Currently, the scientific community around the world has yet to provide a perfect explanation for this issue; only some fragmented theories exist, such as the uncertainty principle of quantum mechanics, zero-point energy, and other theories.
From my understanding of these theories, the origin of matter in the universe can be said to come from nothingness. To explain these theories, we cannot detach from Einstein’s famous equation, E = MC^2. Although this formula is simple, it can explain the profound mystery of the universe: the equivalence of mass and energy, which can be interchanged.
Matter in the universe is transformed from energy, and in extreme cases, it can be converted back to energy and disappear. This is the law of birth and death of the universe.
From a macroscopic perspective, the universe is created from nothing
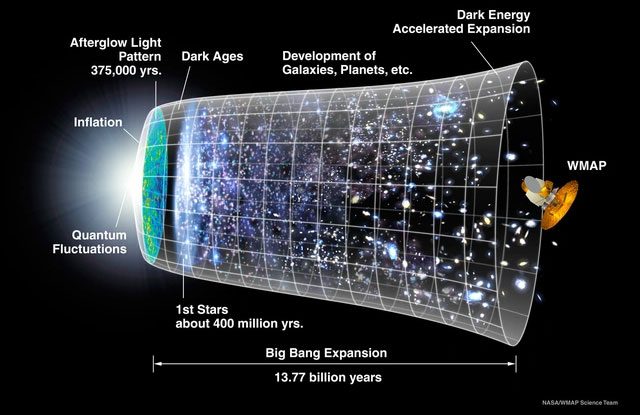
The singularity began from the Big Bang 13.8 billion years ago.
The Big Bang cosmological model has become the standard model of modern cosmology, meaning this theory has become the dominant understanding among astronomers and cosmologists worldwide – the expansion that formed the universe we see today.
The singularity began from the Big Bang 13.8 billion years ago, undergoing a period of inflation and rapid expansion. Currently, it is still expanding at a rate several times faster than the speed of light, resulting in an observable universe with a radius of approximately 46.5 billion light-years.
However, this does not imply that all locations are expanding faster than the speed of light, but rather indicates the overall expansion of the entire universe. At the extreme edge of the observable universe, 46.5 billion light-years away from us, the speed of galaxies receding from us exceeds the speed of light.

It can be said that the boundary between existence and non-existence is called the singularity.
In scientific terms, a singularity is represented by an infinitely small volume, infinite density, infinite curvature, and infinite temperature. So the question arises: what is this singularity? How did it occur? From a macroscopic perspective, it is something that comes from nothing, suddenly appearing from the void.
The boundary between existence and non-existence is called the singularity, a point where the curvature of space and time is infinite, where spacetime ends. General relativity predicts that such singularities must occur, a phenomenon where matter in extreme gravitational fields is influenced by quantum processes and collapses into a set of other spacetime dimensions, such as the singularity of a black hole.
On the other hand, the Big Bang was the result of a rebound from another time and space. In this sense, the singularity is a super spacetime, and it is no longer a matter of spacetime in our universe. The singularity is the expansion from another time and space into our time and space, so it can be said that the universe is indeed created from nothing.
But according to quantum mechanics, the universe is born from…
There are two theories of modern quantum mechanics that explain this phenomenon – the Heisenberg uncertainty principle and the theory of zero-point energy.
The Heisenberg uncertainty principle states that in the microscopic world, it is impossible to know the exact position and momentum of a particle simultaneously, from which it can be inferred that even when the temperature drops to absolute zero, particles still oscillate; otherwise, the uncertainty principle would be violated.
This means that even if the universe perishes, with no spacetime, and only absolute vacuum exists, there will still be particle motion, and if there is particle motion, there will be energy, which is the source of zero-point energy. In the vacuum of absolute emptiness, this energy will exist in the form of quantum bubbles, that is, randomly appearing as virtual particles.

Even if the universe perishes, there is no spacetime and only absolute vacuum exists.
These virtual particles exist in pairs of positive and negative, meaning they randomly appear as matter and antimatter; when positive and negative matter meet, they annihilate (vanishing after releasing energy), so these pairs of virtual particles in the vacuum appear randomly and will be immediately annihilated randomly.
If such a perfectly symmetrical and balanced world existed, our universe would never come to be. However, physicists have discovered that the world is imperfect, with the most representative examples being Yang Chen-Ning, Li Zhengdao, and Wu Jianxiong with their “Law of Non-Conservation of Parity” that they discovered and experimentally confirmed, which won them the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1957.
These theories suggest that our universe is imperfect, but occasionally, violations of non-conservation asymmetry create a continuous change in the world. Therefore, the scientific community has provided a groundbreaking explanation for the Big Bang, stating that these pairs of virtual particles appear randomly in quantum fluctuations that are not 100% annihilated but will be destroyed, becoming cosmic singularities.
Our universe exploded from such a singularity, and there may be many other universes that also exploded from this singularity.
There may be many other universes that also exploded from this singularity.
The anomaly energy that is broken but not annihilated cannot return to nothingness but can only expand, which is the Big Bang of the universe. The Big Bang was extremely hot and dense, initially consisting only of energy and nothing else. Within 1 second after the Big Bang, the universe was inflated. Gravitational forces, gluons, quarks, bosons, leptons, protons, neutrons, and their antiparticles appeared in succession, and then the strong and weak electromagnetic forces interacted with each other and separated.
After 384,000 years of expansion and cooling, the universe became large enough, and the temperature cooled to about 3000K, neutral atoms appeared, and the universe finally surpassed the dark age, with the first light (electromagnetic waves) emerging from the dense universe.
At this time, common substances, including atoms, had appeared. The earliest substances were the simplest elements, hydrogen and helium, along with a very small amount of lithium. These light substances gradually gathered into nebula clusters due to gravitational forces in the universe, then contracted and collapsed. And that was also the moment when stars, and galaxies in the universe were born.
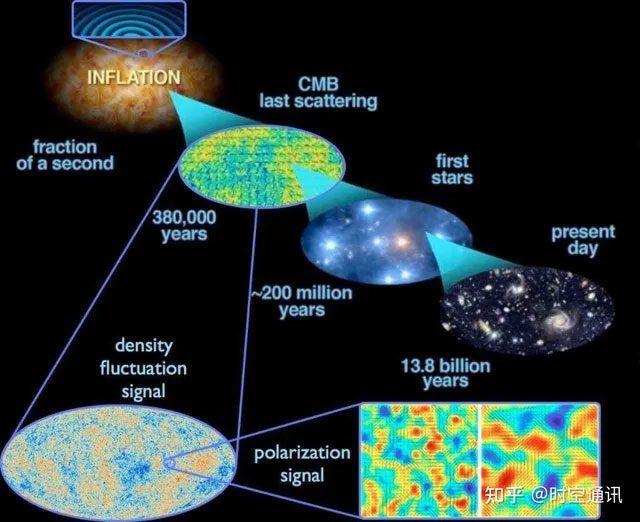
The initial stars were relatively large, so their lifespans were very short. In the process of stellar nuclear fusion and continuous supernova explosions, heavier elements were created successively, and all 118 known elements gradually emerged. These elements constitute all types of matter in the universe and all living beings on Earth.
In this sense, the matter of the universe has existed prior to that. Before the universe was born, this energy was stored in the vacuum, and it is this immense zero-point energy that transformed various substances, aligning with the mass-energy conversion law revealed by Einstein’s mass-energy equation.





















































