A remarkable natural phenomenon that occurs all around our planet is lightning. It is an extremely powerful electrical discharge capable of destroying everything in its path. Thunderstorms, dark clouds in the sky, and the resultant electrical currents create lightning bolts that wait for the right moment to strike the ground where humans reside. This is what lightning is.
What is Lightning?
Lightning is a discharge of electricity in the atmosphere between clouds and the ground or between clouds with different electrical charges. It can also occur during volcanic eruptions or dust storms. When discharging in the atmosphere, lightning can travel at speeds of up to 36,000 km/h.
Thunder is the sound caused by lightning and is a natural phenomenon. Depending on the distance and nature of the lightning strikes, the sound of thunder can be a short clap or a long rumbling sound. Thunder typically follows the flash of lightning.
When the flash of lightning occurs, there is a time delay before the sound of thunder is heard, clearly illustrating that sound travels slower than light. Because of this difference, one can estimate the distance of lightning by measuring the time between seeing the flash and hearing the thunder.
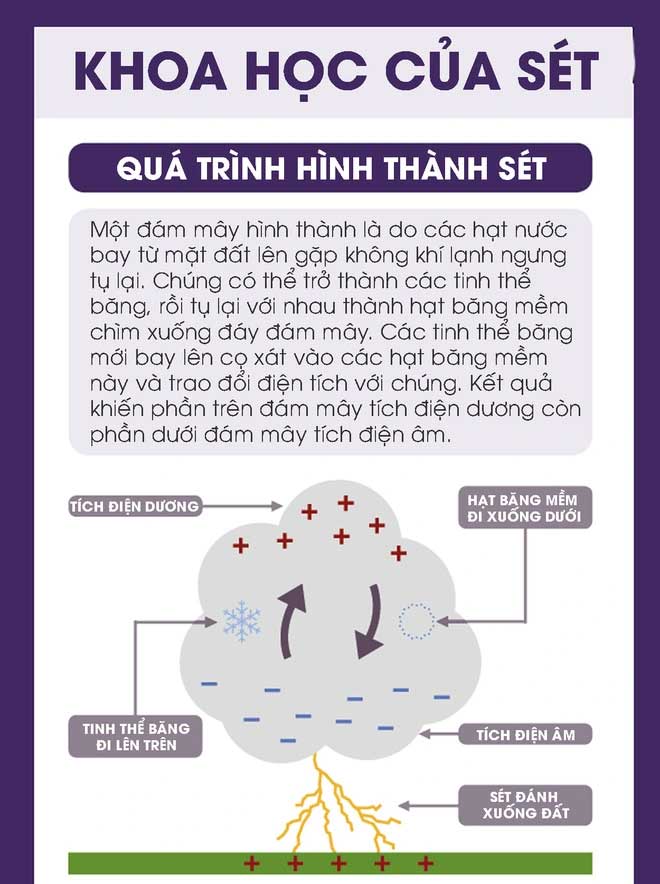
Lightning is the movement of ions, but the image of lightning is created by the glowing plasma stream, which means it can be seen before the sound is heard, as sound travels at only 1,230 km/h under normal atmospheric conditions, while light travels at 299,792,458 m/s.
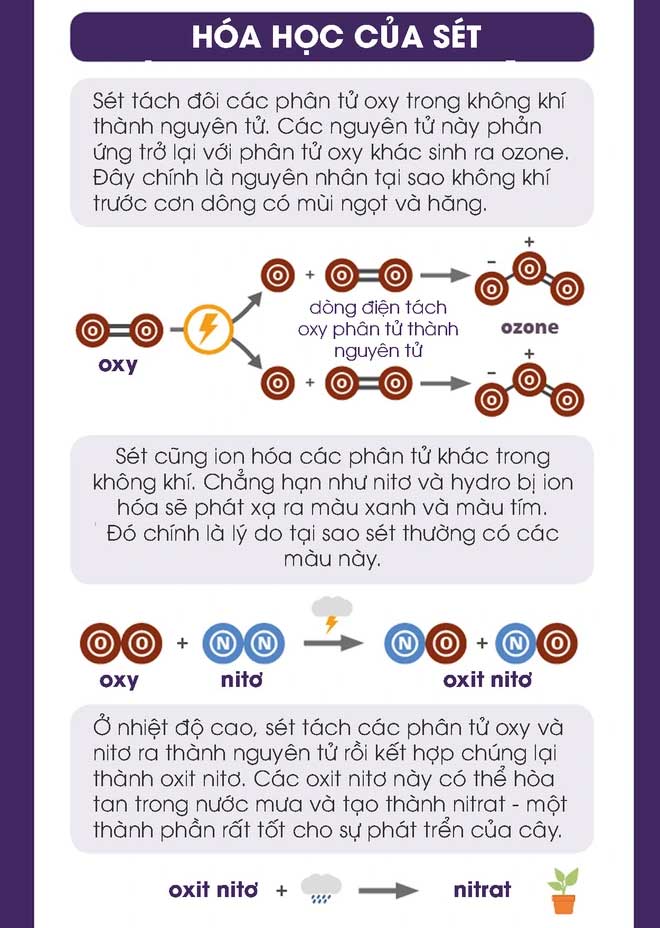
Lightning can reach temperatures of up to 30,000°C, which is 20 times hotter than the temperature needed to convert silica sand into glass.

Lightning is the movement of ions, but the image of lightning is created by the glowing plasma stream.
What Causes Lightning?
When two oppositely charged clouds come close together, the voltage between them can reach millions of volts. A spark discharge occurs between the two clouds, and we see a flash of lightning. A few seconds later, we hear the sound of thunder (due to the faster speed of light compared to sound, we see the flash first). When a charged thundercloud approaches the ground in open areas, if it encounters a tall object such as trees, a person holding a shovel, etc., a spark discharge can occur between the cloud and the ground, which is the phenomenon of lightning.


What are the Safest Ways to Protect Against Lightning Strikes?
- When indoors, stay away from windows, doors, electrical appliances, and wet areas such as bathrooms, water tanks, or sinks. Avoid using the phone unless absolutely necessary.
- Unplug electrical devices before a storm approaches. Telephone and electric lines, being connected to external networks, can be affected by lightning strikes.
- Keep a distance of at least 1 meter from these lines and electrical devices. Remove antennas from televisions during thunderstorms.
- If outdoors, do not use trees for shelter, avoid higher areas, and stay away from metal objects such as bicycles, machinery, and iron fences.
- Seek a dry place; if there are taller trees around, look for a low spot and stay near shorter trees. The person positioned as low as possible is best, hugging their knees with minimal contact with the ground; stand on tiptoe, do not lie down on the ground. Importantly, do not stand in groups close together.
- If you feel your hair standing up (like the static charge when you touch a TV screen), it means you might be struck by lightning at any moment. Immediately crouch down and cover your ears, do not lie on the ground or touch the ground.
How were over 7,000 lightning strikes recorded in Hanoi?
Experts explain the phenomenon of thousands of lightning strikes in Hanoi this morning
454 lightning strikes hit the ground in Hanoi in just 10 minutes


















































