The galaxy is an endless and vast space filled with countless secrets. For thousands of years, humanity has explored and witnessed numerous fascinating astronomical phenomena occurring on this Earth. Among them are extremely rare phenomena that one might only encounter once in a lifetime.
Top 10 Rarest Astronomical Phenomena
1. Halley’s Comet

Regarded as the most well-known comet in the Solar System, Halley’s Comet is named after the astronomer Edmond Halley, who calculated that this star would pass by Earth every 75-76 years.
The last appearance of Halley’s Comet was in 1986, and the next is predicted to be in 2061. According to Space, “when Halley sweeps past Earth in 2061, the comet will be on the same side as Earth and will appear much brighter than in 1986.”
2. Hale-Bopp Comet

Dubbed the Great Comet, Hale-Bopp appeared in 1997 and was discovered by astronomers Alan Hale and Thomas Bopp in 1995. It is known to be one of the most viewed comets in history, shining in the sky for 18 months and visible to the naked eye from Earth.
In fact, NASA maintains an online database with over 5,000 images of this phenomenon. According to NASA, Hale-Bopp was approximately 1,000 times brighter than Halley’s Comet at the time of its discovery.
Calculating the orbit of the comet, astronomers indicate that its last close pass by Earth occurred 4,200 years ago, with the next return predicted to be at least 4,385 years in the future.
3. Blue Moon

You may already know that this phenomenon has nothing to do with the moon turning blue magically. Instead, the name refers to the third full moon in a season that has four full moons. Based on this calculation, there are about 29.5 days between full moons, so months with 30 or 31 days can have two full moons.
According to NASA, a blue moon occurs every 2.5 years. The last blue moon appeared in August 2021, so the next one is likely to occur in 2023.
4. Total Solar Eclipse
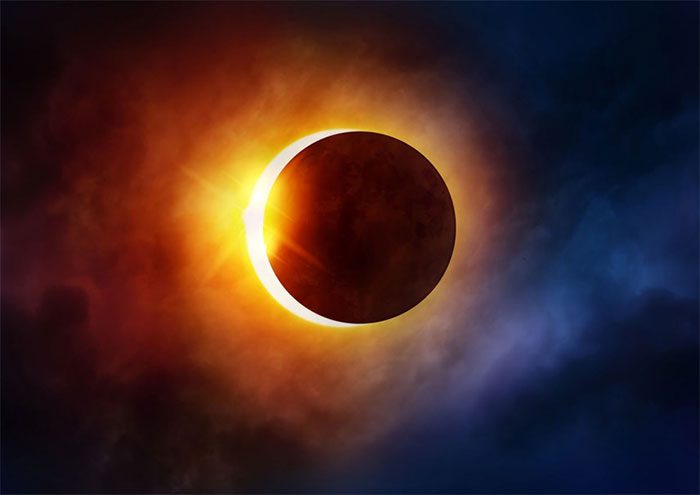

The term “total solar eclipse” is probably no longer unfamiliar to us. While it is not a rare phenomenon globally, it occurs every 18 months but only at specific locations. It can take centuries for this phenomenon to return to the same location.
With this, Belgian meteorologist and astronomer Cassini calculated that a total solar eclipse can only occur at any given location on Earth once every 375 years.
5. Storms on Saturn
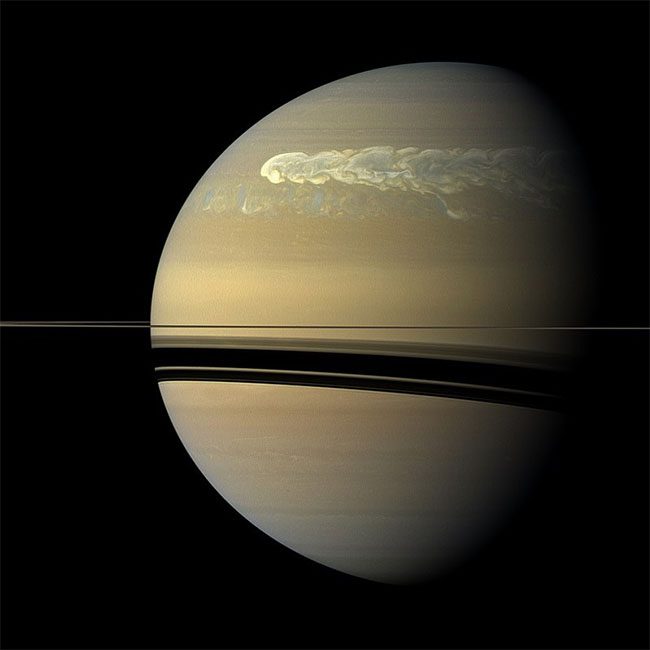

