One day, suddenly, our familiar computer acts up, failing to boot smoothly into the operating system with the familiar screen interface… There are many reasons that can lead to this.
 After ruling out hardware issues, don’t rush to intervene by formatting the drive to reinstall the operating system, as Windows has prepared a safe recovery method through Safe Mode.
After ruling out hardware issues, don’t rush to intervene by formatting the drive to reinstall the operating system, as Windows has prepared a safe recovery method through Safe Mode.
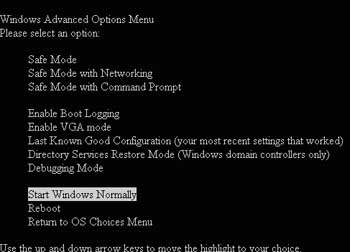
You may have installed many new software applications or updated drivers for certain devices, leading to conflicts. Restart your computer, and when you see the message “Please select the operating system to start,” press the F8 key to enter the boot options with Safe Mode. In this mode, the operating system only loads the most essential files and device drivers. Anything deemed unnecessary will not be loaded. Once you access Windows, you can troubleshoot from the graphical environment or enter Safe Mode, and then simply restart the machine to complete the process. For Windows XP, the Safe Mode options include:
– Safe Mode: Loads the most essential drivers and files as described.
– Safe Mode with Networking: In this mode, in addition to loading files and drivers as usual, additional services are available to enable network functionality.
– Safe Mode with Command Prompt: This option allows you to run programs and invoke the cmd.exe file to operate within a command-line interface environment; of course, users must be familiar with DOS commands.
– Enable Boot Logging: All device drivers and services loaded will be recorded in a file named ntbtlog.txt, which is very useful for reading and pinpointing the exact cause of system issues.
– Enable VGA Mode: Boots and loads basic Windows drivers for the graphics accelerator card. This is quite useful for determining if you recently installed a new driver for the graphics card, which may be causing the problem.
– Last Known Good Configuration: The computer boots using information from the Registry that Windows saved from the most recent complete shutdown.
– Directory Service Restore Mode: Boots and can restore through System Restore.
– Debugging Mode: Allows recovery through Remote Install Service.
The default behavior when running Safe Mode is to highlight the option to boot Windows normally, so to select one of the eight options mentioned above, you must use the arrow keys to navigate and then press Enter. Once the computer successfully enters Safe Mode, identifying the cause and resolving issues to get the operating system back up and running will be much easier than reinstalling the operating system. Of course, this applies to errors and conflicts that are not too serious and that Windows can still fix.
Tạ Xuân Quan

















































