The vast universe holds mysteries beyond human understanding, from the expansive Solar System to distant galaxies billions of light-years away. Although the speed of light is considered the fastest, the continuous expansion of the universe makes the journey of exploration seem like a distant dream.
The vastness of the universe has always been one of the most fascinating mysteries that humanity strives to explore. From the earliest days of observing the night sky, we have gradually come to realize that the space we inhabit is just a tiny part of the Solar System, the Milky Way, and the infinite universe. However, this journey of exploration also means that we must confront the astonishing limits of current science and technology.
The Solar System: Larger Than We Imagine

The vast universe holds mysteries that humanity strives to explore.
Take Voyager 1, one of humanity’s iconic spacecraft, as an example. Launched in 1977, Voyager 1 has traveled through space for over 40 years and is currently about 24 billion kilometers from Earth. This distance seems incredible, but in reality, it is just a small step on the journey out of the Solar System. According to scientists, the edge of the Solar System is defined by the Oort Cloud – a vast region containing icy objects approximately 1 light-year from Earth. This means that even if Voyager 1 could maintain its current speed, it would take tens of thousands of years to reach the edge of the Solar System.
If we assume we had a spacecraft capable of moving at the speed of light – 300,000 km/s, the journey out of the Solar System would still take at least one year. This illustrates that even with technology that imagines far beyond our current capabilities, exploring the Solar System poses a colossal challenge.
Distance to Neighboring Stars
The closest star system to us, Proxima Centauri, is about 4.22 light-years away from Earth. If we could travel at the speed of light, this journey would still take over 4 years. Meanwhile, to escape the Milky Way, humanity would need a journey lasting 3,000 years. Furthermore, to reach the nearest galaxy – the Andromeda Galaxy – the estimated time is 2.54 million years.
These figures not only illustrate the vastness of the universe but also emphasize the limits of current technology. Even the speed of light, which is the fastest speed known to humanity, is not sufficient to explore every nook and cranny of space.
The Observable Universe: An Uncrossable Limit?
According to scientists, the observable universe has a diameter of about 93 billion light-years. This means that even if we could travel at the speed of light, the journey from one end of the universe to the other would take at least 93 billion years. However, the reality is even more complex. The universe is not only vast but also continuously expanding, causing distant objects to move farther away from us.
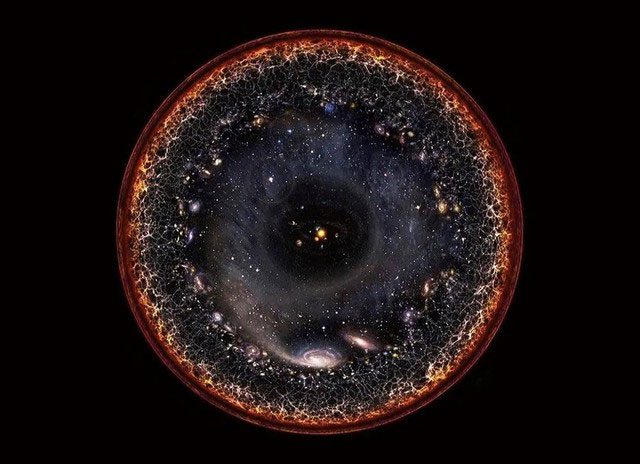

The universe is not only vast but also continuously expanding.
The phenomenon of cosmic expansion was first discovered by astronomer Edwin Hubble in 1929. He noted that distant galaxies were all redshifted, a phenomenon indicating they are moving away from Earth. The space of the universe is constantly expanding, and this rate of expansion can even exceed the speed of light at certain distances. This does not violate Einstein’s theory of relativity because it is the expansion of spacetime itself, not the motion of objects within space.
According to data from the Planck satellite of the European Space Agency, the current rate of expansion of the universe is about 67 km/s per megaparsec (3.26 million light-years). At a distance of 14.5 billion light-years, the rate of expansion has already surpassed the speed of light. And at 93 billion light-years, the expansion rate is many times greater than the speed of light. Therefore, any galaxy more than 93 billion light-years away from us cannot be observed because light from them will never reach Earth.
Limits of the Speed of Light
Although the speed of light is considered the ultimate limit in the universe, it still proves powerless against the accelerating expansion of space. The existence of dark energy – the force driving the expansion of the universe – makes the edge of the universe an unreachable goal.
A theoretical solution to overcome this limit is the use of wormholes or warp drive technology, proposed in Einstein’s theory of relativity. These concepts do not require exceeding the speed of light but rather alter the structure of spacetime, allowing distances in space to be shortened or shortcuts to be created between distant points. However, these remain purely theoretical, and no practical technology exists to bring them to fruition.

The existence of dark energy makes the edge of the universe an unreachable goal.
The Future of Space Exploration
Perhaps, in millions or hundreds of millions of years, humanity will find ways to overcome the current barriers. But at this moment, the universe remains a vast space filled with countless mysteries beyond our reach. The journey of exploration requires not only groundbreaking advancements in technology but also the persistence and unyielding passion of humanity.
The universe holds not only profound questions but also dreams about the existence of humankind. Every step forward, no matter how small, brings new insights, inspires us, and propels us to go further in our quest to conquer space. While waiting for breakthroughs, we can take pride in what has been achieved and continue to dream of the endless possibilities ahead.