Scientists have named this mysterious new human species Juluren, meaning “big-headed person”, which once coexisted with and even interbred with modern humans, Homo sapiens.
The research team, led by anthropologist Xiujie Wu from the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) and anthropologist Christopher Bae from the University of Hawai’i (USA), reanalyzed several fossils previously believed to belong to the ancient Denisovans, excavated in China.

An unknown human species existed alongside ours for 100,000 years in Asia – (Illustration AI: ANH THƯ).
Several new characteristics identified confirm that these fossils are not Denisovans.
However, they are also neither Neanderthals, “upright man” Homo erectus, nor “modern humans” Homo sapiens (which is us).
They represent a previously unknown human species, named Juluren (Homo juluensis), meaning “big-headed person.”
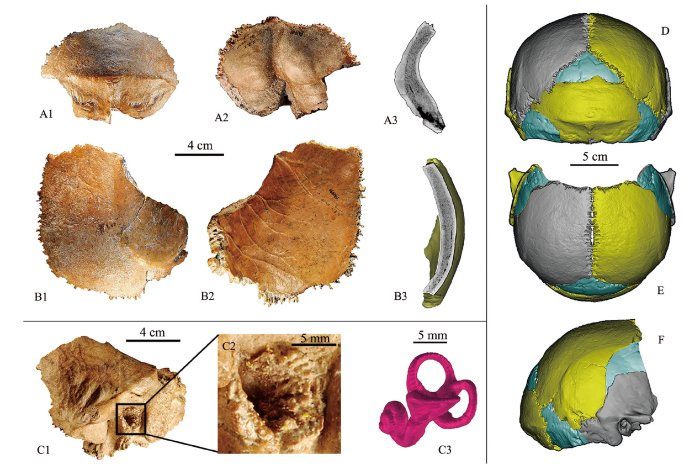
Some fossil remains of the new human species have been analyzed – (Photo: CAS).
According to Science Alert, the combination of features in this new human species indicates a blending of origins from multiple human groups, all of which lived in the same area in Asia from 300,000 to 50,000 years ago.
“Overall, these fossils represent a new form of large-brained human” – the authors wrote in the journal PaleoAnthropology.
The various fossils belonging to Juluren mainly consist of facial and jaw remains, containing dental features similar to those of classic Neanderthals.
However, some characteristics not seen in other known human species, including Denisovans, have also been identified.
Moreover, the authors state that this new human species existed before our Homo sapiens and lived alongside Homo sapiens populations for 100,000 years in East Asia.
It is even possible that these two populations once lived together, leading to many hybridizations.
This is not too surprising, as genetic evidence shows that ancient Homo sapiens also interbred with both Neanderthals and Denisovans.
Besides the “big-headed person,” Neanderthals are also believed to have larger skulls than ours.
Currently, scientists have not specifically analyzed the intelligence and technological level of this new human species, but a larger brain may be associated with good intelligence; for example, Neanderthals were quite skilled and knew how to craft various tools and intricate jewelry.
However, certain complex and “exclusive” structures in the brain are thought to have helped Homo sapiens gradually become superior and remain the only surviving species of the genus Homo.