When a fire is started, the logs underneath ignite while the pot – made of metal with strong chemical bonds – remains unaffected.
Fire requires several essential elements to exist, including oxygen, heat, and fuel. The reason some materials catch fire while others do not is due to the chemical bonds and the energy required to change or break those bonds.
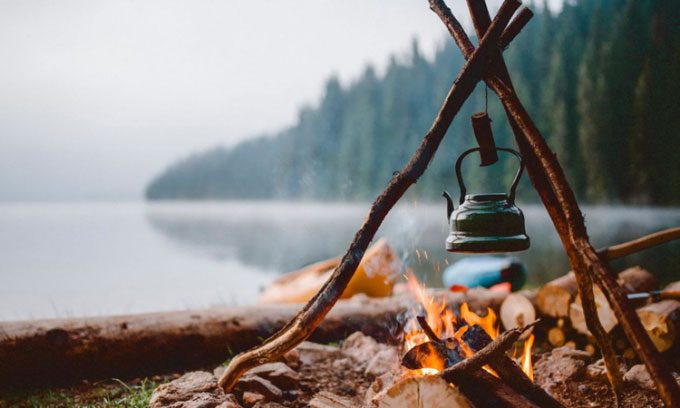

The metal pot does not catch fire like the wooden logs underneath. (Photo: ArtistGNDphotography)
Oxygen is a type of gas present in the air. Heat can be generated by friction, such as striking a match, or in other ways, for example, lightning. Fuel is any combustible material, which can be anything formed from organic material, according to Carl Brozek, a chemist at the University of Oregon. In this context, “organic” refers to molecules primarily composed of carbon and hydrogen, sometimes including oxygen or other atoms like phosphorus and nitrogen.
Fire is a chemical reaction that releases energy from an unstable system with relatively weak chemical bonds. Brozek explains that everything seeks to be more stable, especially organic molecules containing carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, and some other elements. Flammable materials like wood and paper are made from cellulose – a molecule containing bonds between carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen.
“When something burns, it releases a lot of energy because the system is transitioning to a lower energy state. This energy has to go somewhere,” Brozek says.
When a wooden object catches fire, cellulose converts into CO2 and water vapor – both of which are very stable molecules with strong bonds. The energy released from this chemical reaction excites electrons in the gas atoms, emitting visible light. Humans refer to that light as fire.
So why do the logs ignite when starting a campfire to boil water, while the metal pot does not? The difference between wood and the metal pot relates to the material’s ability to distribute energy when exposed to fire, which depends on the strength of the chemical bonds, Brozek explains.
The strong chemical bonds in metals are not easily broken. Wood lacks such strong bonds, so it cannot absorb energy from the fire. Instead of absorbing energy, wood releases energy by catching fire. In contrast, the metal of the pot can absorb and disperse energy effectively, which is why touching the pot feels hot.
Increasing heat absorption can prevent wood from igniting. Brozek notes that if you ignite a paper cup filled with water, the cup will not burn because the water inside can absorb the heat.
However, some metals can still catch fire, such as potassium and titanium, which are used to make fireworks. The metals in fireworks are in powdered form, providing a larger surface area to react with heat and oxygen more rapidly, Brozek explains. When these metals are exposed to sufficient heat to react with oxygen, the energy released causes them to burn in different colors.