Stroke incidence is rising due to an increase in cardiovascular and metabolic diseases. This condition reduces blood flow to the brain, leads to blockage in cerebral blood vessels, or results from low blood pressure.
| This article is professionally advised by Master’s Degree, Dr. Nguyen Thi Huong – Neurologist – General Internal Medicine Department, Vinmec Times City International General Hospital. |
1. What is a Stroke?
A stroke is a pathological process that reduces blood circulation to a specific area of the brain due to narrowing or blockage of cerebral blood vessels or due to low blood pressure. Cerebral ischemia is the condition where a part of the brain stops receiving blood supply. If this lack of blood supply is not remedied or persists, that part of the brain will undergo necrosis due to a deficiency of oxygen and glucose. The area of the brain that suffers necrosis due to lack of blood supply is called a stroke.
Strokes account for approximately 80% of all strokes, while 20% are due to hemorrhagic strokes or subarachnoid hemorrhages. The annual incidence rate of strokes is relatively high, about 130 per 100,000 people per year.
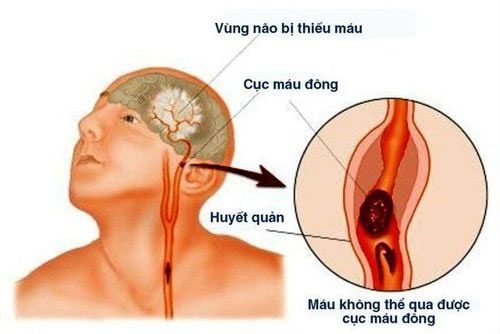
Stroke poses a high risk of cerebral hemorrhage.
2. Causes of Stroke
Common causes of stroke include:
- Atherosclerosis in major blood vessels accounts for 50%, with large extracranial vessels representing 45% and large intracranial vessels representing 5%.
- Cardiac causes leading to thrombus formation such as valvular heart disease, atrial fibrillation, heart rhythm disorders, heart failure, etc., account for 20%.
- Blockage of small blood vessels in the brain, commonly seen in patients with hypertension and diabetes, accounts for 25%.
- Non-atherosclerotic arterial diseases account for a certain percentage.
- Blood disorders such as coagulopathy, blood cell disorders, congenital vascular abnormalities, etc.
3. Diagnosis of Stroke
Symptoms of stroke occur suddenly, often while the patient is at rest. Typical symptoms include unilateral paralysis, numbness on one side of the body, difficulty speaking, and facial drooping. There may be altered consciousness if the patient has extensive ischemic damage, bilateral hemisphere infarction, or brainstem infarction.
3.1 Paraclinical Diagnosis
- CT Scan of the Brain: In the acute phase, 3-6 hours after the onset of symptoms, changes seen in CT imaging are very subtle, primarily due to edema in the ischemic area.
Early signs of stroke on CT imaging include loss of the gray-white matter boundary, obscured gyri, narrowing of the Sylvian fissure, loss of the insular ribbon, narrowing of the ventricles and basal cistern, and increased density of blood vessels in the area of the Circle of Willis due to thrombus, particularly in the middle cerebral artery.

MRI of the brain for diagnosing stroke.
CT scans can show a low-density area in the cortex, subcortex, or white matter after a stroke has formed, indicating the ischemic region corresponding to the affected artery.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): The advantage of MRI over CT in the acute phase of stroke is that MRI has specialized sequences such as DWI, ADC, FLAIR, and MRA, which accurately assess the acute nature of lesions and treatment intervention possibilities without the need for contrast injection. The disadvantage of MRI is the longer scanning time compared to CT, making it less ideal for emergency stroke intervention.
- Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA): This invasive technique aims to accurately diagnose cerebrovascular diseases while simultaneously providing emergency treatment to remove thrombus via a catheter: after identifying the blockage through angiography, instruments are used to remove the thrombus (suction devices, catheters).
4. Signs of Stroke
When observing a patient with FAST symptoms (an English acronym): F (face) facial drooping, A (arm) weakness in arms, S (speech) speech difficulties, T (time) immediate hospital transfer is necessary.
Other warning symptoms of stroke include dizziness, headache, numbness or weakness in limbs, facial drooping, slurred speech, loss of consciousness, and seizures. Upon noticing these signs, it is crucial to take the patient to the hospital promptly for treatment. The golden window for treatment is within the first 6 hours after symptom onset, with a preferable window being 4.5 hours, and the ideal window being the first hour from the onset of symptoms. Delayed treatment can result in severe disability.
5. Preventing Stroke Recurrence

Regular check-ups to prevent stroke recurrence
- Manage underlying causes of stroke: conditions such as hypertension, diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and dyslipidemia.
- Adopt a proper diet: Implement a low-fat, low-salt diet (for hypertension), reduce carbohydrates and sugars (for diabetes), increase vegetable intake, engage in daily exercise for 30 minutes, quit smoking and alcohol, and avoid obesity.
- Regular follow-ups and treatment per the physician’s guidance.
- If there are signs suggestive of stroke, the patient should be hospitalized immediately.
When experiencing stroke-suggestive symptoms such as unilateral weakness, facial drooping, or speech difficulties, the patient must quickly go to the hospital and must not self-treat at home. Early and accurate diagnosis allows doctors to choose the most suitable treatment method. The sooner the patient arrives at the hospital, especially within the first 6 hours after the incident, the higher the chances of recovery.
Currently, Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI/MRA) is considered the “gold standard” for stroke screening. MRI is used to examine the status of most organs in the body, especially valuable for detailed imaging of the brain or spinal cord. Due to its high resolution and contrast, MRI images can detect abnormalities hidden behind bone layers that are difficult for other imaging methods to recognize. MRI provides more accurate results than X-ray techniques (except for DSA for vascular assessment) in diagnosing brain, cardiovascular, and stroke disorders. Moreover, MRI scanning does not cause side effects like those experienced with X-rays or CT scans.


















































