Researchers Discover 182 Fossils of a 505 Million-Year-Old Jellyfish Species at Burgess Shale.
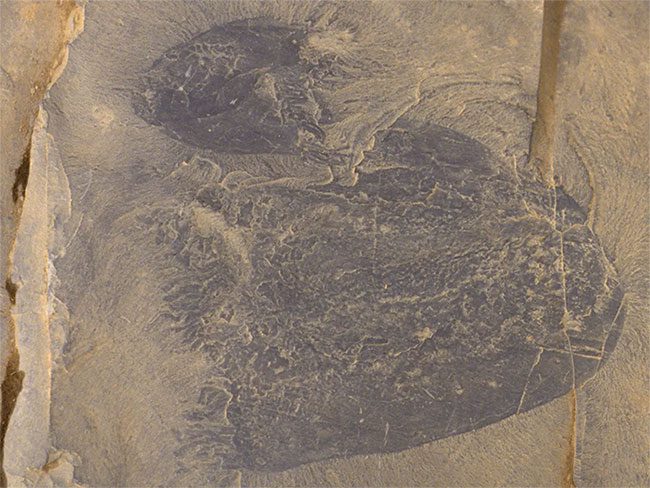
Fossil of Burgessomedusa phasmiformis.

Reconstruction of the jellyfish Burgessomedusa phasmiformis. (Photo: Christian McCall).
The fossils of the oldest jellyfish species on Earth, estimated to be 505 million years old, have been discovered in the Rocky Mountains, Canada. Researchers found 182 fossils encased in rock at the famous Burgess Shale fossil site.
The newly discovered 182 fossils belong to a previously unknown jellyfish species, named Burgessomedusa phasmiformis. The excellent preservation quality of these fossils has astonished scientists, as soft-bodied animals, which are composed of 95% water, are difficult to store and preserve.
“The discovery of additional preserved animal species in the rock layers of this mountaintop is a wonderful finding. This adds another remarkable species that Burgess Shale holds from the evolutionary history of life on Earth,” said Dr. Jean-Bernard Caron, a co-author of the study.





















































