The Earth’s magnetic field serves as a crucial barrier, protecting us from cosmic radiation. However, the recent significant decline in global magnetic field strength, decreasing by up to 9%, has raised concerns.
Causes of Global Magnetic Field Strength Decline
The Earth’s magnetic field is an essential protective shield that defends the planet against solar storms and cosmic rays. In recent decades, scientists have noted a gradual decline in the strength of the global magnetic field. This phenomenon has attracted widespread attention and research. So, what exactly causes this decline? Through in-depth studies of changes in the internal movements of the Earth’s core, we can uncover some answers.
The Earth’s core is the deepest part of the planet, composed of molten metals such as iron and nickel, functioning like a gigantic natural generator. The movements within the Earth’s core are driven by convection in the mantle caused by high temperatures and immense pressure. This convection creates magnetic fluid flows that generate the magnetic field.

The movement of the Earth’s core is a highly complex process influenced by various factors, including the Earth’s rotation, heat transfer, and physical and chemical changes within the Earth’s core. (Image: Zhihu)
The Earth’s rotation speed is constantly changing, directly impacting the movements within the Earth’s core. Variations in the Earth’s rotation speed will affect the velocity and direction of the magnetic fluid flows inside the core, subsequently altering the strength and direction of the global magnetic field. For instance, when the Earth slows down its rotation, the flow within the core also decreases, leading to a reduction in global magnetic field strength. Furthermore, the material flow inside the Earth’s core can also cause disturbances and changes in the geomagnetic field.
Physical and chemical changes within the Earth’s core also affect the global magnetic field. Complex heat transfer phenomena within the core alter the temperature and density distribution, which in turn changes the patterns and intensity of the fluid flows inside the core. Simultaneously, chemical reactions in the core can modify the properties and movement patterns of the core materials, impacting the Earth’s magnetic field.

Studies have shown that the occurrence of geomagnetic reversal is often associated with rapid changes in the flow within the Earth’s core. (Image: The Guardian).
The geomagnetic reversal phenomenon also significantly impacts the changing strength of the global magnetic field. Geomagnetic reversal refers to the sudden 180-degree shift in the direction of the geomagnetic field, a phenomenon that has occurred multiple times throughout Earth’s history. Geomagnetic reversals are closely related to changes in material flows within the Earth’s core.
The decline in global magnetic field strength is closely linked to changes in the internal movements of the Earth’s core. These changes include variations in the Earth’s rotation speed and the impacts of physical and chemical changes within the Earth’s core.

