Like our ancestors, our bodies have evolved significantly to adapt to modern life.
Top 7 Changes in the Human Body Over the Past 150 Years
For us, the concept of “evolution” is no longer unfamiliar. Many people mistakenly believe that human evolution occurred thousands of years ago and that this process is a part of history.
However, the truth is that to adapt to society and the surrounding environment, we are still continuing to evolve, leading to many changes in the human body today.
1. Increased Height
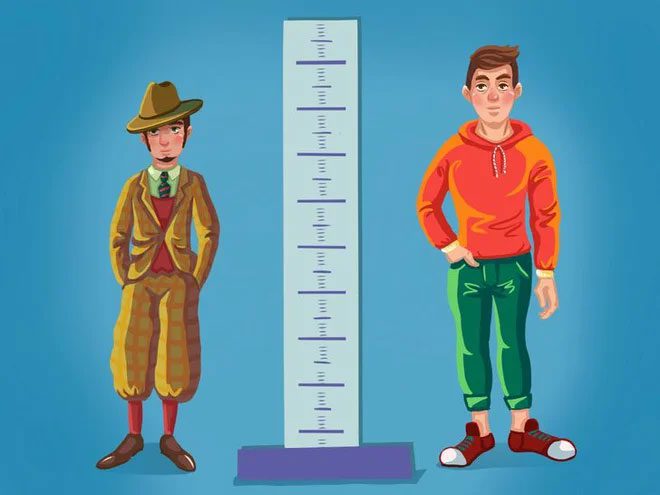

Both men and women in many countries around the world are getting taller.
This is perhaps the most noticeable sign of human development. Research shows that human height has significantly increased over the past 200 years. A study from the journal eLife indicates that both men and women in many countries are experiencing height increases, particularly South Korean women and Iranian men, whose average heights have increased by 20.2 cm and 16.5 cm, respectively.
2. Body Temperature
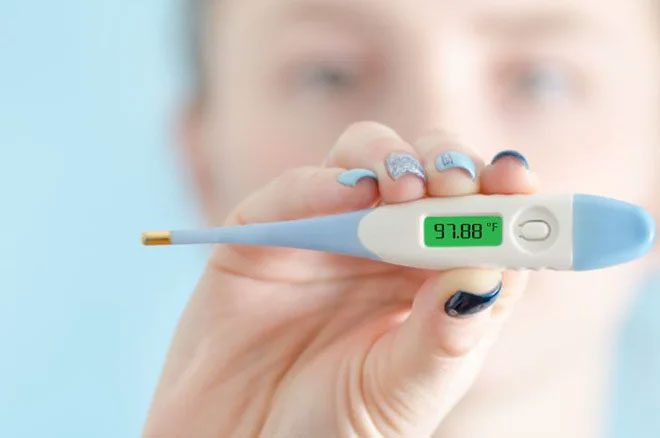
Human body temperature is showing signs of decreasing.
While the planet’s temperature is rising, human body temperature is showing signs of decreasing. Researchers from Stanford University have confirmed that the body temperature of men in the 21st century has decreased by 1.06ºF, while women have seen a decrease of 0.58ºF compared to data from the 19th century.
3. Early Puberty

Boys and girls are experiencing puberty at a much earlier rate.
Compared to previous decades, both boys and girls are entering puberty much earlier. This is attributed to improved nutrition. According to research from the University of California, 15% of girls are beginning puberty at age 7, which is estimated to be one to two years earlier than recorded data from the early 20th century.
4. Longevity
The human lifespan has increased due to advancements in hygiene, nutrition, and other environmental factors. A report from the Santalucía Institute in Spain predicts that life expectancy will continue to rise, potentially reaching 120 years by the end of the 21st century. Comparing data from the early 20th century, when only about 26.2% of the population lived to age 65, this represents a significant advancement for the human body.
5. New Body Parts and Organs
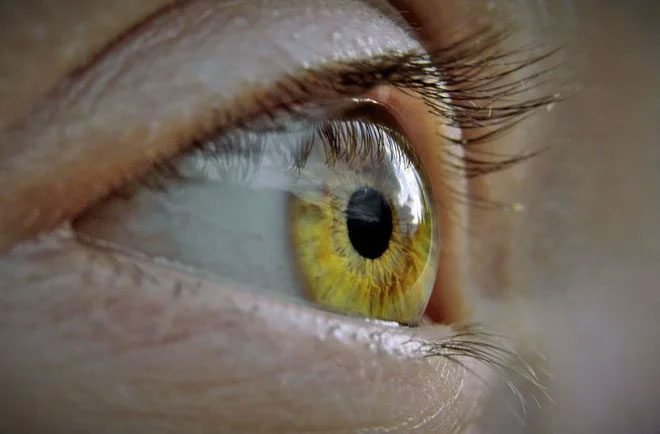

In 2013, the sixth layer of the eyeball was discovered, measuring just 0.04 inches thick.
Thanks to advancements in science and technology, recent studies have identified new body parts previously unknown, including the interstitium, an organ located beneath tissue that may help protect our tissues and other organs. In 2013, the sixth layer of the eyeball was also discovered, measuring just 0.04 inches thick.
6. Disappearing Body Parts
As some body parts are being born, several others are disappearing over time. Some people are born without wisdom teeth, also known as third molars. This is due to the reduction in jaw size resulting from dietary changes. Another example is the palmaris longus muscle, which runs from the elbow to the wrist. Some individuals are born without it, as it was primarily used to aid climbing.
7. Obesity

Obesity has nearly tripled since 1975.
It is no surprise that we are now less fit and toned, as the prevalence of junk food, fast food, and sugary snacks continues to rise. According to the World Health Organization, obesity has nearly tripled since 1975. Data from 2016 shows that over 1.9 billion adults were overweight, with more than 650 million classified as obese.


















































