The Earth – our familiar home, continuously orbits the Sun, creating the marvelous scenery of seasonal changes. However, have you ever thought about what changes would occur for us if the Earth gradually moved away from the Sun?
Causes and Mechanisms of Temperature Decrease
As the Earth moves away from the Sun, the temperature will drop because the distance between the Earth and the Sun directly affects the amount of solar radiation it receives. So what are the causes and mechanisms behind this temperature decrease?

As the Earth moves away from the Sun, the main causes of decreasing temperatures include: reduced solar radiation diameter, absorption and scattering of solar radiation by the atmosphere, fewer hours of sunlight, and smaller angles of incidence in the Northern Hemisphere. (Image: Zhihu).
The distance between the Earth and the Sun is not fixed but moves in an elliptical orbit. As we know, the Earth is closest to the Sun at perihelion and farthest at aphelion. When the Earth moves away from the Sun, the amount of energy from solar radiation decreases, leading to lower temperatures.
During the annual winter solstice, the Northern Hemisphere moves away from the Sun while the Southern Hemisphere moves closer. This results in cooler temperatures in the Northern Hemisphere, while the Southern Hemisphere remains relatively warm.
As the Earth moves away from the Sun, the relative duration of sunlight also shortens. The reduction in sunlight hours decreases the amount of solar energy absorbed by the surface, resulting in lower temperatures.
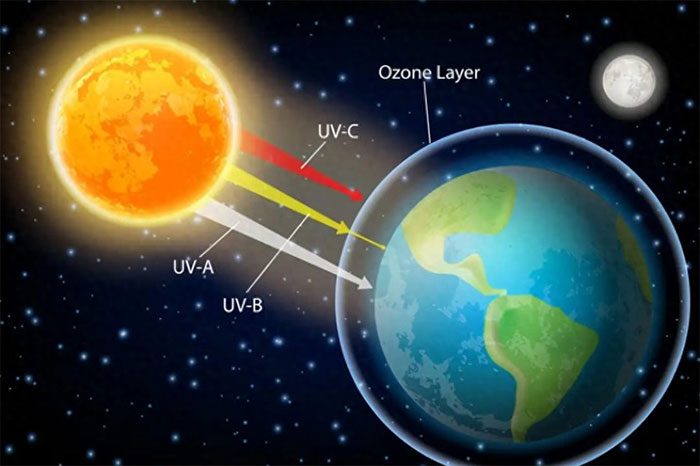
When the Earth is farther from the Sun, due to the smaller angle of sunlight, solar radiation must travel longer through the atmosphere, and a relatively large amount of energy will be absorbed and scattered by the atmosphere rather than reaching the surface. This also contributes to the drop in temperature.
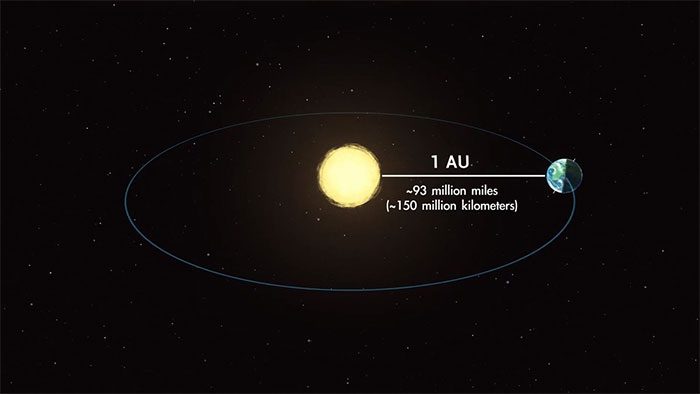
The distance between the Earth and the Sun is not fixed but moves in an elliptical orbit. (Image: Zhihu).
Impacts on Earth’s Ecosystems
As the Earth moves away from the Sun, we experience cold seasons, commonly referred to as winter. This is due to the changes in Earth’s axial tilt and movement, leading to less direct solar energy reaching the Earth. This process has significant effects on Earth’s ecosystems, including the growth and migration patterns of plants and animals.
For plants, cold conditions can limit their growth and reproduction. Cold temperatures and fewer daylight hours slow down plants’ metabolic rates, causing them to grow more slowly. Some plants become dormant, while others store nutrients above ground and rely on their root systems below to provide nourishment to cope with the frigid winter months.
The movement of the Earth away from the Sun is a common phenomenon known as the rotation of the Earth. This cyclical phenomenon has widespread impacts on Earth’s ecosystems. (Image: Zhihu).
Animals are also affected by the Earth’s movement away from the Sun. Some animals choose to migrate to warmer areas in search of better habitats and food sources. Birds, mammals, and fish all migrate in unique ways to adapt to temperature changes and shifting resources. This migratory phenomenon plays an important balancing role in the ecosystem and affects the stability of food chains.
The Earth’s movement away from the Sun also affects weather patterns and the water cycle. With lower solar radiation, less water evaporates, resulting in decreased rainfall. This can lead to drought and water scarcity, while cooler temperatures may slow glacier and permafrost melting, significantly impacting the polar regions of the Earth. This profound effect will impact the survival and reproduction of animals and plants in polar areas.

