Currently, the technique of PET CT scanning (or CT PEP) is increasingly being applied widely. PET CT scanning has significant advantages in helping to detect, diagnose, and treat cancer, providing patients with a higher chance of survival.
What You Need to Know About PET CT Scanning
- What is PET CT Scanning?
- Why is PET CT Scanning Necessary?
- When Should You Get a PET/CT Scan?
- Advantages and Disadvantages of PET CT Scanning
- What is the Procedure for PET CT Scanning?
- Frequently Asked Questions About PET Scanning
- How Much Does PET CT Scanning Cost?
- Where is the Best Place for PET CT Scanning?
This article is professionally consulted by the Medical Information Center, Tam Anh General Hospital, Ho Chi Minh City.
What is PET/CT Scanning? What is the purpose of PET/CT scanning, and why is this technique considered a golden hope for cancer patients? Is PET CT scanning painful or dangerous? How long does a PET CT scan take? These are the questions many people have when discussing this imaging diagnostic technique.

Let’s explore the basic information about the PET CT scanning method in the following article.
What is PET CT Scanning?
PET CT scanning (Positron Emission Tomography and Computed Tomography) is an advanced imaging diagnostic technique that applies nuclear medicine technologies, providing superior results compared to most common imaging techniques.
The structure of a PET CT machine bears many similarities to a conventional computed tomography (CT) machine or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) machine. The difference lies in the operational method.
By injecting a radioactive tracer into the bloodstream, this substance appears in tumors or areas of inflammation. The scattering process of this substance is recorded by the signal detection chamber of the PET CT machine and reconstructed into images. Currently, the most commonly used tracer is FDG, a compound similar in structure to glucose (the primary nutrient source for cells). By locating and quantifying this compound, specialists can easily identify inflammatory foci or cancer cells that have metastasized to hard-to-detect areas.
PET CT Scanning is one of the effective imaging diagnostic methods.
Why is PET CT Scanning Necessary?
In most diseases, common imaging diagnostic methods such as computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can meet most diagnostic needs. However, PET CT scans still hold a unique advantage when applied in certain specialized fields as follows:
1. Application of PET/CT in Oncology
All cells use glucose to generate energy, including cancer cells. However, due to the rapid growth rate of cancer cells, they have a higher demand for glucose than any other cells in the body. Thus, injecting a radioactive tracer with a structure similar to glucose, such as FDG (18-fluorodeoxyglucose), will be sensitive to these cancer cells. This allows doctors to identify where these dangerous cell lines are located to prepare appropriate treatment plans.
PET scans can detect both primary tumors, which are the main manifestation of cancer, and are very sensitive in detecting the metastasis of these tumors. Additionally, the application of PET CT can help answer questions such as:
- Is this tumor benign or malignant?
- What is the origin of this tumor?
- Which organs have metastasized?
- What is the effectiveness of post-cancer treatment? Is it completely cured or has it recurred locally?
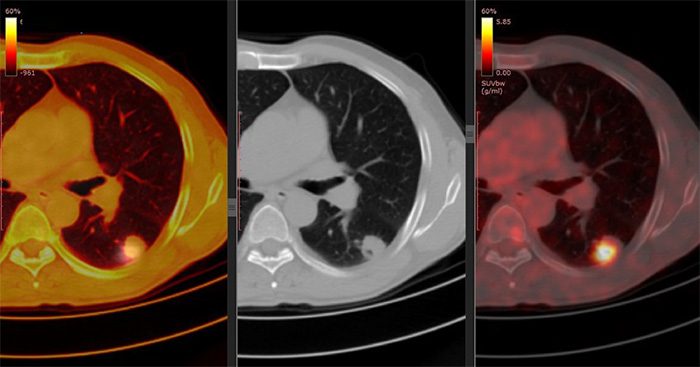
PET CT Scanning helps detect primary tumors and metastatic tumors.
2. Application of PET/CT in Cardiology
Aside from its strong applications in oncology, PET CT application also enables earlier treatment plans and better prevention in cardiovascular diseases. Among these, the most concerning issue is myocardial ischemia.
Some applications of PET CT in cardiovascular disease include:
- Identifying regions of the heart muscle that are ischemic or dead
- Helping to predict the risk of myocardial infarction and the feasibility of surgical interventions, stenting, etc.
- Assessing the metabolic processes of heart tissue
Some later generations of PET CT have inherited the advantages of previous techniques and are gradually being applied in major cardiovascular centers like SPECT, PET-MRI, etc.
3. Application of PET/CT in Neurology
In neurological diseases, PET CT can be used to evaluate the vascular system and the ability to supply oxygen to brain tissues, for example, in stroke, dementia, memory disorders, seizures, or brain tumors…
Some neurotransmitters used for localization through PET CT include dopamine in the diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease.
When Should You Get a PET/CT Scan?
CT PET is not a routine indication in clinics or hospitals. Due to its advantages, PET CT scanning is indicated in certain situations:
- When evaluating the status of distant metastasis of a tumor
- When accurately diagnosing the condition of a primary tumor, if other means cannot provide an appropriate answer
- When investigating chronic coronary artery disease causing myocardial ischemia.
- Assessing the status of brain ischemia, brain tumors…
Depending on specific diseases, a specialist will advise and provide appropriate indications.
PET CT Scanning has its own advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages and Disadvantages of PET CT Scanning
Every method has its own advantages and disadvantages; PET CT is no exception. Patients need to be aware of the following pros and cons of this advanced imaging diagnostic technique:
1. Advantages of PET CT Scanning
- Evaluates both structural and functional aspects of the body.
- Compared to exploratory surgery, the application of nuclear medicine such as PET CT Scanner can reduce treatment costs and provide better prognoses for interventions after scanning.
- Highly reliable in distinguishing between benign and malignant tumors.
- Provides near-optimal results regarding invasiveness and metastasis.
