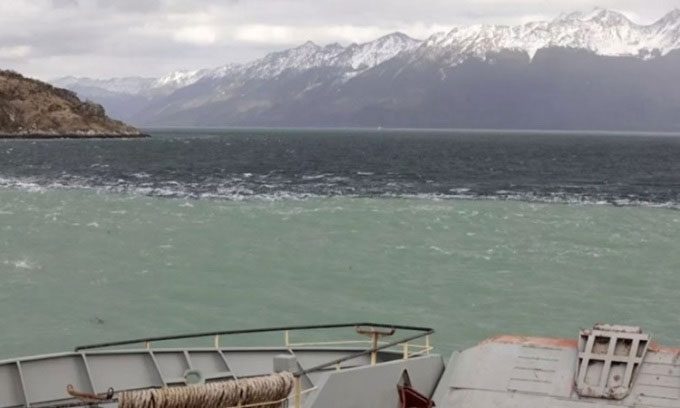

The intersection of the Pacific and Atlantic Oceans at the Beagle Channel in Tierra del Fuego, Chile. (Image: Dea).
The largest ocean is the Pacific Ocean, spanning from the Southern Ocean to the Arctic Ocean. Its eastern boundary runs along the coastlines of North America and South America, ultimately meeting the Atlantic Ocean at Cape Horn along a straight line extending from Tierra del Fuego to the Southern Ocean. The western boundary is defined through the East Indies, the Philippine Sea, the Sea of Japan, and the Sea of Okhotsk in the northern hemisphere, and the coastline of Australia in the southern hemisphere. The Pacific Ocean meets the Indian Ocean at the southeastern tip of Tasmania.
The Atlantic Ocean, the second-largest ocean in the world, stretches from the Southern Ocean between the Americas, Africa, and Europe to the Arctic Ocean. It meets the Pacific Ocean at Cape Horn and the Indian Ocean at Cape Agulhas, located on the southern tip of Africa.
The Indian Ocean, the third-largest ocean, extends north from the Southern Ocean to India, the Arabian Peninsula, and Southeast Asia. In the west, it follows the coastline of Africa until it meets the Atlantic Ocean at Cape Agulhas. In the east, the Indian Ocean borders the Pacific Ocean near Tasmania.
The boundaries of the Arctic Ocean are more complex due to the fragmented land in the region. The Arctic Ocean covers the North Pole, bordering North America in the Western Hemisphere and Scandinavia and Siberia in the Eastern Hemisphere. It meets the Atlantic Ocean near Greenland and Iceland and connects with the Pacific Ocean at the Bering Strait.
The Southern Ocean has the clearest boundaries. It forms a perfect circle surrounding Antarctica at the latitude of 60 degrees south. However, not all countries agree with this proposed boundary, so it has yet to be ratified by IHO members.