Torticollis in adults is a neck injury that causes painful sensations. The neck may twist to one side, and movement of the neck is often painful and severely limited. Patients may experience significant muscle spasms, pain, and difficulty turning their heads. Even getting out of bed can be painful and challenging.
Essential Information About Torticollis in Adults
Acute torticollis can last from 7 to 10 days or up to several weeks. If left untreated, this condition may develop into a chronic issue, becoming severe and increasing the likelihood of recurrence in the future. This condition can also be referred to as cervical dystonia or spasmodic torticollis.
1. Causes of Torticollis in Adults
Most individuals with torticollis often do not know the exact cause. Anything from sudden, forceful movements, sports activities, or neurological injuries can trigger torticollis. Sometimes, previous neck injuries may make one more susceptible to acute torticollis.
Some people may wake up with stiffness or pain, which can also lead to torticollis. The cause may be due to a pillow that is too high, improper sleeping positions, etc.
Additionally, other conditions may also contribute to torticollis in adults, such as:
- Injury to the neck or spine, causing muscle spasms
- Infection in the head or neck, where inflammation causes muscles to contract
- Abscess in the throat or upper respiratory tract
- Infections in other parts of the body, such as the ears, sinuses, jaw, teeth, or scalp
Less common causes of torticollis include:
- Scar tissue
- Cervical spondylitis
- Vascular abnormalities
- Drug abuse leading to muscle control issues
- Use of certain medications
- Tumors

The causes of torticollis in adults are not clear. (Image: Internet).
2. Symptoms of Torticollis in Adults
The symptoms of torticollis vary from person to person. The most apparent sign of this condition is the neck being twisted or leaning to one side.
Other possible symptoms of torticollis in adults include:
- Limited or abnormal neck movements
- Severe pain on one side or in the middle of the neck
- Headaches
- Back pain
- Pain that may radiate down the arm. Occasionally, you may feel tingling, numbness, or weakness in the arms or legs.
- Swelling of the neck muscles
- The chin may tilt to one side and hurt if attempting to correct it
- Movements that exacerbate the pain
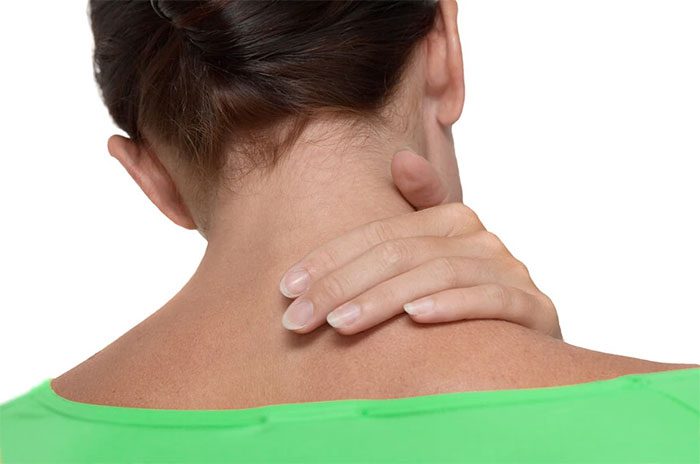
The clearest sign of torticollis is the neck being twisted or leaning to one side. (Image: Internet).
3. How to Diagnose Torticollis in Adults
The symptoms of torticollis are relatively typical and easy to recognize. However, to accurately diagnose the underlying cause, individuals should visit a hospital for examination.
Doctors will diagnose torticollis through a physical examination and by asking about family history. They may also inquire about any current medications the individual is taking.
Doctors may request X-rays of the neck to determine if the issue is due to a fracture or dislocation.
A CT scan may be necessary to diagnose torticollis due to abnormalities or more challenging conditions to detect. These can include degenerative arthritis of the spine.
Overall, depending on the condition, factors like whether you have experienced it before or if it occurs frequently, doctors will provide appropriate examination directions for the patient.
4. Treatment for Torticollis in Adults
In some cases, torticollis may resolve on its own after a few days if the person rests and avoids moving their neck.
Other treatment methods for torticollis may include:
- Applying ice packs.
- Using medications prescribed by a doctor. A doctor may prescribe muscle relaxants and anti-inflammatory medications for torticollis caused by injury or as a side effect of medication.
- Using physical devices to keep the neck stable.
- Physical therapy.
- Massage therapy.
- Stretching exercises.
Individuals with torticollis may also try home remedies to help manage pain and discomfort, such as:
- Getting more sleep and rest: Neck pain symptoms may subside during sleep, so resting more and lying down can help alleviate symptoms and provide comfort.
- Using hot or cold compresses: These devices can relieve pain and soothe tense muscles.
- Keeping a relaxed mindset: Stress can cause muscle tightness and may exacerbate torticollis symptoms.
- Doing stretching exercises: Exercises performed by gradually trying to move the head in the opposite direction, making small attempts each time until the muscles get accustomed to the movement. This can help improve movement and reduce discomfort.
Below are massage and acupressure techniques to relieve acute torticollis symptoms that individuals can apply:
1. Massage
You can use a little oil to rub the area of the neck and shoulder on the affected side. Using four fingers, except for the thumb, gently massage the neck and shoulder area 20 to 30 times. Then, continue to knead and pinch the tendons in the shoulder area 20 to 30 times. When massaging, do not use too much force; gentle rubbing helps relax the muscles.
2. Acupressure
The principle when massaging and applying acupressure to treat torticollis is to avoid pressing directly on the painful muscle area. Because when torticollis occurs, the muscles in the neck and back are tightly bound together, pressing or kneading in this area will only cause the muscles to contract further, making the patient feel more discomfort and pain.
Instead of directly pressing on the painful muscle area, individuals should apply pressure on the attachment points to the tendon, to the bone of the muscle by pressing on points such as Fengchi, Dazhui, Jianjing, Latchan, and Houxi. Each point should be pressed for 1 to 2 minutes in a clockwise direction.
– Location of Fengchi point: This point is located in the dip below the occipital bone, outside the prominent muscle mass at the back of the neck, and feels heavy when pressed.

