Since its inception in the 1990s, online banking has become a cornerstone of e-commerce. However, account management and security challenges have not prevented unfortunate losses, especially as Internet financial crimes continue to proliferate.
Since its inception in the 1990s, online banking has become a cornerstone of e-commerce. However, account management and security challenges have not prevented unfortunate losses, especially as Internet financial crimes continue to proliferate.
Cybersecurity remains a significant challenge for any bank.
One can sit in Vietnam and order a gift for a loved one in France. Utility bills and phone payments can be automatically settled. You can buy a Swiss watch online, and it will be delivered to your home in the UK. Over 53 million Americans are gradually becoming accustomed to this form of banking.
An online banking system typically includes a user-friendly banking function. Customers can access their accounts to retrieve information, conduct transactions, and manage financial transfers. It’s simple; just log into your account via the Internet, which is both fast, convenient, and accurate.
A recent 18-month study by Bank of America also indicated that customers who use online services tend to be more “loyal.” Furthermore, online banking is currently a free service. Convenience and cost-effectiveness are the main advantages of this payment method.
Current Security Situation
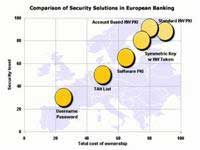 |
|
Comparison chart of online banking security solutions usage in Europe |
Recent reports on breaches, circumvention, and fraud in the financial sector have made customers wary of online financial transactions. Internet scams are easy to execute, less risky, and more cost-effective.
According to the latest research from Javelin and Pew Research, the majority of errors are not due to the bank but rather the customers themselves. For instance, in cases of stolen account information, offline causes account for 68%, including lost wallets, notebooks, and credit letters. Online fraud only accounts for 11.6%.
5% of Americans fall victim to online financial attacks, including both individuals and businesses, with losses amounting to approximately $53 billion annually.
However, customers who regularly monitor their accounts can effectively minimize their financial losses. Since these accounts are checked more frequently, any potential losses are likely to be minimal. Early detection of theft can significantly reduce the amount of money lost.
Customers who do not use online banking have a higher probability of losing account information because they leave behind more physical traces such as notebooks and receipts, making it easier for thieves to access their financial information.
Multi-Factor Authentication
Multi-factor authentication is being considered as a replacement for the current single-factor system to address one of the major financial security issues. In a single-factor system, having just a password is sufficient, which can easily be stolen without the user realizing it.
In contrast, the multi-factor system typically requires a password combined with a form of “non-stealable” information, possibly a personal question along with its answer. This method is employed by Bank of America with its SiteKey program.
Another approach involves using key systems, which could include a decryption device located at the user’s personal computer, requiring a unique PIN to operate. This makes it easier for the owner to detect a lost key rather than remembering a string of characters.
Biometrics is also emerging as one of the solutions being integrated into multi-factor authentication systems. This is seen as a future solution, with some companies already beginning to produce biometric keyboards for authentication tasks. However, the cost is still relatively high.
Addressing the authentication method is just one of the solutions aimed at creating a safer environment for online banking. There is no such thing as an entirely secure environment.
TRAN HUY