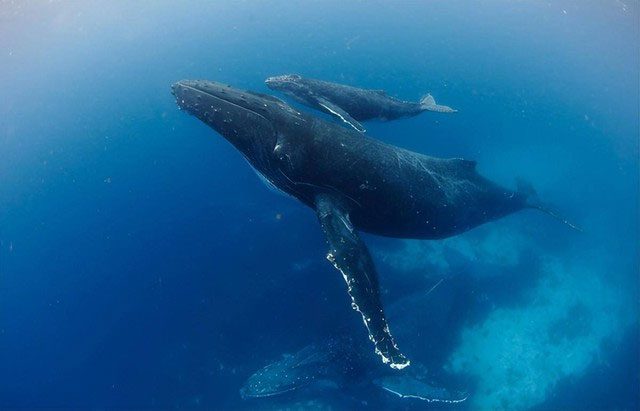
The deep diving ability of whales is the result of evolutionary adaptation over millions of years. Thanks to their special body structure and efficient energy-saving capabilities, whales can live and feed at depths that humans cannot reach.
Whales are the largest mammals on Earth and also the best diving animals known to humanity. Their dive times can reach up to 20 minutes, and they can dive to depths exceeding 3,000 meters.
This capability also surprises marine biology experts. They believe that the diving ability of whales is simply stronger than that of nuclear submarines. So how does a whale’s body adapt to the high-pressure environment of the deep sea?

Whales are the best diving animals known to humanity.
Whales have a uniquely structured body to adapt to high pressure in the deep sea. Their bones are primarily made of cartilage, which is highly elastic and can withstand greater pressure compared to human bones. The muscles of whales are also very strong, allowing them to contract their ribcage to regulate internal body pressure. Additionally, whales have a special circulatory system that helps manage the blood flow in their bodies at great depths.
The key to explaining why whales can survive in the ocean is their unique respiratory system. When at the surface, they inhale fresh oxygen through their lungs and then expel carbon dioxide from their bodies.
The lungs of whales are much larger than human lungs. In a deep breath, whales can inhale tons of air, which also allows their lungs to store a significant amount of oxygen when they dive. Over time, their circulatory process can meet the demands of long dives, and during the dive, whales can determine the oxygen levels in their blood and distribute it accordingly.

The lungs of whales are much larger than human lungs.
Whales are mammals, but they have a completely different respiratory system compared to humans. Whales possess very large and efficient lungs that help them optimize oxygen exchange even at great depths. The blood of whales also has a higher oxygen storage capacity than human blood, allowing them to maintain normal activity for extended periods underwater.
Moreover, whales can adapt to underwater pressure environments by smartly adjusting the control of volume and pressure within their bodies. As whales continue to dive, the density and pressure of the water increase, allowing their bones to change volume freely so they can swim freely and maintain balance in the water.

Whales can intelligently balance internal and external pressure.
Whales have a thick layer of blubber covering their bodies to help keep them warm in cold water environments. Additionally, whales can also regulate their body temperature by adjusting blood flow to different organs.
When diving, whales can intelligently balance the internal and external pressure by inhaling and exhaling seawater, thus protecting their organs and reducing the impact of high external pressure.
In this way, whales can reduce energy consumption when surfacing. This method is akin to adding a “buffer layer” for whales, making their surfacing process more stable and less affected by the outside world.

The blood of whales also has a higher oxygen storage capacity than human blood.
Whales have a streamlined and smooth body shape, which helps minimize water resistance when moving. This allows whales to conserve energy and dive deeper than objects of different shapes.
Nuclear submarines, although equipped with advanced technology, are limited by several factors:
- Construction materials: The hull of submarines is made from steel, a material that cannot withstand high pressure at great depths.
- Ventilation systems: Submarines need to use oxygen from the air to operate engines and support the crew’s respiration. Providing oxygen at great depths is challenging and costly.
- Size: Submarines are large, creating significant drag when moving through water, making deep dives more limited.

Whales are an important part of the ocean ecosystem.
Whales are large and majestic creatures, being the largest mammals on Earth. They inhabit all oceans around the world and come in various sizes and shapes. Whales play a crucial role in maintaining the health of the ocean ecosystem, and it is essential that we protect them from human threats to ensure their continued existence for generations to come.
Overall, whales can dive deeper than nuclear submarines thanks to their bodies adapted to high pressure, efficient gas exchange systems, energy conservation capabilities, high CO2 tolerance, and structural advantages.
However, it is important to note that whales and nuclear submarines are designed for different purposes. Whales need the ability to dive deep to search for food and avoid predators, while nuclear submarines are designed for military operations.