What is more valuable than rare earth elements? The “technology metal” leading global conversations today?
It is beryllium, an alkaline earth metal that is gray in color. Beryllium occurs naturally in the Earth’s crust, air, soil, and water. However, beryllium is scarce in the universe as it is only formed in supernova explosions.
Finding beryllium ore is significant, often likened to discovering a treasure, because of its applications in a wide range of electronic devices. Moreover, experts predict that beryllium will become a new material for aerospace in the future.
Treasure Found in Xinjiang, But Not Easily Exploited?
In recent years, survey teams in China have uncovered numerous deposits of rare metals. Among them, researchers have discovered one of the rarest elements: beryllium.
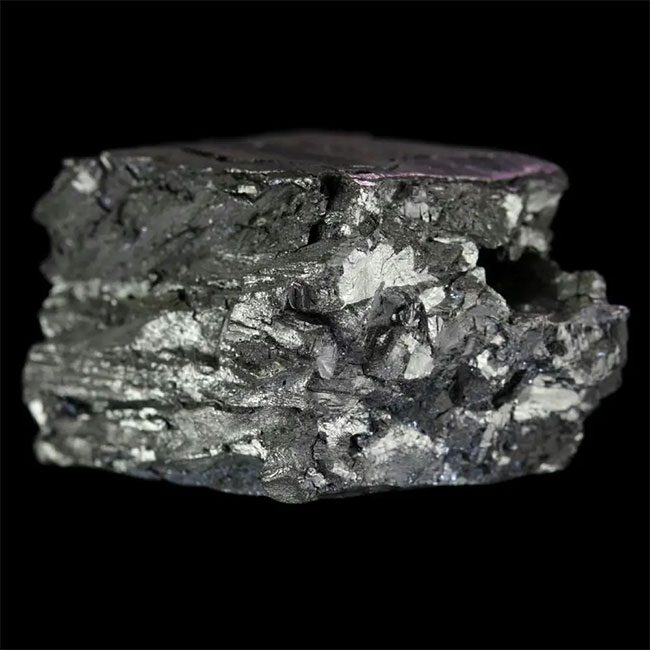

Beryllium is a metal rarer than rare earth elements. (Photo: Theodore Gray)
This highly toxic metal is an essential raw material in the aerospace, aviation, and metallurgy industries, as well as a great material for satellites.
Although not classified as a rare earth element, beryllium’s scarcity and unique properties make it highly sought after by many countries around the world. Currently, only three countries— the United States, China, and Kazakhstan—are mining and processing commercially viable beryllium ore.
According to experts, beryllium is mostly found in ores, with global reserves estimated at around 400,000 tons. The actual reserves of beryllium found in China amount to approximately 21,000 tons, with over 4,000 tons discovered in Xinjiang, an autonomous region in Northwest China.
This new discovery could make the beryllium mine in Xinjiang the largest in the world, potentially giving the country an advantage in the space race and enabling the production of a variety of advanced weapons.

Beryllium ore found in Xinjiang. (Photo: Xinhua)
However, exploiting the beryllium mine discovered in Xinjiang will not be easy for future aerospace materials.
The reason is that the mining costs are very high. Additionally, extracting beryllium ore, similar to rare earth elements, requires a significant amount of chemicals, including radioactive elements. This can cause severe environmental damage.
Moreover, the beryllium ore is located in Huoerguosi, Xinjiang, which is also known for its Huoerguosi jade, a famous type of jade in China. However, due to long-term mining, the environmental pollution in Huoerguosi is quite severe.
Therefore, to protect the local environment, the newly discovered beryllium mines will not be exploited in the near future.
On the other hand, learning from the past experiences of rare earth mining, authorities need to collaborate with experts to devise the most reasonable extraction plans for future beryllium mines.
Why is Beryllium More Precious than Rare Earth Elements?
Beryllium is the fourth element in the periodic table. Perhaps not many people are familiar with this lightweight metal; however, it is an essential material in many high-tech fields.
Beryllium is an alkaline earth metal.
Beryllium does not dissolve in water even at high temperatures due to a protective oxide layer. However, it can dissolve in strong alkali solutions or molten alkali to form beryllates.
Unlike metals such as magnesium and calcium, beryllium and its salts are toxic and harmful to the human body, with the potential to cause cancer. Therefore, experts advise caution when handling items containing beryllium.
Due to its slow elimination from the human body, beryllium can cause internal organ damage and even cancer.
Among the six elements that are alkaline earth metals, including beryllium (Be), magnesium (Mg), calcium (Ca), strontium (Sr), barium (Ba), and radium (Ra), beryllium is referred to as a light rare metal.

Researchers found a massive beryllium ore deposit in Xinjiang. (Photo: Shutterstock)
Even in small quantities, beryllium has a significant impact. This metal is used in aerospace, nuclear power plants, and more. Especially, due to its stable properties, beryllium can be used to manufacture rockets.
According to experts, using traditional materials would increase the rocket’s weight by 500 kg. This is a considerable obstacle, as weight calculations are critical for aerospace devices.
In practice, in the aerospace field, commonly used metals are aluminum and titanium. In contrast, although beryllium has a much lower density than these two metals, it is four times stronger than steel. Therefore, using beryllium instead of aluminum and titanium can effectively reduce the weight of rockets.
Additionally, beryllium allows X-rays to pass through, and neutrons are released when this metal is bombarded by alpha particles from radioactive sources. Thus, beryllium is an important fuel source in the nuclear industry.
To protect the surrounding environment from neutron attacks, most nuclear reactors have an outer shielding layer. This layer contains beryllium to prevent excess particles from escaping and posing a danger.
In fact, one of the most expensive scientific projects in history also utilized beryllium as a key material. Specifically, NASA’s $10 billion James Webb Space Telescope is said to contain 18 hexagonal segments made from beryllium in its mirrors. Since this super telescope is exposed to temperatures of -240 degrees Celsius, its mirrors must be made of beryllium, a material capable of withstanding extremely low temperatures.


















































