Lithium batteries are widely used in electric bicycles and motorcycles today. If a fire occurs, it is very difficult to extinguish it with regular fire extinguishers, and using water can even cause an explosion.
Why Can’t Electric Vehicle Batteries Be Extinguished with Mini Fire Extinguishers?
According to experts, if there is a short circuit or close contact with a fire source, electric vehicles and internal combustion engine vehicles have the same risk of fire. However, in reality, extinguishing fires in electric vehicles is more challenging than in gasoline vehicles. A combustion engine vehicle can be put out with a fire extinguisher or by covering it with a wet blanket to cut off the oxygen supply. In contrast, the only way to control a burning electric vehicle is to manage the source of the fire and isolate the vehicle, as it may reignite multiple times, even after the flames have been extinguished for a while.
Experiment on extinguishing electric vehicle battery fires. (Source: VTV).
Meanwhile, lithium-ion battery fires occur due to chemical reactions and the movement of ions within the battery cell, allowing them to burn without needing oxygen. The fire cannot be extinguished; it can only be isolated to prevent it from spreading while waiting for the chemical reaction to finish.
Experts state that lithium batteries are commonly used in electric bicycles and motorcycles today, and if they catch fire, they are difficult to extinguish with ordinary fire extinguishers. In fact, using water can cause explosions, as water turns into hydrogen when exposed to high temperatures.

Fire and explosions are likely to occur in electric motorcycles and bicycles.
Currently, only a few foreign products, like water-based fire extinguishers using molecular coating technology, can rapidly reduce temperatures to extinguish fires. However, this type of extinguisher is not common and is significantly more expensive than standard types.
Lecturer Trần Văn Đồng from the Fire Prevention and Fighting University states that fire and explosions are likely to occur in electric motorcycles and bicycles—a product line equipped with a lower safety coefficient for batteries, due to mechanical impacts or a lack of knowledge and skills among some users.
According to Mr. Đồng, first, most incidents are due to overuse leading to increased heat; second, during charging, heat builds up; third, lack of maintenance leads to aging and circuit short circuits.
What to Do When an Electric Vehicle Catches Fire?
In a recent report titled “Electric Vehicle Batteries: Gaps in Fire Safety Management VTV24”, practical experiments attempting to extinguish electric vehicle battery fires have shown that no ordinary fire extinguishers can put them out.
In the experiment, when the electric vehicle battery caught fire, flames erupted, breaking through the plastic casing of the electric vehicle. As the temperature rose sharply, the battery exploded. Even when using a powder extinguisher and emptying a 4kg extinguisher, the flames continued to flare up.

Electric vehicle battery fire causing intense flames.

Ordinary fire extinguishers cannot stop the flames from electric vehicle battery fires.
After switching to a CO2 extinguisher and continuously emptying it, the flames still continued to flare up.
Fire prevention experts advise:
- When witnessing an electric vehicle on fire, individuals should not attempt to use water, mini fire extinguishers, or regular blankets to suppress the flames. These methods can cause the battery to explode and the fire to intensify.
- As there is no way to extinguish the source of the fire, which consists of the chemicals inside the battery, a fire-retardant blanket (specialized type) can be used to cover the vehicle to prevent flames from spreading to other materials.
- If a fire-retardant blanket is not available, call the fire department immediately and notify them that it is an electric vehicle fire so that they can prepare appropriate measures.
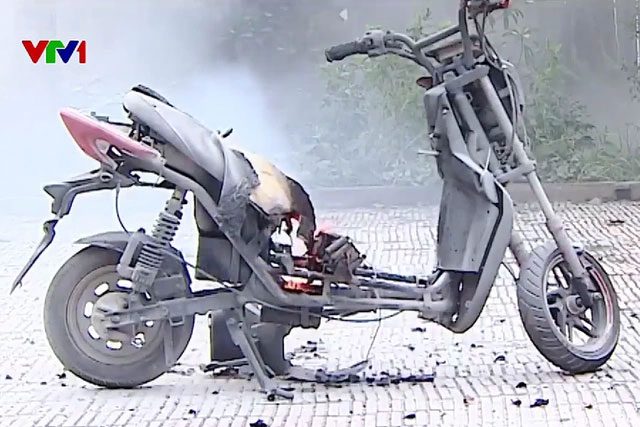

In the VTV experiment, the fire only stopped when the battery was completely burned out.
Mr. Trần Thành Vinh, Head of the Technical Science Department at the Vietnam Fire Prevention and Fighting and Rescue Association (PCCC-CNCH), believes that although the speed of electric vehicle development is high, there are currently no specific standards or regulations to ensure fire safety for lithium-ion batteries and electric vehicles. This involves the entire process from manufacturing, transportation, storage to usage and maintenance, with responsibility shared among various agencies and sectors.
“Currently, we are collaborating with the Ministry of Science and Technology to research and propose issuing standards related to ensuring safety for electric vehicle batteries and electric vehicles. Once the standards are established, the association will work with relevant agencies to propose solutions to control the goods circulating in the market,” said Mr. Vinh.
How to Prevent Fire and Explosions in Electric Motorcycles and Bicycles
The Fire Prevention and Fighting Police Department (Ministry of Public Security) has reported that some electric motorcycle and bicycle users have a habit of charging their batteries overnight, which poses a high risk of fire and explosion.
To ensure safety during the use of electric motorcycles and bicycles and to prevent fires and explosions, the Fire Prevention and Fighting Police Department recommends:
- 1. Charge the battery when it is nearly depleted, using a suitable and stable power source (according to the voltage recommended by the manufacturer). Do not charge immediately after riding; wait for the battery to cool down for about 20 minutes before charging. Avoid overnight charging and do not charge for more than 8 hours continuously. If the vehicle is not used for a long time, charge the battery fully and remove it from the vehicle to extend its lifespan.
- 2. Store the battery properly by placing the vehicle in a dry and well-ventilated location. Do not leave the battery in hot, humid areas. Avoid applying strong force to the battery.
- 3. Do not alter the vehicle’s structure or add accessories or devices that may affect the wiring system and power supply of the vehicle (incompatible devices or voltage differences can cause the battery to explode).
- 4. Regularly maintain the battery and the vehicle’s electrical system. Approximately every 3 months, have the vehicle checked for battery condition, charging system, and the vehicle as a whole to detect and address any issues promptly.
- 5. Wash the vehicle properly. Do not use high-pressure water jets or spray directly into areas under the seat. After washing, dry the battery and brake areas before restarting. After riding in the rain, place the vehicle in a dry, breezy location to dry and check for any water entering the battery area.
During usage, while rare, electric vehicle battery fires can still occur. If you notice the battery heating up unusually while charging, immediately unplug it. If possible, remove the battery and place it in a metal container, preferably one filled with sand, and keep it away from flammable materials. Never adjust the technical specifications of the electric vehicle or replace devices, components, batteries, chargers… with incorrect types, unknown sources, or those not synchronized with the vehicle’s design specifications. Adding accessories or devices that affect the vehicle’s wiring system and power supply can lead to discrepancies, causing battery and battery fires.
It is advised not to charge overnight in apartments or in parking garages without necessary supervision. In case of fire, immediately call the fire department and inform them that it is an electric vehicle fire so they can prepare appropriate measures. Firefighting related to lithium-ion batteries needs to be handled differently from regular fires. Do not attempt to pour water directly on the battery, as water and lithium can create hydrogen gas, making the situation more explosive. Standard fire extinguishers may be used.