Innovative startup Airloom Energy introduces a revolutionary wind turbine that generates energy from all wind directions.
This turbine design helps reduce installation and maintenance costs, enabling rapid access to clean energy at a lower price.
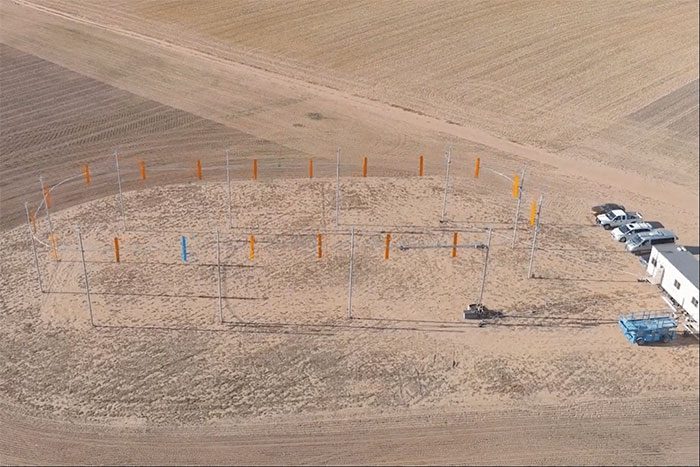

The prototype wind turbine promises to transform the wind power generation industry. (Image: Trust my science).
The world is currently undergoing a strong energy transition, making this an urgent global requirement, with the wind power generation industry finding itself at a technological crossroads.
Startup Airloom Energy, based in Wyoming, USA, is challenging conventional concepts of wind turbines. It may redefine the economics of electricity generation from this technology.
Airloom Energy’s innovation promises to significantly reduce the cost of producing green energy while causing less disruption to landscapes and ecosystems that are already heavily impacted by traditional wind turbines.
A New Era for Wind Energy?
This emerging technology features a completely innovative design, differing from traditional turbines that require tall towers and long blades.
Additionally, to increase electricity production efficiency to meet energy demands, current turbine types require increasingly larger sizes. This raises production, transportation, installation, and maintenance costs.
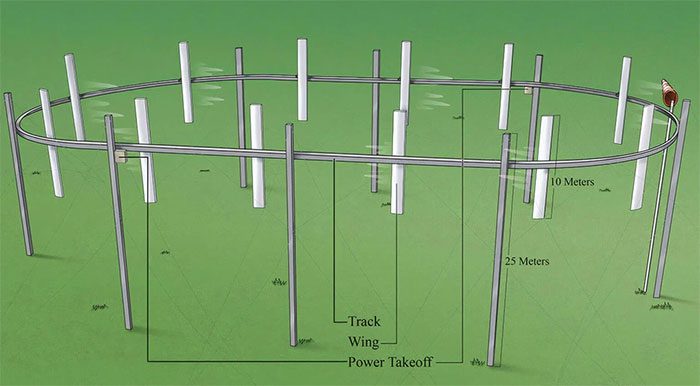
The wind turbine model created by Airloom can capture wind from all directions. (Image: Trust my science).
Airloom’s approach is much more compact and cost-effective. Its system features 10-meter-long blades, fixed on cables that run along an oval track, supported by 25-meter-high pillars. Each small system can achieve a total capacity of up to 2.5 MW.
Like a sailboat, the new turbine captures wind energy from nearly any angle, with blades moving along the track, designed to flexibly pivot for effective wind capture.
Wind will cause the blades to move, pulling cables connected to generators and producing energy.
Unlike conventional wind turbines that mainly harness energy from the leading edge of the blades, Airloom’s design allows the entire blades to contribute to electricity generation along the entire circumference of the track.
Reducing Costs and Increasing Potential for Optimal Energy
This new system structure will enable deployment in environments where traditional turbines cannot be installed, thereby opening opportunities for countries to harness wind in areas not suitable for conventional turbines.
This flexibility could accelerate the adoption of wind energy.
Moreover, Airloom Energy claims that their wind farms can be built at 25% lower cost compared to a conventional project. This is due to the lower cost of materials used in the turbine and the ease of construction, which does not require large machinery or specialized facilities.
Airloom’s initial prototypes, despite their small scale, have demonstrated sufficient potential to attract attention and funding from investors seeking sustainable innovation.
The company’s confidence is based on exploring technological capabilities that can disrupt the market through profitability and product flexibility.
Consequently, after raising $4 million in initial capital, Airloom Energy is preparing to demonstrate the effectiveness of its innovative wind power generation technology with an initial testing system with a capacity of 50 kW.
This prototype serves as a prelude for larger-scale commercialization. The promise from this startup is bold: to reduce wind energy costs to about one-third of the current price per kilowatt-hour.
If Airloom can maintain its promise of lower costs and adaptability to diverse environments, including offshore, the impact of this discovery could truly resonate in the green energy sector.
By facilitating the deployment of wind energy, the company could play a crucial role in accelerating the decarbonization process in energy production.
This progress would then serve as a powerful lever to achieve international climate goals by increasing the share of renewable energy in the global energy mix and reducing dependence on fossil fuels, which are more polluting and a major cause of climate change on Earth.