Fengchi point. (Image: Internet).
– Location of Dazhui point: Located at the largest protrusion, at the bony prominence of the seventh vertebra. You can identify it by slightly bowing your head and locating the seventh cervical vertebra (the bony prominence that moves the most under your fingers is the seventh cervical vertebra). This point is located just below the seventh cervical vertebra.
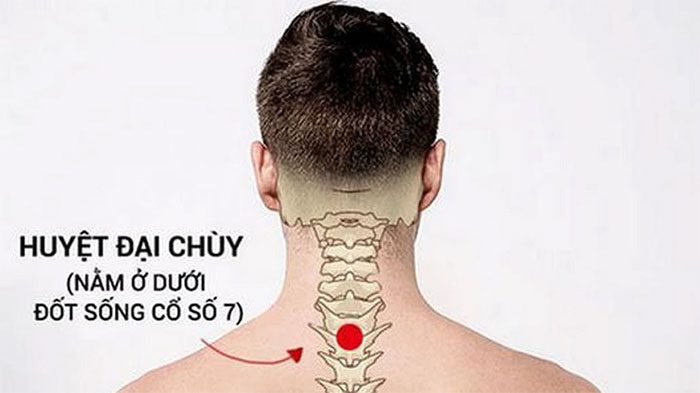
Dazhui point. (Image: Internet).
– Location of Jianjing point: This point is located on the shoulder, at the junction of the horizontal line connecting the seventh cervical vertebra and the midline of the scapula, in the depression at the middle of the shoulder.

Jianjing point. (Image: Internet).
– Location of Latchan point: Located on the back of the hand between the index finger and middle finger, about 0.5 cun (approximately 1.1cm) behind the knuckle joint, and feels heavy when pressed. This acupoint is particularly effective in treating torticollis, hence it is called Latchan point. You can use your fingertip or the end of a pen to apply pressure from light to strong.
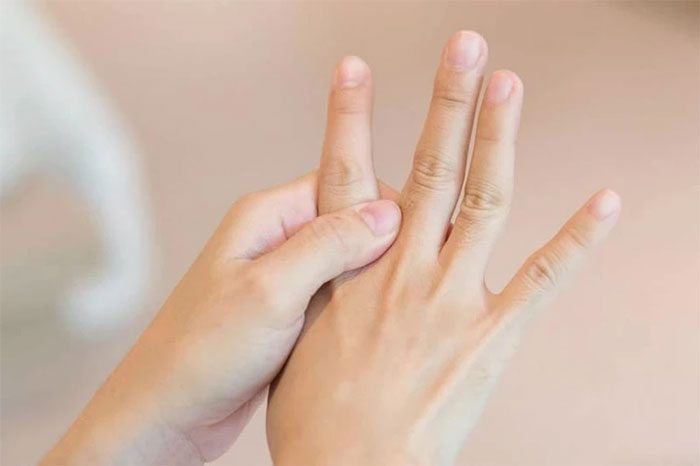

Latchan point is located on the back of the hand between the index finger and middle finger. (Image: Internet).
– Location of Houxi point: Located in the depression just behind the finger bone and palm. The depression behind the fifth finger joint and hand. It is level with the heart line on the palm, the point of contact between the palm and the back of the hand.
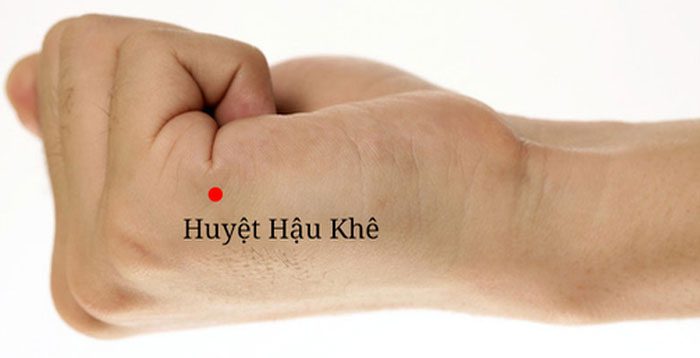
Houxi point. (Image: Internet).
The above information covers torticollis in adults and its treatment methods. Due to the unclear causes of the condition, there are no specific recommendations for prevention. This condition may resolve on its own, but for some individuals, it may develop into a chronic issue. Therefore, you should visit a hospital for an examination and seek advice from a doctor when experiencing this condition.