Public computers in schools, internet cafes, and public Wi-Fi hotspots are often available for anyone to use. However, these computers can also be attractive targets for hackers. Moreover, even well-meaning users sometimes accidentally delete important files or install harmful software. So, how can we protect these types of computers?
Microsoft’s free Shared Computer Toolkit may be a suitable solution in these cases. This toolkit allows you to configure a PC specifically for internet browsing, running designated software, preventing system changes, and blocking the execution of binary programs or harmful software. Let’s take a closer look at this toolkit.
You can download the software at the following address: www.microsoft.com/sharedaccess. This software requires the system to be running Windows XP Service Pack 2 or Windows XP Tablet PC Edition 2005.
To install the toolkit, you need to log in to the system administrator account, which will also serve as the administrator account for the Shared Computer Toolkit. You can install the software just like any other application.
Have you completed the installation? Let’s explore this toolkit:
The first step typically involves adjusting the hard drive partition to create space for Windows Disk Protection (WDP). WDP requires a separate space on the hard drive, which must be located on the primary partition of the drive—also known as the boot partition. The minimum space allocated for WDP should be 10% of the boot partition’s capacity and no less than 1GB. Windows does not provide built-in tools for managing non-destructive partitions, so it is recommended to use third-party applications like PartitionMagic. Once activated, WDP will undo any changes made to the boot partition each time the PC restarts. Therefore, do not activate WDP until all configuration steps are completed.
The second step involves gathering and activating security settings. An important option is to remove the administrator account of this toolkit from the Welcome screen when the operating system starts. But how do you log in if that account is hidden? You can do so by pressing the Ctrl-Alt-Del key combination twice at the Welcome screen and entering your username and password in the dialog box. Another security feature of this toolkit prevents users from shutting down or restarting the PC and restricts access to unauthorized user accounts. The Test Your Password feature allows you to ensure that you are not using a blank or weak password for your account.
The next step is to create a public user account following the standard account creation process in Windows. It is advisable to create this account with Limited privileges; however, sometimes you may need to create it with Administrator privileges since certain software may not run with a Limited account. After creating the account, log in to configure or install software, then log out and return to the toolkit administrator account.
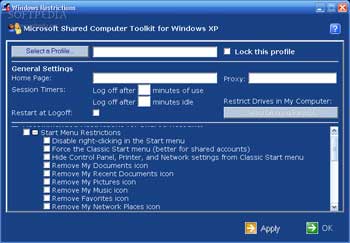
Utilizing User Restriction options provided by the toolkit gives you various security choices that limit user capabilities from simple restrictions to complete prohibitions. The Lock This Profile option informs the system not to save Internet history or any other user changes. You can also restrict access to specific websites or limit which drives are visible in the My Computer window to prevent users from installing software from USB drives or floppy disks. Additionally, you can set the PC to restart each time a user logs off, which is crucial if you activate Windows Disk Protection.
If you check the box for Recommended Restrictions, you will effectively lock down the system. The Start menu will revert to a traditional format, lacking icons such as Control Panel or My Network Places, and right-clicking on the Start menu will no longer work. Other restrictions include removing the Recycle Bin, blocking access to tools like Command Prompt, Registry Editor, and Microsoft Management Console, as well as preventing access to Task Manager. In Internet Explorer, users will be unable to use right-click, access Internet Options, or change toolbar buttons. Restrictions in Office include disabling Macro and VBA activations and preventing other unauthorized changes. The Software Restriction Policy will block any software not found in Windows or Program Files or any tools used to bypass the security features of the toolkit.
Furthermore, you can block the public account from accessing the Internet, preventing Windows Messenger or Internet Explorer from functioning, and even disabling Microsoft Office. You can also sever any links from this account to other accounts on the PC so that items on the Start menu are exclusive to this public account.
The next step is to test the newly created account to ensure that all security features are functioning correctly.
Now, log in with the toolkit administrator account and activate Windows Disk Protection. Once WDP is activated, it will control all software requests to read or write data to the Windows drive. Write requests will be monitored and recorded, but no changes will be made to the drive. For read requests, WDP will read the actual data on the hard drive but will not allow any alterations.
Another technique is to add an additional layer between the system and the hard drive by using other software like Altiris Protect or Shadows User. While WDP lacks the flexibility of these applications, it compensates by being able to self-update through Windows Update.
Once WDP is activated, even changes made by the toolkit administrator account will not be applied after a system restart. Therefore, whenever you need to make changes, you should disable this feature first.
Your system is now ready for public use.
If you decide to uninstall this toolkit, proceed with caution. Some limitations may still exist simply because they are Windows features, which could cause inconvenience. Remember to disable WDP before uninstalling the software.
If you think you can remove the software by restoring from your disk backup image, be careful. WDP uses non-standard configurations for backup partitions and data storage. If your disk imaging recovery tool does not support it, you may need to completely delete that partition to install and restore it to another empty partition. Therefore, you will also need the Master Boot Record recovery tool.
You can learn more about this toolkit here.