Kissing someone can lead to a range of illnesses, from mild conditions like oral herpes to more serious issues such as viral meningitis or mumps.
Saliva plays a natural cleansing role due to its cleaning action. Additionally, saliva contains antibodies and other antibacterial proteins (such as lysozyme). The normal flora in the mouth (the “good” bacteria) also helps prevent the growth of “bad” bacteria.
The fact is that our bodies harbor all sorts of natural viruses, including in the mouth. People are more susceptible to oral infections when their natural defenses in the mouth are weakened. While kissing offers many health benefits, it can also transmit harmful bacteria and viruses when someone is sick.
A kiss can contain up to one billion bacteria from 278 different species. While 95% of these bacteria are harmless, research published in The American Journal of Medicine indicates they can still lead to health issues.
Here are some illnesses you may contract from kissing someone, according to Medical Daily.
Oral Herpes
Types of viruses considered part of the herpes family include Epstein-Barr, varicella-zoster (causing chickenpox), and herpes simplex (causing cold sores). The herpes simplex virus can spread through direct contact with the virus while kissing.
Herpes is most contagious when blisters are forming or have erupted. The virus can be “shed” (transmitted to others) from the site of the blister even after they have healed. Chickenpox is highly contagious from person to person through direct contact, droplets, or airborne transmission.
In sexual terms, kissing may seem relatively harmless; however, many people are unaware that kissing can transmit sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) and sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
This does not mean you need to stop kissing, but it is essential to take precautions if you or your partner are infected with the herpes simplex virus (HSV), as it can transmit STIs to your partner while kissing.
Viral Meningitis
You may be at risk of viral meningitis if you come into contact with someone else’s saliva while kissing. This easily transmissible disease causes inflammation of the thin membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord.
Initial symptoms of viral meningitis include headaches, fever, chills, fatigue, nausea, and neck pain. If you suspect you have the illness, you should see a doctor immediately.

A kiss can contain up to one billion bacteria from 278 different species. (Photo: kevinmd.com).
Cytomegalovirus
Your first kiss as a teenager could expose you to Cytomegalovirus (CMV). This virus spreads through bodily fluids such as saliva, blood, and urine and will remain in the body indefinitely.
CMV rarely causes severe consequences, but children, pregnant women, or immunocompromised individuals are at risk of pneumonia, hepatitis, and rash. Infants exposed to the virus while in the womb often face neurological and developmental issues. Teenagers and adults who contract the disease may experience fatigue, muscle aches, headaches, fever, and swollen liver and spleen for about three weeks.
Mumps
Mumps spreads through respiratory secretions. The first sign of mumps is swelling of the salivary glands around the ears, as the disease primarily affects this area. Additionally, mumps patients may experience fever, headaches, muscle aches, fatigue, and loss of appetite.
Flu
Flu viruses easily spread from person to person through mucus or saliva. Common symptoms include muscle pain, headaches, sore throat, high fever, and runny nose.
Moreover, poliomyelitis is another disease transmitted through kissing, although it has nearly disappeared thanks to vaccination.
Mononucleosis (Mono), also known as the kissing disease
Mononucleosis is a common term for a viral infection caused by the Epstein-Barr virus. The virus spreads through saliva, and infection occurs through contact.
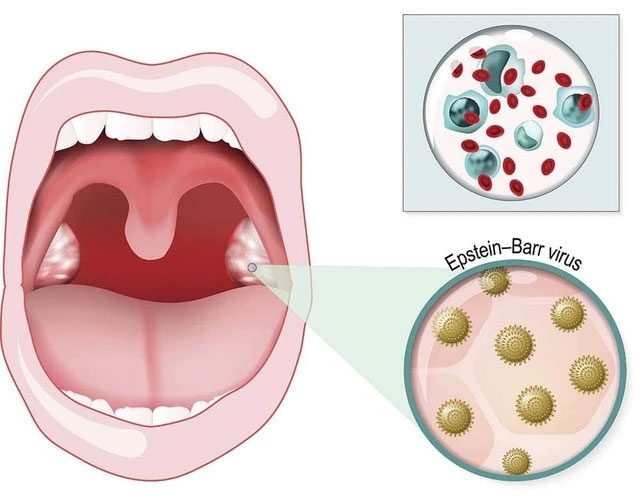
Infectious mononucleosis caused by the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) is characterized by fatigue, fever, sore throat, and swollen lymph nodes.


















































