At night, when the sun sets, the world is enveloped in darkness; without light, the sea becomes pitch black. However, in some places, the sea glows with bioluminescence, and waves crashing against rocks emit a greenish light, resembling a magical world. This phenomenon is known as “bioluminescent sea”, and it actually occurs in many coastal regions.
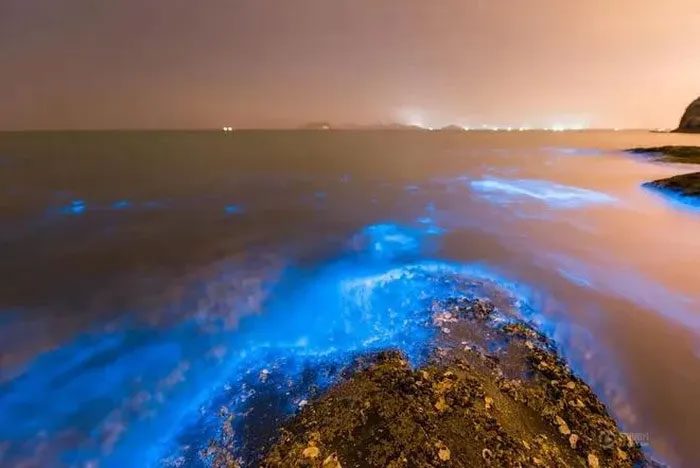

Bioluminescent sea phenomenon.
So, what causes the bioluminescence in the sea? In fact, the glow in seawater comes from a type of algae that thrives in ocean waters – Noctiluca, a type of algae that can emit bioluminescence at night, primarily spherical in shape. Considering the shape and function of this algae, it may seem cute, but in reality, it is not favored because it is also associated with red tide phenomena in the ocean.
When seawater becomes nutrient-rich, this type of algae can proliferate, leading to red tides. Red tide can deplete oxygen in the seawater; due to the lack of oxygen, other marine organisms do not receive enough oxygen, leading to the death of creatures like fish, shrimp, and other algae. Therefore, the appearance of bioluminescent seas is not a positive phenomenon; while beautiful, during red tides, many fish and shrimp in the same area die, making fishermen dislike this phenomenon, as it brings significant damage to their livelihoods.
Interestingly, this type of floating algae can only bioluminesce in saltwater, while all experiments related to freshwater environments have failed.
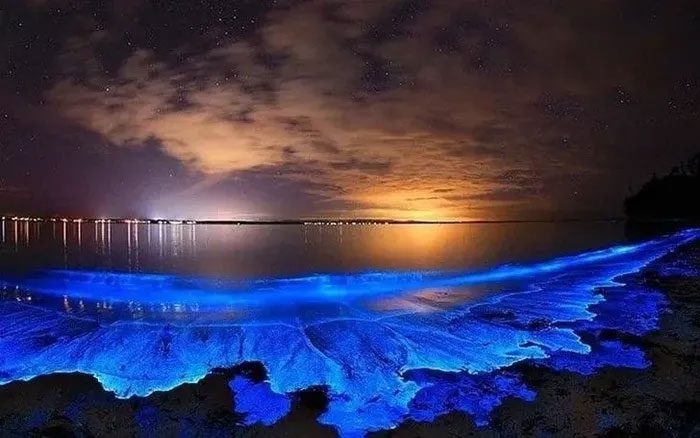

This type of algae can proliferate in seawater, leading to red tide.
To date, the exact mechanism behind the bioluminescence of this floating algae has not been fully explained. According to the latest research findings, a special substance has been discovered on the cell membrane of this plankton. This substance exhibits a unique biochemical reaction and is sensitive to electrical signals, which may be the cause of the glow.
Scientists from Rush University in Chicago have confirmed that this algae possesses all the necessary elements to activate bioluminescence. It allows positively charged protons to pass through, creating an electrical impulse that spreads throughout the protons inside, triggering chemical reactions. Ultimately, it activates a protein called luciferase to produce blue neon bioluminescent light.
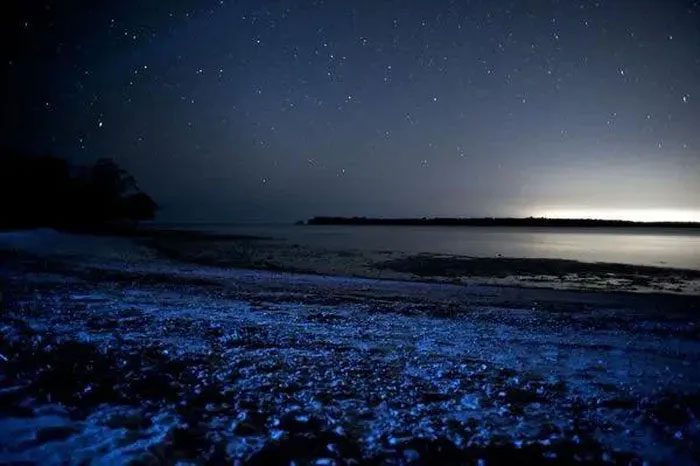

This type of algae has all the necessary elements to activate bioluminescence.
Additionally, some bioluminescent algae can be toxic to humans and marine life, such as fish. This toxicity appears to be a result of the algae releasing certain toxins during the bioluminescence process, which can lead to widespread poisoning of fish.