In the diagnosis and treatment of Covid-19 patients, the use of X-ray imaging is an accessible diagnostic method.
According to a recent study published in Medical Daily, the first step in detecting and treating suspected Covid-19 patients is to determine whether they are indeed infected with the virus.
Typically, confirming whether a person is infected with SARS-CoV-2 requires rRT-PCR testing. This testing must be conducted in laboratories and requires a significant workforce.
Moreover, the rRT-PCR testing process often takes a considerable amount of time (approximately 2 hours or more) to yield accurate results. In many cases, it is essential to determine whether a person has Covid-19 more quickly, especially for severely ill patients who need immediate treatment. Rapid diagnosis is a crucial factor.
Given these considerations, a research team from the University of West Scotland and Durham University sought quick methods that could serve as alternatives to PCR by utilizing readily available hospital equipment, particularly X-ray machines.
Covid-19 Signs in X-ray Images
Computed Tomography (CT) or X-ray technology can assist doctors in analyzing and searching for traces of Covid-19 through imaging.
Some studies from the early stages of the pandemic have also shown that there are abnormalities in the chest X-ray images of patients infected with the virus.
Based on this, the World Health Organization (WHO) has recommended the use of X-ray technology to diagnose Covid-19 patients when rRT-PCR testing is not available, especially for patients with severe symptoms.
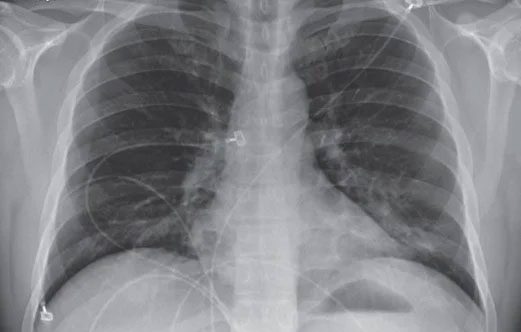
Lattice and consolidation patterns in the lung bases on the chest X-ray of a Covid-19 patient. (Image: BVTWQĐ108).
However, the use of X-ray technology also requires healthcare personnel. Diagnostic doctors need to have expertise and analyze images thoroughly, as the signs of Covid-19 are often difficult to detect. Therefore, the research team developed a program using artificial intelligence to facilitate quicker diagnosis.
This program is based on an algorithm commonly used for image recognition and analysis. The algorithm can filter out prominent features in images and classify them based on similarities and differences.
The research process utilized data from approximately 3,000 X-ray images (this data included images of Covid-19 patients, healthy individuals, and those with viral pneumonia).
From this, the researchers selected an algorithm with outstanding effectiveness. They then input a completely new set of X-ray images into the algorithm to identify Covid-19 patients, achieving an accuracy rate of 98.04%.
How to Use
Based on these results, the researchers continued to develop an application that can be used outside the laboratory. This application does not require much internal memory or power to operate. Therefore, it can be installed on standard personal computers or laptops.
The application is also designed to function without any additional supporting devices. Patients’ X-ray images can simply be uploaded via USB or a website, after which the algorithm will automatically analyze the images and return results confirming whether they have Covid-19.
This method will not completely replace PCR testing. However, it will provide significant benefits in emergency situations for severely ill patients. The application will allow for quick chest X-ray imaging and analysis. If a patient is diagnosed with Covid-19, they will receive immediate treatment rather than waiting for laboratory results.
In the near future, the research team will test this new technology in Pakistan to evaluate its effectiveness in real-world scenarios.


















































