In the energy sector, fossil fuels are the primary energy source due to their relatively low cost. However, our energy demand is predicted to increase in the future, and we can no longer rely on finite and polluting energy sources.
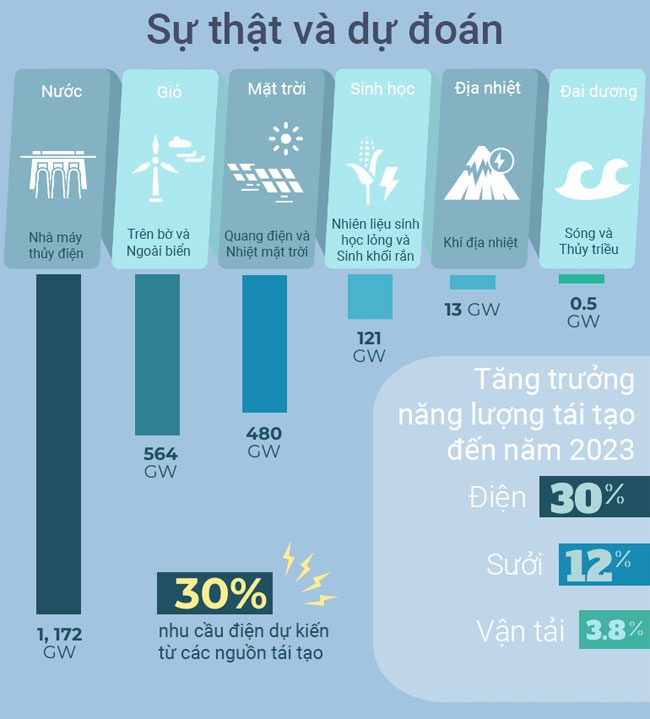
Solar panels, onshore and offshore wind turbines, and hydropower are some of the alternative energy technologies that will meet our future energy needs. Our dependence on natural gas and petroleum is the biggest reason for environmental degradation, particularly in the energy sector. Accordingly, alternative energy sources will be a major focus to mitigate the impacts of climate change on our planet.
Potential Alternative Energy Sources
With the population expected to reach 9.7 billion by 2050, the widespread use of large-scale solar farms may not be the ideal solution, as they require a substantial amount of land. Minimizing land usage is essential, or designing more efficient technologies, such as wind energy converters.
Wind energy is currently one of the most important alternative energy sources in the UK. Offshore wind is still underdeveloped due to high maintenance costs and deep water locations, but in the future, we will be able to generate energy more efficiently from oceans and deep waters.
Design flaws in current wind turbines limit the potential for wind energy utilization, particularly at higher altitudes where winds are stronger and more stable. Future airborne technology could improve this by extending operational ranges up to 500 meters.
One of the more expensive early-stage projects includes sourcing solar energy from space. Prototypes consist of optical reflective mirrors, photovoltaic cells that convert sunlight into energy, and a circuit that converts electrical energy into radio frequency. An integrated antenna would then transmit the energy back to Earth.
In the future, this innovative alternative energy source could meet the energy demands of our growing population without limitations, by harnessing continuous sunlight from space.
The Challenge of Efficient Energy Storage
The challenge of efficiently storing energy is crucial for the broader adoption of alternative energy sources. Solar photovoltaic energy relies on direct sunlight exposure, meaning a significant amount of energy is not utilized or wasted due to the lack of integrated solar energy storage batteries.
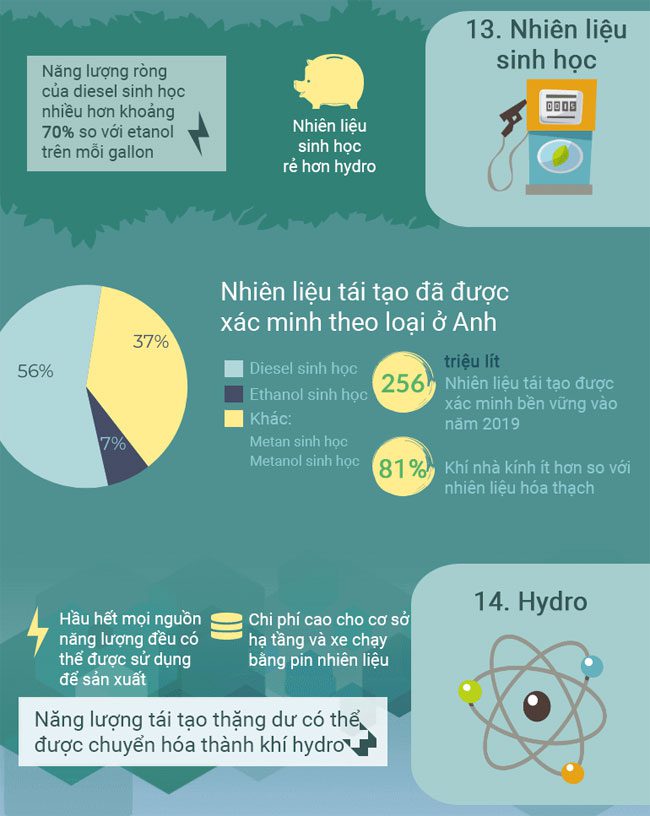
In the future, hydrogen will be a driving energy source. Currently, it is primarily produced from fossil fuels. However, surplus renewable energy can also be used to produce hydrogen gas. Its uses are highly versatile—hydrogen can be supplied to the natural gas grid or converted into electrical energy using fuel cells. Hydrogen could be widely utilized in the transportation sector as we develop more cost-effective solutions for the widespread deployment of such renewable energy sources.
Hydrogen has the highest density compared to any fuel type, making it easier to distribute and store. Its stable chemistry also means it can retain energy better than any other means.
In the future, establishing an infrastructure for supply and storage will allow for more efficient hydrogen use. Future plans for hydrogen include building an underground storage system, where surplus wind energy could be converted into hydrogen through the process of electrolysis.
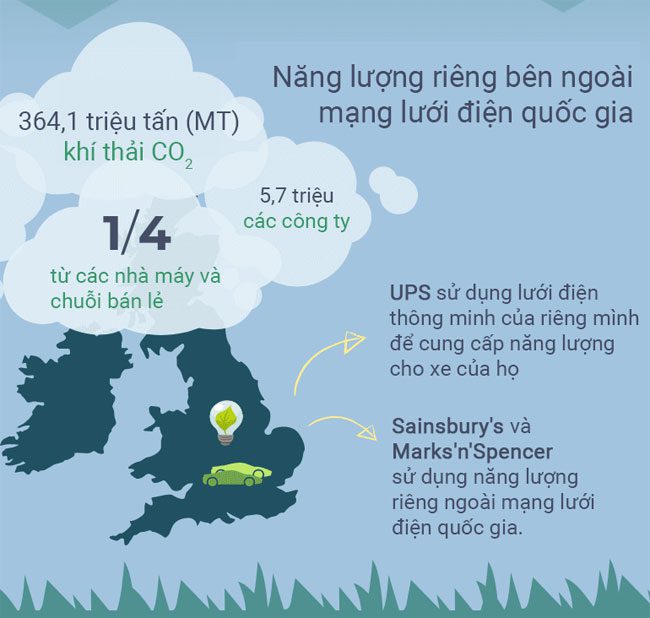
Our current global infrastructure is only adapted to fossil fuels. Constructing a new one will take many years and a significant amount of resources. In recent years, off-grid technologies based on renewable energy have managed to provide electricity to remote locations in the form of microgrids or local grids.