In the future, scientists will need to continue researching and exploring the mechanisms of movement within the Earth’s core to better understand the phenomenon of global magnetic field changes and make accurate predictions and assessments about its future transformations. (Image: Zhihu).
Effects of Global Magnetic Field Strength Decline
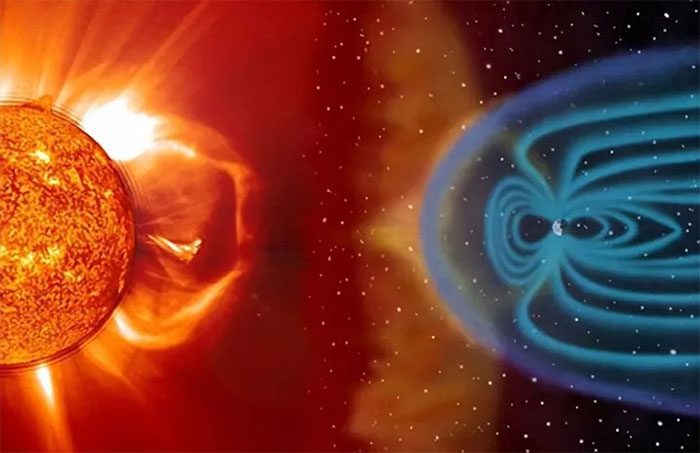
The Earth’s magnetic field is a frequently overlooked yet crucial aspect of our lives. However, in recent years, scientists have observed a decline in the global magnetic field strength. This issue has garnered widespread attention because the weakening of the magnetic field can lead to a range of effects, including increased solar wind and cosmic radiation.
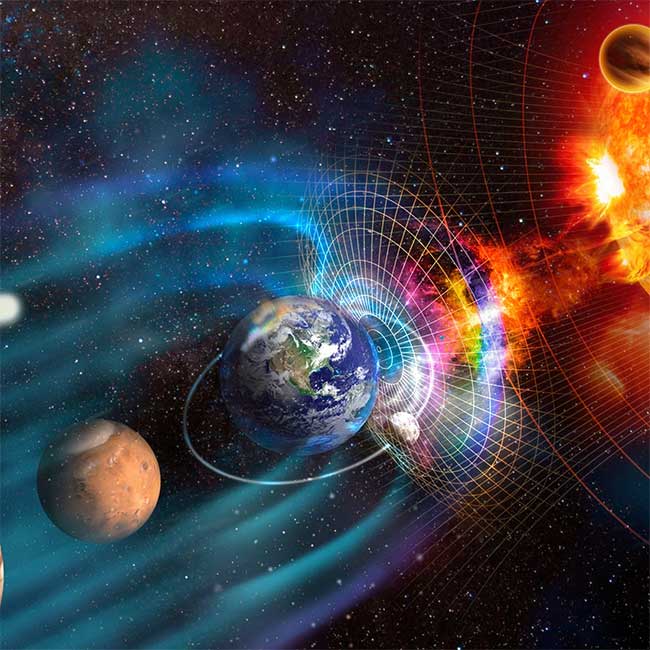
Solar wind is a stream of high-speed charged particles from the Sun that travels through the solar corona and bursts into activity in the solar atmosphere before entering the Earth’s magnetic field. As the strength of the global magnetic field decreases, the accessibility of solar wind increases. This results in more solar wind entering the Earth’s atmosphere, having a more pronounced effect on the ionosphere and the Earth’s electromagnetic environment.
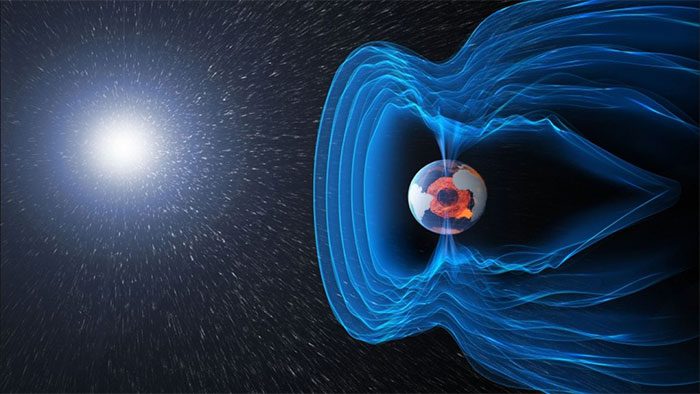
The ionosphere is a layer of ionized gas located in the outer layer of the Earth’s atmosphere. It can reflect or refract radio waves and affect radio communication and navigation systems. Increased solar wind can cause changes in the ionosphere, impacting the reliability of communication and navigation systems. The energy of charged particles in the solar wind can also damage satellites and other space devices, increasing the risk of space weather events. (Image: Universe Today).
Cosmic rays are high-energy particles that come from deep space, including protons, heavy ions, and electrons. The Earth’s magnetic field can resist the intrusion of cosmic rays, protecting us from cosmic radiation. However, with the decline in global magnetic field strength, cosmic rays can penetrate more easily.
The potential impact of cosmic rays on humans and the Earth is a matter of significant concern. High-energy cosmic rays can penetrate living organisms and cause devastating effects on human tissues, increasing the risk of cancer and other chronic diseases. Cosmic rays can also affect the Earth’s atmosphere, causing radiation issues at high altitudes and enhancing ultraviolet rays. This can have negative effects on biodiversity and ecosystem balance.
The increase in solar wind and cosmic rays due to the decline in global magnetic field strength has significant implications for the Earth and humanity. They can not only disrupt the normal operation of communication and navigation systems but also damage space equipment and satellites. (Image: Smithsonian Magazine).
Radiation from cosmic rays poses potential risks to human health and the environment. Scientists and governments should intensify research on global magnetic field changes and implement appropriate preventive measures to mitigate the impacts of these potential risks and protect our planet and human health.
Potential Consequences of Global Magnetic Field Strength Decline
The decline in global magnetic field strength will lead to more damage to everyday electronic devices. The magnetic field forms a protective layer around the Earth that can withstand the direct impact of cosmic rays and solar wind on our planet. It plays a crucial role in preventing high-energy particles from penetrating the atmosphere and damaging sensitive electronic components.
As the magnetic field strength decreases, this protective ability also diminishes, making electronic devices more susceptible to particle radiation. This could lead to significant failures in scientific research and data loss, resulting in substantial financial losses for individuals and companies. Particularly for critical equipment such as medical devices and aerospace instruments, malfunctions could have even more severe consequences.
As the magnetic field strength decreases, the protective ability also diminishes. (Illustration: Zhihu).
The decline in global magnetic field strength could also lead to severe disruptions in communication between electronic devices. Wireless communication is a critical foundation of modern society, from mobile phones to satellite information; wireless data transmission has become an indispensable part of human life.
A weakened magnetic field will affect the quality of wireless signal transmission, resulting in weakened, lost, or distorted signals. This will directly impact communication and information exchange among people. Network service providers and telecommunications companies will face significant challenges, requiring them to invest more resources to maintain signal quality and stability to ensure the smooth progression of wireless communication.
Weak magnetic fields will affect the quality of wireless signal transmission. (Illustration: Livescience).
The decline in global magnetic field strength could also have other impacts on the normal operation of electronic devices. For instance, the magnetic field is crucial for the accuracy of compasses and navigation systems. However, as the magnetic field strength weakens, errors may occur in compass navigation, and the accuracy of positioning devices will also be affected. This can severely hinder the navigation and positioning capabilities of individuals, potentially leading to disasters, especially in maritime, aviation, and military operations.
The impact of the decline in global magnetic field strength on electronic devices is multifaceted. From device malfunctions and communication interruptions to navigation errors, these adverse effects can result in significant losses for individuals and society. Scientists are paying close attention to this issue and are striving to find solutions to counteract this global change. In the future, we need to enhance the protection of electronic devices to minimize losses caused by these adverse effects and provide a more reliable operating environment for our electronic equipment.


















































