A horrific tragedy occurred on July 1, 2002, when two airplanes collided perpendicularly in mid-air, resulting in the death of all passengers and crew members on both aircraft.
Rare Mid-Air Collision Between Two Airplanes
On the night of July 1, 2002, residents in the Überlingen area of Germany heard a loud explosion. Shortly after, the night sky was illuminated in red by the burning debris from the dreadful collision of the two airplanes.
Hundreds of rescue workers and police arrived at the scene to search for survivors, but miracles did not happen. The catastrophic crash claimed the lives of all passengers and crew on both planes.

Two airplanes collide perpendicularly in mid-air, resulting in the loss of all passengers and crew.
This accident is considered the most unusual and horrifying aviation disaster in the history of aviation in Germany. Not only was the cause tragic, but the aftermath left many people with lingering pain. So what exactly happened?
The Most Horrific Aviation Disaster in German History
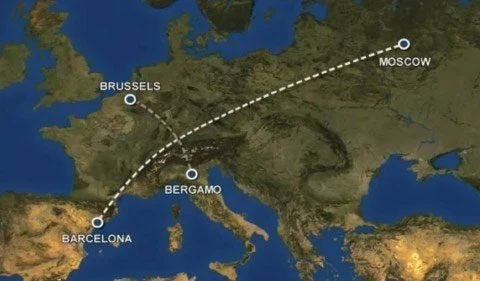
On the night of July 1, 2002, flight number 2937 of Bashkirian Airlines departed from Moscow, Russia, heading to Barcelona, Spain. This was a “special flight” operated by the talented pilot G. Alexander, who had over 30 years of experience.
It is called a “special flight” because most of the passengers were gifted children from Ufa, Bashkortostan. The flight was a vacation funded by the local UNESCO committee for talented children from the region to the beaches of Costa Daurada in Catalonia, Spain.
While flying over the airspace of Überlingen in Germany, due to a conflict between the air traffic controller’s instructions and the Traffic Collision Avoidance System (TCAS), both the airplane 2937 from Russia and the DHL Flight 611 were flying at the same altitude of 36,000 feet (approximately 11,000 meters).
This accident is considered the most unusual and horrifying aviation disaster in the history of aviation in Germany. (Photo: Internet).
Forty-five seconds before the disaster, Captain G. Alexander noticed the issue and tried to adjust the airplane’s altitude, but due to the short time available, the two aircraft collided perpendicularly. The tail of DHL Flight 611 sliced through the fuselage of flight 2937, causing the plane to break in half. Flight 2937 subsequently caught fire and fell immediately. The cargo plane DHL 611 also crashed shortly after losing its tail balance.
Causes of the Tragedy
According to investigations, the primary cause of the tragedy was due to ineffective communication and warning systems of Skyguide, Germany. Additionally, the lack of personnel forced air traffic controller Peter Nielsen to manage two areas simultaneously, leading to delays in processing and issuing danger warnings, which contributed to the tragedy.
Haunting Aftermath
The collision resulted in the death of all passengers and crew members on both airplanes; statistics indicate that 71 people died in this collision, heartbreakingly including 46 children.
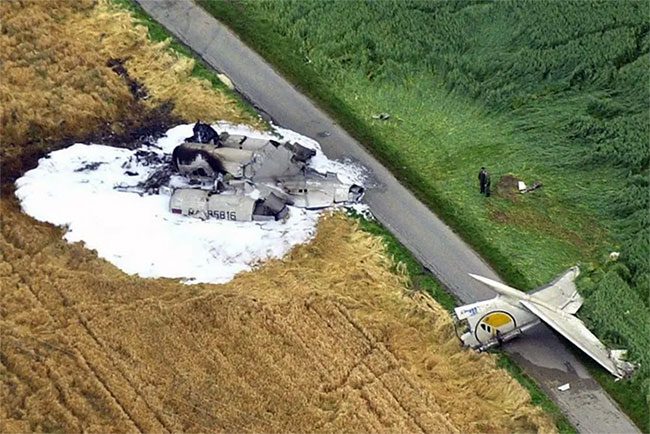

The collision resulted in the death of all passengers and crew on both airplanes. (Photo: Internet).
Initially, Skyguide blamed the Russian pilot, but later had to accept full responsibility and sought forgiveness from the victims’ families. They also agreed to pay a substantial amount in compensation to the victims’ relatives. In 2008, Skyguide filed for bankruptcy under Russian law.
Air traffic controller Peter Nielsen, who was directly involved in the guidance and control during the tragedy on the night of July 1, 2002, required medical care due to psychological trauma. Shortly after, on February 24, 2004, Peter Nielsen was stabbed to death at his home. The perpetrator, a Russian architect, was driven by grief over the deaths of his wife and two children on flight 2937 and decided to take revenge on Peter Nielsen. This prolonged incident is considered one of the most unusual and horrifying aviation disasters in the history of aviation in Germany.
After this catastrophic accident, the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) issued a statement. In situations where there is a conflict between the instructions of air traffic controllers and the automated TCAS collision avoidance system, aircraft should adhere to the TCAS instructions and disregard the air traffic controller’s guidance.