For a long time, the Big Bang theory has been widely accepted as an explanation for the origin of the entire universe. According to the Big Bang theory, the universe originated from a small, hot state containing dense amounts of matter. Everything expanded only after a massive explosion occurred.
A common interpretation is that space is self-expanding after the Big Bang explosion, causing galaxies to move away from each other, similar to points on an inflating balloon. Since its inception, the universe has been continuously expanding at a significant rate.
However, after nearly 13.8 billion years, the universe is now gradually entering a “recession” phase as signs of stagnation appear, and it is expected to begin contracting within the next 65 million years.
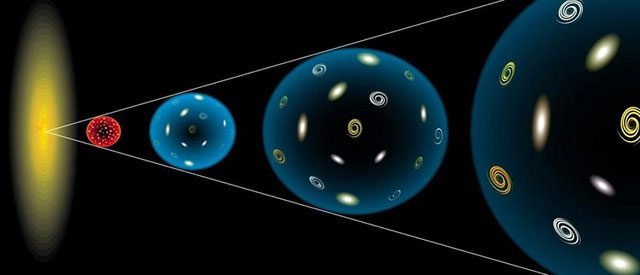
Description of the expansion of the universe.
Scientists have used previous observations of the universe’s expansion to try to model dark energy, a mysterious force that makes up about 70% of the universe. The push of this type of energy is causing the universe to expand faster than ever before, but experts believe its influence is now showing signs of weakening.
According to calculations, the acceleration of the universe could quickly come to an end within the next 65 million years. After that, within 100 million years, the universe may completely cease to expand and begin to contract.
Dark energy is an invisible, mysterious entity that many researchers believe works in opposition to gravity by pushing the heaviest objects in the universe away from each other instead of pulling them closer together.
This means that as dark energy weakens, gravity will become the more dominant force affecting the universe, leading to stars, galaxies, and planets being pulled closer together, resulting in collisions. Following this line of reasoning, the universe would face a scenario of self-destruction.

Dark energy showing signs of weakening.
Experts state that the contraction of the universe will occur so slowly that if humans are still alive on Earth at that time, they may not even notice the change. However, in reality, after a few billion years, the universe will reach a size that is only half of what it is today.
Researchers believe that the cyclical expansion and contraction of the universe will create a repeating process of destruction and rebirth. The universe will contract until it collapses before the next Big Bang occurs, giving birth to a new universe.
This is one of several controversial theories regarding the fate of the universe, alongside the Big Rip theory, where galaxies are torn apart, and the Big Freeze theory, which suggests that matter will clump together but decay into radiation as the universe expands.