Not just red eyes, many other conditions can also cause eye redness. Some conditions require prompt treatment; otherwise, they can affect vision and lead to serious complications.
Symptoms in the eyes can be one of the ways your body signals health issues. Bloodshot eyes may indicate problems such as conjunctivitis, lack of sleep, contact lens irritation, or styes.
Causes of Red Eyes and Treatment Options
1. Alcohol Consumption
After consuming a large amount of alcohol and getting drunk, you may notice your eyes becoming red. This is not a dangerous symptom; it’s simply a side effect of alcohol.
Alcohol causes the small blood vessels in the eyes to dilate, increasing blood flow through these vessels. The contrast between the white of the eye and the red of the blood makes the eyes appear bloodshot.
In addition to redness, heavy drinking can also cause eye irritation, such as itching and discomfort. Prolonged use can lead to blurred vision, poor reflexes, dry eyes, or an increased risk of other eye conditions.
Management
Redness from alcohol will resolve once you stop drinking and the alcohol level in your body decreases. However, if you feel discomfort in your eyes at that time, over-the-counter (OTC) eye drops can help reduce the redness.
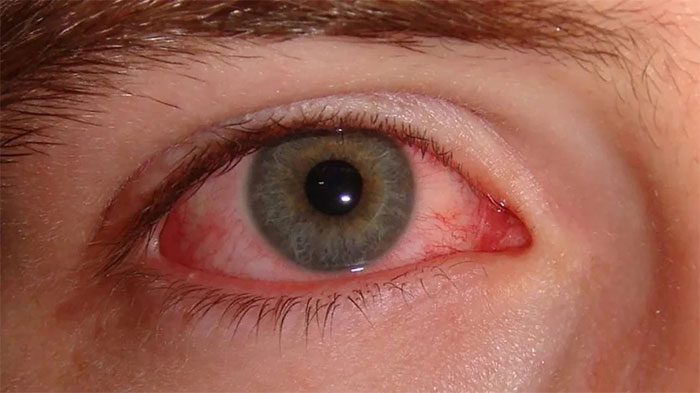
Alcohol can cause bloodshot eyes but it will quickly disappear. (Image: Internet).
2. Conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis, or pink eye, is caused by bacterial or viral infections, leading to one or both eyes becoming bright red, swollen, watery, and itchy. This is an inflammation (redness) of the conjunctiva, the transparent tissue lining the inner surface of the eyelids and covering the outer surface of the eye. While it rarely becomes serious, conjunctivitis spreads quickly.
Treatment
For bacterial conjunctivitis, the most common treatment is antibiotic eye drops. Other cases not caused by bacteria or certain viruses (such as herpes simplex or varicella-zoster) may resolve on their own.
To alleviate symptoms, individuals can implement several home remedies:
- Warm compresses
- Saline drops or non-prescription eye drops
- Avoiding contact lenses or rubbing the eyes
3. Allergies
Red eyes can be caused by allergic conjunctivitis. This condition leads to red, itchy, irritated, and watery eyes in response to allergens like pollen, pet dander, or dust mites.
Identifying the allergen and avoiding contact can help the redness subside. Additionally, you can treat and reduce symptoms with other measures such as:
- Antihistamine medications
- A cool compress or clean washcloth over the eyes, and rinsing the eyes with saline
- OTC eye drops for allergy relief

Allergic conjunctivitis occurs due to exposure to allergens like pollen, pet dander, and dust mites. (Image: Internet)
4. Corneal Injury
Red eyes can occur due to corneal injury—the rounded, transparent front part of the eye that helps focus light, such as scratches or tears in the cornea.
Causes of corneal injury include rubbing the eyes, dry eyes, foreign bodies, or sharp objects poking the eye.
According to WebMD, if you have a scratched cornea, you should rinse your eyes with clean water or saline once or twice to remove any foreign matter (if present) or soothe the eyes. Be careful not to rinse too often, as this may worsen the condition. Patients should avoid rubbing or pressing on the eyes.
Afterward, seek medical attention. A doctor may prescribe antibiotic eye drops or ointments to prevent infection, and drops to reduce pain and redness. Patients may also be advised to wear an eye patch to shield against light exposure.
A scratch can heal within one to two days or up to a week, depending on the size of the scratch.
If you have a corneal tear, seek medical care immediately. Surgery is a typical treatment to prevent further damage to the eye and to remove any foreign objects from the eye.
