Chinese Scientists Develop New Method to Convert Carbon Dioxide and Water into Glucose and Fatty Acids.
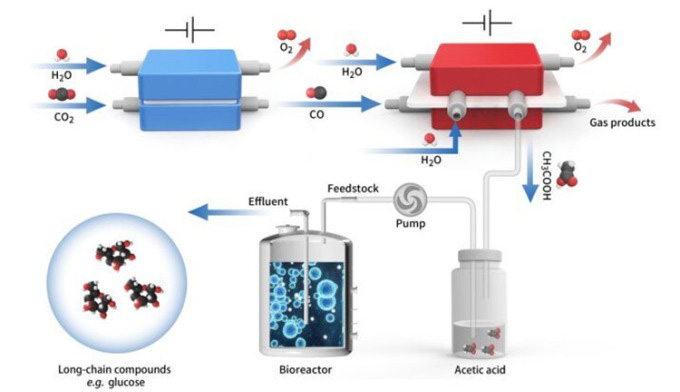
Diagram of glucose synthesis from CO2 and water. (Image: Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology)
A research team from the University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, the Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology, and the University of Science and Technology of China has developed a hybrid bio-electrochemical system that combines carbon dioxide (CO2) electrolysis in space with yeast fermentation, enabling efficient conversion of carbon dioxide into glucose with high yields.
Initially, they convert carbon dioxide into pure acetic acid using an electrolysis reactor with a nano-structured copper catalyst, and then employ genetically modified yeast to produce glucose in vitro from acetic acid. This method has also demonstrated the ability to generate other products such as fatty acids.
“This process can be understood as converting carbon dioxide into vinegar and using yeast to produce glucose and fatty acids,” described the lead author of the study, Zeng Jie, from the University of Science and Technology of China.
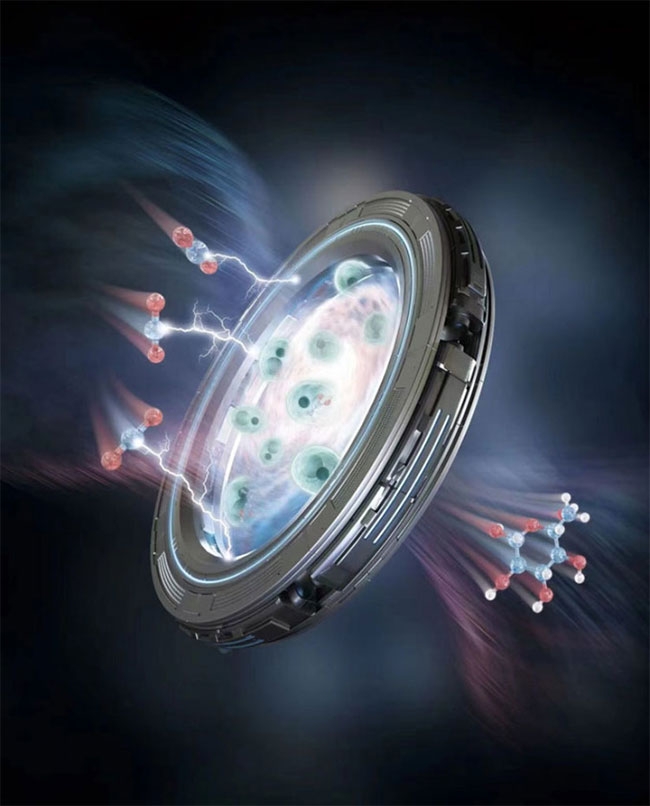

The conversion of CO2 into glucose and fatty acids is achieved through an electrochemical process combined with biological fermentation. (Image: Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology)
The researchers noted that transforming carbon dioxide into value-added products showcases the remarkable potential of a manufacturing sector utilizing renewable energy, opening opportunities to address environmental issues and achieve a circular economy.
“With an electrolysis reactor and various microorganisms, we could produce artificial starch, pigments, or pharmaceuticals in the future,” added co-author Xia Chuan from the University of Electronic Science and Technology of China.
This research was published in the journal Nature Catalysis last week.