African cuisine always surprises people, and sometimes even frightens them. Notably, some animals that are of normal size in our country are much larger in Africa, with the Goliath frog being the most prominent example. This species can live both underwater and on land. The Goliath frog has been confirmed by biologists as the largest frog species in the world.
The Largest Frog in the World
They are commonly found in the rainforests of West Africa, where fast-flowing rivers and humid tropical forests provide a warm environment year-round. Like other frogs, the Goliath frog is amphibious, capable of living both in water and on land.

The length from the mouth to the end of the legs of the Goliath frog reaches 1m.
The weight of female Goliath frogs can reach up to 7 kg, while males can weigh up to 8 kg when fully grown. The length from the mouth to the end of the legs can reach 1m, with the frog’s weight often depending on its living conditions. They do not thrive in captivity, even in controlled environments such as zoos with regular feeding.
They are prone to dying easily, with the longest lifespan in semi-natural environments being only 5 years. However, in the wild, Goliath frogs can live up to 15 years. Their dorsal skin is green or black olive, often patterned, which helps them camouflage from predators.
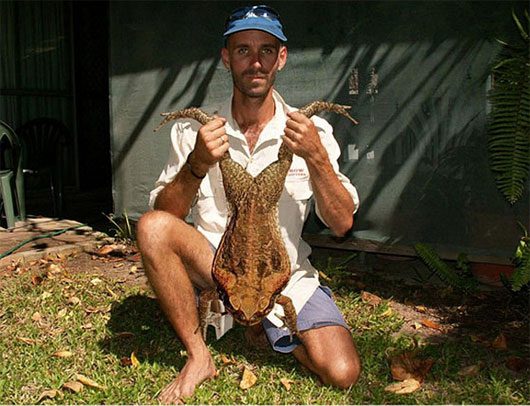

The Goliath frog can swim very fast and jump very far.
Given their bulky appearance, you might think they only sit still. In reality, Goliath frogs can swim very quickly and jump quite far, with jumps reaching up to 3 meters. With their long tongues, these frogs can easily catch prey in an instant. Even a mouse would find it hard to escape when a Goliath frog shoots out its tongue.
However, their favorite foods include various insects, shrimp, crabs, small snakes, and small fish. Occasionally, they might even eat smaller Goliath frogs.

The Goliath frog’s favorite foods include insects, shrimp, crabs, and small snakes…
Nature has endowed Goliath frogs with excellent hearing, but they are unfortunately “mute” as they lack vocal sacs. Like other frogs, male Goliaths take on the role of incubating eggs in their mouths during the breeding season. In each spawning, thousands of tadpoles are produced.
Unlike other frogs, which croak loudly to attract mates during breeding season, male Goliath frogs do not make any sounds, making their mating attraction methods a mystery to scientists.

Goliath tadpoles face significant survival challenges in the wild.
Despite being a giant species, Goliath tadpoles are relatively small, measuring only about 1.4 cm in length. These tadpoles and juvenile Goliath frogs struggle to survive in the wild due to numerous threats from other species. They also cannibalize each other, leading to a very small number reaching adulthood.
Are These Frogs Edible?
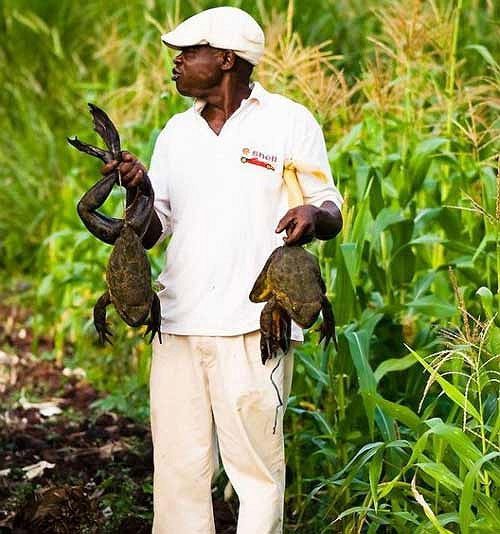
The meat of this giant frog is white and sweet, which is why many food enthusiasts are willing to pay a significant amount to enjoy it. Some even go to great lengths to obtain and keep them as pets in their gardens.

The meat of this giant frog is white and sweet, making it highly sought after.
Currently, habitat conditions are shrinking, rivers are becoming polluted, and overfishing has severely reduced the population of Goliath frogs.
The Evolutionary History of Frogs
Darwin mentioned in his theory of evolution that all organisms on Earth developed from a few branches of species from the beginning. Many species that seem unrelated can be traced back to a common ancestor, and frogs are no exception.
As amphibians, the ancestors of frogs likely originated from the earliest amphibians that appeared at the end of the Devonian period, retaining many fish-like features.
Furthermore, their ancestors were bony fish that crawled onto land at the start of the Devonian period. To adapt to life on land, they began to change their shape, becoming the first vertebrates capable of breathing air on Earth.
Later, as they entered the Carboniferous period, amphibians began to evolve, continuously diversifying into new species. By the Permian period, amphibians had become rich and diverse, a time often referred to as the age of amphibians on Earth.
So, when did frogs appear? In terms of time, the earliest frogs on Earth had not yet emerged by this point; it was not until the Triassic period that the most primitive frogs officially appeared, showing significant differences.
By the Jurassic period, when dinosaurs began to thrive, frogs had developed the ability to jump, and their presence increased as they evolved to adapt to their environment, similar to modern frogs. They also diversified into many species.
Toads also appeared during this time, and today we know that both frogs and toads are beneficial animals on Earth and can eliminate many harmful species. Similarly, as a vital link in the food chain, they also provide many food sources for other animals, including the African Goliath frog.
However, due to human activities, many frog species are at risk of extinction, and we need to protect them, as frogs play a crucial role in nature.