The movement of the Earth away from the Sun will cause temperature changes, with widespread effects on Earth’s ecosystems. (Image: Zhihu).
The impact of the Earth moving away from the Sun on ecosystems will also extend to marine ecosystems. Biological populations in the ocean may be affected by cyclical changes during the Earth’s revolution. Many organisms become inactive or migrate in winter to adapt to changes in temperature and food availability. At the same time, temperature changes can affect nutrient chains and biodiversity in the ocean.
This change has significant consequences for the biological life cycle, migration patterns, and reproduction of plants and animals. Climate patterns and the water cycle will also change, affecting water resources and marine ecosystems. We need to study and better understand these impacts to protect and manage Earth’s ecosystems effectively.

As the Earth orbits the Sun, the distance to the Sun is not constant during this process but changes cyclically.
Human Adaptation Strategies and Climate Change
Although we are currently in an ice age, we are facing the threat of rising global temperatures due to human-induced climate change.
With the rapid development of industrialization and human activities, a large amount of greenhouse gases has entered the atmosphere, leading to global climate change. These greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide and methane, create a “greenhouse effect” in the atmosphere. This phenomenon raises surface temperatures on Earth and causes extreme weather events, rising sea levels, and damage to ecosystems.
In the face of this challenge, addressing climate change is critically urgent and important. We must develop sustainable development strategies, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and strive to adapt to the inevitable changes in climate.

To reduce greenhouse gas emissions, we need to shift to cleaner and more renewable energy sources. (Image: Zhihu).
The increase in greenhouse gas emissions from urbanization and industrialization can be mitigated through measures such as urban planning and transportation reforms. For example, adding green spaces and public transportation systems, as well as promoting sustainable transport methods like electric vehicles, are effective strategies for reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Adapting to climate change is also very important. We must be aware of the impacts of climate change and take steps to mitigate its negative effects. For instance, in areas facing drought, technologies for water conservation and improved irrigation methods could be promoted to ensure sustainable agricultural development. In areas experiencing rising sea levels, flood prevention systems could be built, and coastal cities could be improved to protect their residents.
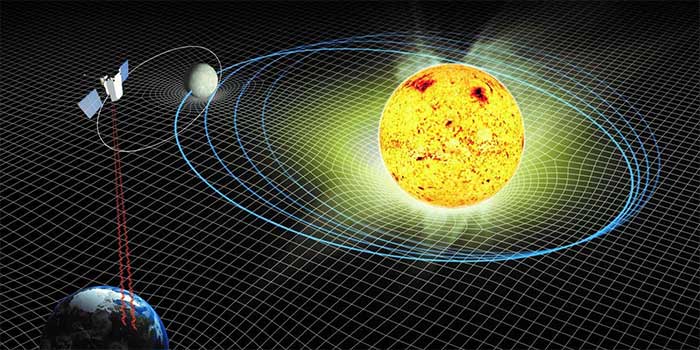
Collaboration between international organizations and governments can enhance global climate change management and provide a stable environment for sustainable development in the future. (Image: Zhihu).
To combat climate change, cooperation from the international community is crucial. Countries should work together to develop and implement emission reduction policies, collaborate on scientific research and technological innovation, and share experiences and best practices.