The Great White Spot, also known as the Great White Oval, are massive periodic storms visible from Earth through telescopes due to their distinctive white appearance.
These storms typically appear in cycles of 20-30 years and can cover hundreds to thousands of kilometers. To date, only six storms have been observed in Saturn’s atmosphere since 1876, with the last occurrence recorded in 2010.
6. Transit of Venus
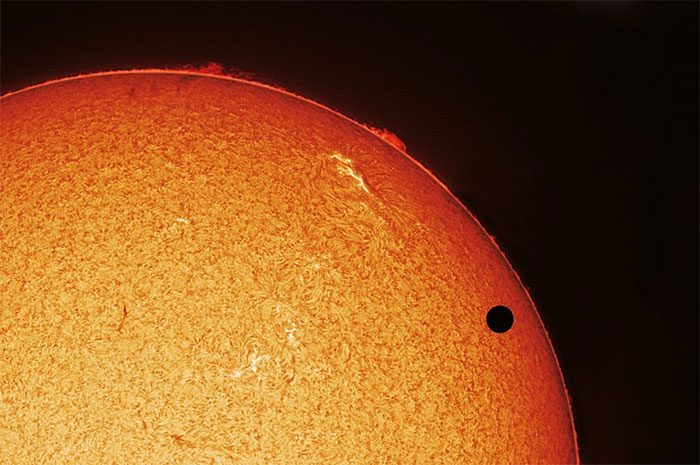

The Transit of Venus is an astronomical phenomenon that occurs when Venus passes directly between Earth and the Sun. During this time, people on Earth see a small black dot on the Sun’s disc. According to scientists, this event usually occurs in cycles of 8 years, with Venus’s position on the Sun’s disc continually changing. Additionally, it takes about 110 years for the previous position to repeat. The last occurrence of this phenomenon was in 2012.
7. Planetary Alignment

Astronomers believe that the alignment of planets in the Solar System is extremely rare. It is estimated that Mars, Venus, Mercury, Jupiter, Saturn, and the Moon will align in 2040.
Previously, scientists recorded the alignment of Mars, Saturn, Venus, Mercury, and Jupiter in 2000. Meanwhile, in May 2011, astronomers also noted a moment when Jupiter, Mercury, and Venus aligned.
8. ISON Comet
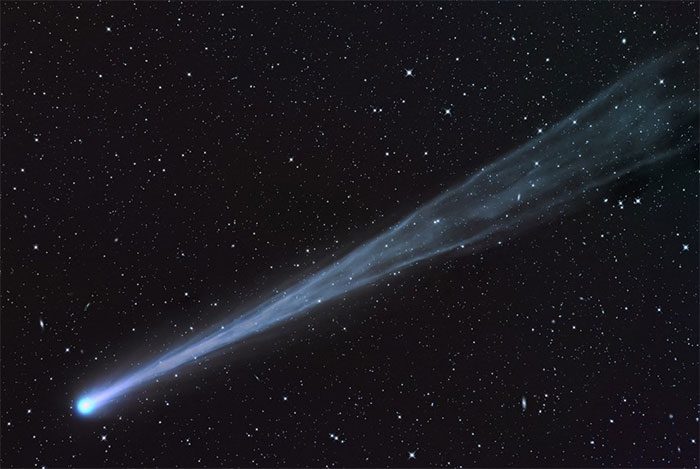

ISON is a comet with a very close orbit to the Sun, discovered by Russian astronomers Vitali Nevski and Artyom Novichonok on September 21, 2012. However, it completely disintegrated on November 28, 2013.
Astronomers noted that when it came in contact with the Sun at a distance of over one million kilometers, the material on this comet began to heat up, vaporize, and then break apart into smaller pieces, releasing dust into space in streaks.
9. Leonid Meteor Shower

The Leonid meteor shower occurs when Earth passes through the orbit of the Tempel-Tuttle comet. This stunning astronomical event was first discovered in 1833 and lasts for over 15 minutes. During this event, people on Earth can see around 1,000 meteors per hour streaking across the sky.
Astronomers even believe that the Tempel-Tuttle comet can produce about 100,000 meteors per hour.
10. Churyumov-Gerasimenko Comet
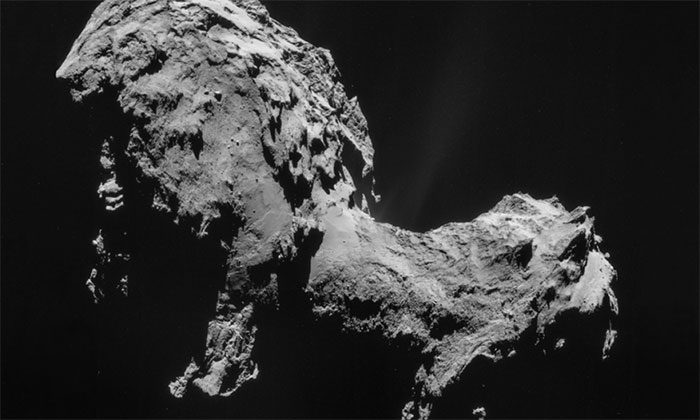

The Churyumov-Gerasimenko Comet orbits the Sun with a cycle of six years. This comet originates from a body near Neptune, and its closest approach to Earth is about 3.5 astronomical units. The Churyumov-Gerasimenko Comet was first discovered in 1969.