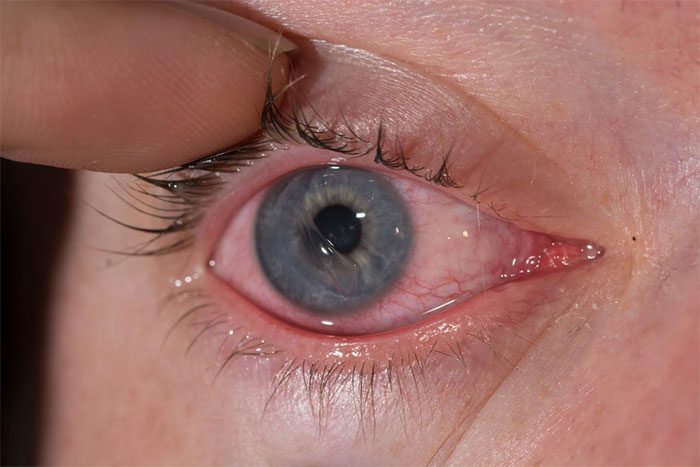
Corneal injury causes redness, watering, or sensitivity to light. (Image: Internet).
5. Glaucoma
Glaucoma is a common eye condition where the optic nerve connecting the eye to the brain is damaged. This is often due to fluid buildup in the front part of the eye, increasing internal pressure.
Glaucoma often does not cause symptoms initially, making it difficult to detect. Individuals with this eye issue may experience blurred vision or see rainbow-colored circles around bright lights. Both eyes are usually affected, though the condition may be worse in one eye.
Additionally, glaucoma can also cause redness, eye pain, and headaches, but these symptoms usually occur later.
Treatment can vary depending on the type of glaucoma. Some treatment options include:
- Eye drops
- Laser treatment
- Medications or intravenous drugs to reduce internal eye pressure
- Surgery
Glaucoma can lead to vision loss if not diagnosed and treated promptly. Therefore, if you suspect you have this eye condition, it is essential to visit a hospital for an examination, especially if you experience severe eye pain or sudden vision loss.
6. Contact Irritation
Contact irritation is often caused by wearing contact lenses. If you wear contact lenses improperly and do not clean them properly, you may experience eye redness due to irritation.
Contact lenses can restrict oxygen supply to the eyes, causing them to appear bloodshot and uncomfortable. Wearing contact lenses for too long or while sleeping can lead to redness, infection, and, in severe cases, corneal ulcers.
If you experience pain or redness after wearing contact lenses, you should stop using them. If symptoms do not improve, consult a doctor.
Additionally, you can prevent eye irritation from contact lenses by:
- Strictly following instructions for using and cleaning contact lenses.
- Avoiding prolonged wear of contact lenses.
- Not wearing contact lenses while sleeping.
- Rinsing your eyes with saline or eye drops after wearing contact lenses.
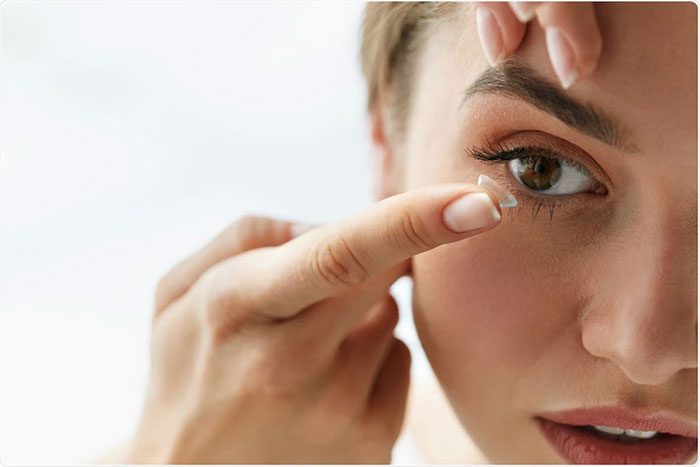

Wearing contact lenses can cause eye irritation. (Image: Internet).
7. Keratitis
Keratitis is a condition where the cornea—a dome-shaped, transparent part at the front of the eye covering the pupil and iris—becomes inflamed. Causes of keratitis may or may not be related to infection. Non-infectious keratitis is often due to relatively minor injuries, such as wearing contact lenses for too long or having a foreign body enter the eye. Infectious keratitis can be caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites.
In addition to redness, other symptoms of keratitis include: eye pain, tearing, discharge, blurred vision, reduced vision, light sensitivity, and a sensation of something in the eye.
When experiencing keratitis, patients should seek medical examination and treatment as directed by a doctor. For mild keratitis, a doctor may recommend lubricating eye drops and allow the eye to heal on its own.
