A Newly Discovered Crater Reveals Complex and Diverse Geological Features on Mars.
The Mars Express Orbiter from the European Space Agency (ESA) has recently captured images of the Martian surface, revealing a gigantic crater that appears quite ominous, resembling a giant eye.
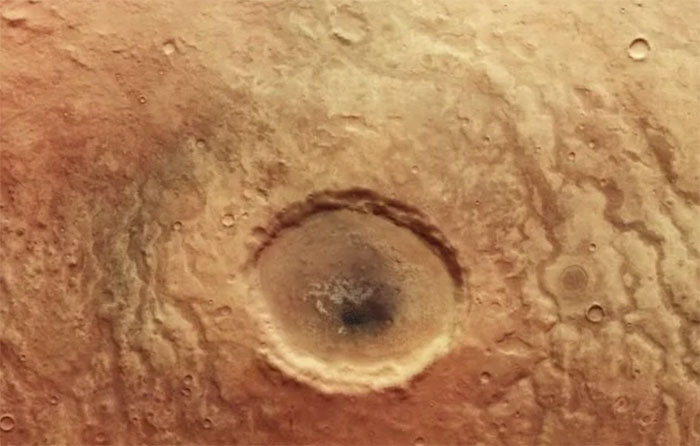
“Demon Eye” found on the surface of Mars. (Image: ESA).
Estimated to have a diameter of about 30 kilometers, the crater is located in an area known as Aonia Terra, situated in the southern hemisphere of Mars.
Geologists believe that regions like Aonia Terra could hold clues to the mysteries of Mars’ internal composition. According to them, a sufficiently strong impact could expose materials hidden deep beneath the planet’s surface, contributing to the formation of new surface components and geological features.
The newly discovered crater indicates that the surface composition in this area is highly complex and diverse.
This unnamed crater is situated in a terrain characterized by numerous deep channels that stretch around it. Scientists speculate that these may have been formed by countless small rivers on the Martian surface billions of years ago.
Below these flows, traces of darker materials can be observed. Some of these materials even rise to the surface, possibly remnants of erosion-resistant materials that settled in the dry riverbeds and remain to this day.
At the center of the crater, darker materials can also be seen, existing in the form of a rippling sand dune.
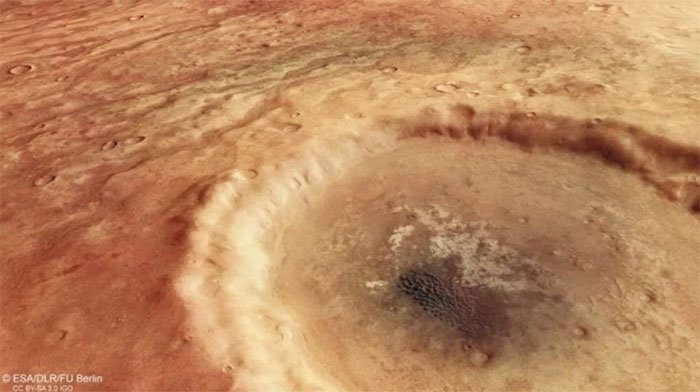
Unnamed crater from another angle. (Image: ESA).
Despite its striking appearance, it is still much smaller than other craters on Mars, such as the Lowell crater, which has a diameter of approximately 200 kilometers.
According to Science Alert, Lowell and many other craters in the region are believed to have formed due to geological impacts around 4 billion years ago, during a time when the early Solar System was extremely active, often referred to as the “heavy bombardment period.”
In fact, a similar process occurred on Earth, which laid the groundwork for the “seeding” of the Blue Planet, helping to create water and essential organic compounds for life.
However, for Mars—a planet that is inherently much drier and quieter than Earth—the transformation processes necessary for the emergence of life have certainly faced some obstacles, or something has wiped out all potential for life. This is what scientists are striving to clarify.