- Assesses the stage of cancer.
- Investigates recurrence status and treatment response in oncology, cardiology, and neurology…
- Early diagnosis of cardiovascular ischemic disease.
2. Disadvantages of PET CT Scanning
- Radiation risk: Performing a PET CT scan carries a radiation exposure risk equivalent to that of a conventional CT scan. This is because the amount of radiation from the tracer is very small, not enough to cause harm, so the radiation absorbed by your body is equivalent to that of a CT film. This amount of radiation will gradually clear and does not have adverse effects.
- Increased blood sugar: Using FDG can cause unstable blood sugar levels during the procedure; however, this drawback can be well controlled.
- Narrow space: The process requires lying in a confined chamber for a relatively long time, which can be uncomfortable for patients.
What is the Procedure for PET CT Scanning?
1. Preparation Before PET Scanning
After being consulted and indicated for PET CT scanning, patients need to pay attention to several matters as follows:
- Patients should fast for 4 hours prior to the scan.
- You may drink water up to 2 hours before the procedure. It is best to use clear, flavorless water, preferably plain water. Aim to drink plenty of water, about 0.5-1 liter, before the scan.
- Prescription medications can be taken as usual. However, diabetic patients currently taking Metformin should consult their doctor, as they may need to stop the medication 48 hours before the PET CT scan.
Preparing the patient before a PET CT scan is very important.
- Choose loose-fitting clothing without zippers or metal. You may be asked to wear hospital clothing if necessary.
- Metal objects can interfere with imaging and skew results, so personal items such as bags, phones, and other belongings should be left outside the scan room or at home. Hearing aids, dentures, and medical devices can be worn, but it’s advisable to inform the doctor in advance for optimal results.
- Keep your schedule flexible, as a PET scan can take 40-60 minutes.
Here are some situations in which you should discuss with your doctor before undergoing a PET CT scan:
- You are pregnant, suspect you might be pregnant, or are breastfeeding.
- You are undergoing treatment for diabetes.
- The medications you are currently taking.
- Your allergy history, particularly to medications, food, pollen, etc., especially if you have had allergic reactions to contrast agents or radiotracers previously.
2. Conducting the PET CT Scan
Before beginning the scan, the doctor will ask the patient to lie down on a stretcher and review some of the medical history noted above, before administering a radiotracer via an intravenous injection in the arm.
Depending on the individual, the radiotracer may take about 30-60 minutes to disperse throughout the body, which is also the time required for cells to “consume” the radiotracer. During this time, patients should rest quietly and avoid movement or talking.
In certain situations, the doctor may ask you to drink a contrast solution to differentiate between the digestive tract and other structures. However, this step is not commonly performed.
After the dispersion period, you will be taken into the PET CT scanner room to begin the scan. The scanning duration typically ranges from 20-30 minutes, depending on whether the doctor is assessing a specific organ or the entire body.
For cardiovascular conditions, the procedure may take longer, approximately 2-3 hours, as patients may require two PET scans before and after intervention to evaluate the area of heart tissue that was ischemic before and after treatment.
The process of performing a PET CT scan is safe yet not overly complicated.
3. Post-PET CT Scan Considerations
If there are no additional instructions, patients can return home and resume normal activities after the PET scan.
A very small amount of the radiotracer will remain in the patient’s body and will be excreted through urine and feces. Therefore, it is important to drink plenty of water after the scan to help the body clear the injected radiotracer quickly.
Frequently Asked Questions About PET Scans
1. What is the difference between PET CT and CT scans?
PET CT and computed tomography (CT) share some similarities in structure and equipment, including a scanning room and X-ray generation and detection. However, the scanning techniques differ. PET CT combines both CT scanning with the use of a positron emission radiotracer to pinpoint locations.
Functionally, CT provides structural images of organs in the body, allowing for observation of tumors at certain sizes. In contrast, PET CT can detect smaller tumors and distant metastases that CT may not identify. Additionally, the density quantification of the radiotracer can indicate whether a tumor is benign or malignant.
2. Is PET CT harmful?
Some risks associated with undergoing a PET CT scan include:
- Radiation exposure: Studies over the years have concluded that residual radiation levels after a CT or PET CT scan do not adversely affect health. Specifically for PET, the residual radiotracer is minimal and is typically cleared within a few days post-scan, thus not posing a significant concern for patients.
- Allergic reactions: Any substance, including radiotracers, can potentially cause an allergic reaction. However, instances of allergic reactions to radiotracers (FDG) are extremely rare.
3. Is isolation required after a PET CT scan?
Due to the low levels of residual radiation in the patient’s body, which are completely eliminated within a few days, patients do not need to be isolated after a PET CT scan.
4. When will the PET scan results be available?
Typically, PET CT scan results will be available within 2-5 days post-scan. The doctor will schedule a follow-up appointment for the patient on the day the results are received to discuss further treatment options.
How Much Does a PET CT Scan Cost?
In general, the cost of a PET CT scan is relatively high. The price per scan can range from 20,000,000 to 25,000,000 VND. This cost may vary depending on the healthcare facility. For instance, scans conducted at larger hospitals with advanced equipment tend to be more expensive.
Where is the Best Place to Get a PET CT Scan?
When undergoing a PET CT scan, patients should choose reputable hospitals or healthcare facilities, especially large hospitals specializing in cancer treatment, to ensure a swift and smooth scanning process without adverse effects.
PET CT scans are regarded as an advanced imaging diagnostic technique that provides high efficacy in diagnosing various serious conditions. As a result, this method is increasingly being utilized and is expected to become a common diagnostic approach in the future. If you are referred for a PET CT scan, relax, do not worry, and cooperate with the technician in the scanning room for the best possible results.




















