If keratitis is due to infections from viruses, bacteria, or fungi, the doctor may prescribe antiviral, antibiotic, or antifungal eye drops. Anti-inflammatory and pain relief drops may be used after antibiotic, antifungal, or antiviral eye drops. In some cases, surgery may be necessary.
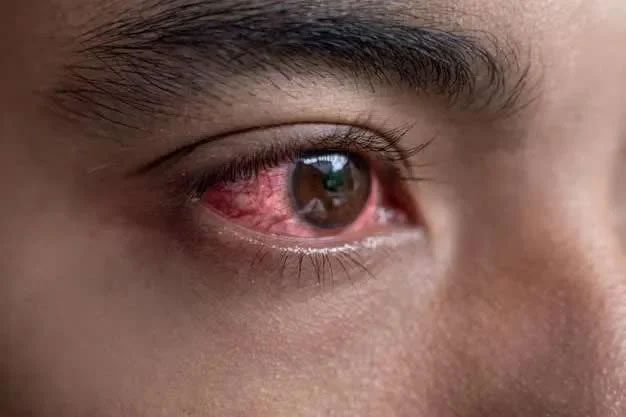

Keratitis causes symptoms such as red eyes, tearing, discharge, and blurred vision. (Image: Internet)
8. Lack of Sleep
Tired eyes due to lack of sleep often appear red and irritated. If you keep your eyes open for an extended period because of insufficient rest, the cornea may not be properly lubricated, leading to dryness and redness.
In a study, researchers reported a positive correlation between sleep deprivation and dry eyes.
Getting more sleep, if possible, may alleviate redness caused by fatigue. Over-the-counter eye drops and cool compresses can also be beneficial.
9. Stye
A stye is a small red bump that forms on the eyelid (or the lower edge of the eye) and can resemble a pimple. Styes typically develop on the outside of the eyelid, but they can sometimes occur inside the eyelid as well.
Styes are caused by a bacterial infection in the oil-producing glands of the eyelid. One of the first signs of a stye is a painful red swelling along the eyelid; if you rub it too much, it can cause redness throughout the eye, along with pain, itching, tearing, and a sensation of having something in your eye.
While a stye does not affect your vision, it can still be quite uncomfortable. Styes usually resolve on their own within one to two weeks. However, to reduce discomfort or pain from a stye, you can apply warm compresses and keep the eyelid clean. Avoid squeezing the pimple, rubbing or scratching your eyes, and refrain from wearing eye makeup or contact lenses.
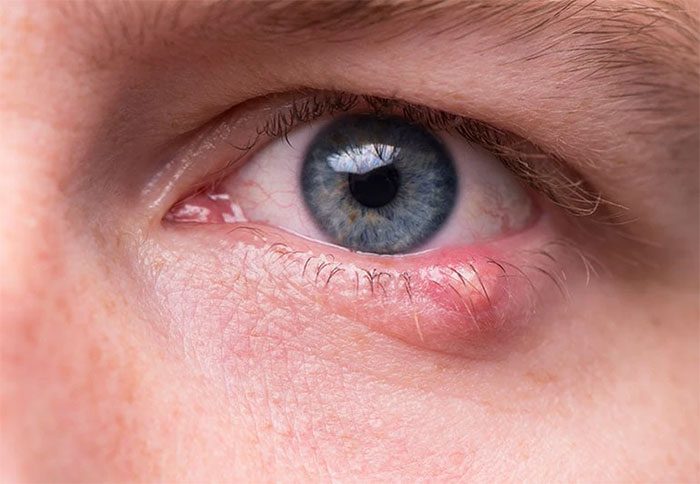
A stye is not dangerous but can cause discomfort for the patient. (Photo: Internet).
10. Subconjunctival Hemorrhage
A subconjunctival hemorrhage occurs when blood vessels beneath the surface of the eye rupture. When this happens, blood gets trapped and forms a bright red patch on the white part of the eye.
Subconjunctival hemorrhages usually happen without any apparent harm to the eye. Even a strong sneeze or cough can cause blood vessels in the eye to break.
While subconjunctival hemorrhage may look alarming, it is a harmless condition. It does not require treatment, as the patches will typically disappear within two weeks or longer.
Above are 10 causes of red eyes and their treatments. When experiencing eye conditions, it’s essential to avoid rubbing or applying strong pressure on the eyes to prevent further injury. It is advisable to see a doctor if symptoms occur suddenly or do not improve.


















































