Not an uncommon condition, back pain when breathing can cause discomfort, fatigue, and anxiety in patients. Most cases are typically due to musculoskeletal issues. However, it can also be a warning sign of some serious health conditions.
Causes of Back Pain When Breathing Everyone Should Know
1. Scoliosis
Scoliosis is a condition where the spine curves to one side. While this health issue can affect individuals of all ages, it is most commonly seen in adolescents or teenagers.
The curvature associated with scoliosis can cause back pain when breathing due to pressure from the thoracic cavity and spine on the heart and lungs.
In addition to back pain when breathing, scoliosis may include other symptoms such as: back pain, weakness and numbness in the arms and legs, uneven shoulders and hips, difficulty standing straight, and shortness of breath. Symptoms of scoliosis can develop gradually and may initially go unnoticed, impacting early treatment.
Treatment Options
To treat scoliosis, patients need to visit a hospital for a thorough examination and appropriate treatment recommendations from a doctor. For individuals with mild to moderate curvature, doctors may recommend wearing a back brace. Those with more severe scoliosis may require spinal fusion surgery to straighten the spine. Treatment options will also depend on the condition’s severity, gender, age, etc.

Scoliosis is one of the causes of back pain when breathing. (Image: Internet).
2. Kyphosis
Kyphosis is a condition where the spine curves forward, which can also lead to back pain when breathing. This curvature may develop during adolescence, after spinal injury, or due to aging.
Kyphosis can also cause back pain, swelling, and balance issues. Symptoms may worsen over time, potentially leading to shortness of breath or difficulty eating in some individuals.
Treatment for kyphosis may include physical therapy, wearing a brace, and taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). In cases of severe kyphosis, surgery may be recommended.
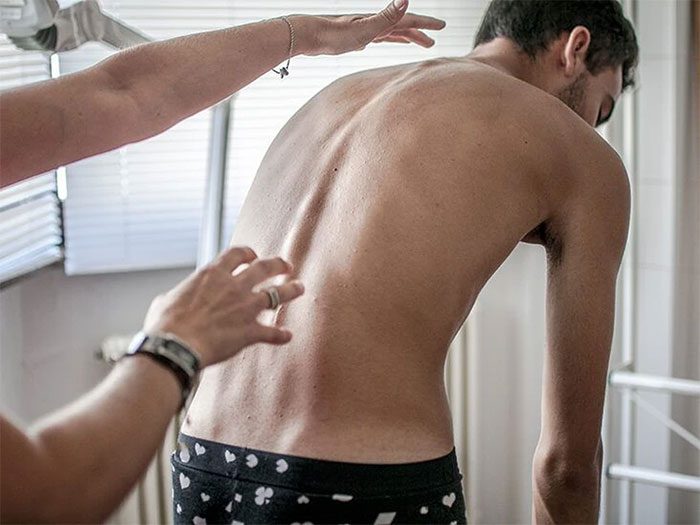
A person with kyphosis (hunchback). (Image: Internet).
3. Heart Attack
A heart attack can also be a cause of back pain when breathing. Heart attacks can cause feelings of pressure or pain in the chest and can particularly radiate to the back. However, not everyone experiences these symptoms.
To identify whether you are having a heart attack, you can look for symptoms such as chest pain, a feeling of pressure or tightness in the chest, pain in one or both arms, jaw pain, shortness of breath, dizziness, nausea, and vomiting.
A heart attack is a medical emergency. Therefore, if you suspect you are having a heart attack, seek medical attention immediately or call emergency services.
Prevention Tips
While we cannot always prevent a heart attack, adopting certain measures and a healthy lifestyle can minimize risk. According to Mayoclinic, to prevent heart disease, we should maintain the following lifestyle:
- Avoid smoking and steer clear of secondhand smoke
- Engage in regular physical activity and aim for at least 30 to 60 minutes of exercise daily.
- Follow a heart-healthy diet, including plenty of fruits and vegetables, legumes, lean meats, and fish, low-fat or non-fat dairy, whole grains, and healthy fats like olive oil and avocado.
- Maintain a healthy weight and avoid becoming overweight or obese.
- Ensure quality sleep, as most adults need at least 7 hours of sleep per night. Children typically need more.
- Avoid stress and anxiety
- Protect your body from infections
- Get regular health check-ups to detect any abnormalities in your body
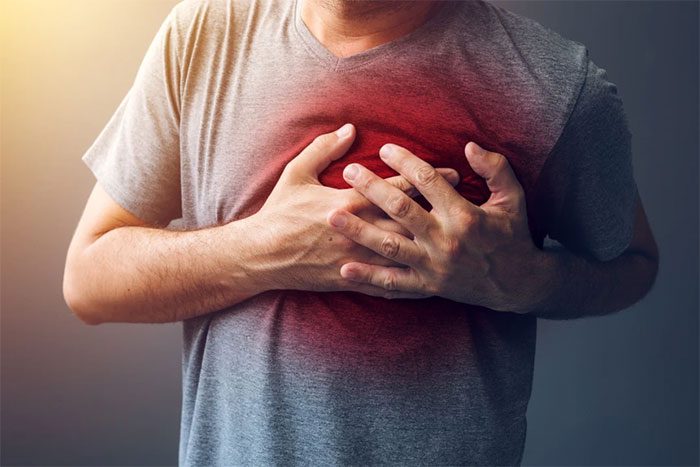

Heart attacks can cause feelings of pressure or pain in the chest, which can radiate to the back. (Image: Internet).
4. Obesity
Why does obesity cause back pain when breathing? Excess body weight adds pressure on the back, joints, and other parts of the body. Furthermore, some individuals with obesity may experience respiratory issues and feel discomfort or even pain in the back or other areas when taking deep breaths.
Weight Management Strategies
Managing weight is one of the best ways to alleviate back pain and joint pain, as well as prevent various diseases. Losing weight through a calorie-restricted diet and regular exercise can help achieve a healthy body shape. If your obesity is related to hormonal issues, you should consult your doctor for further advice.
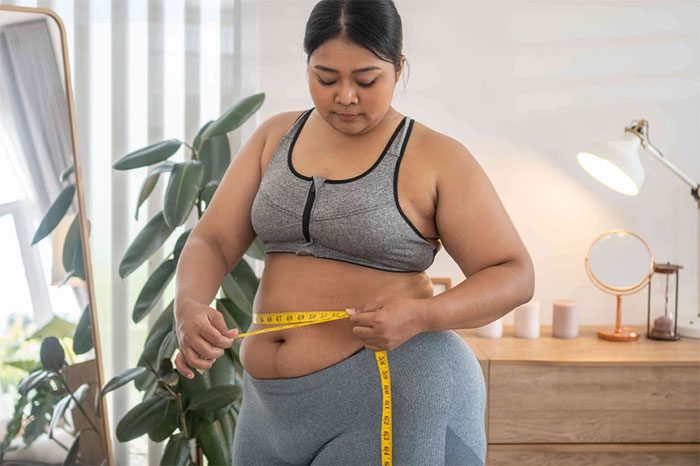

Obese individuals are more likely to encounter respiratory problems, and excess weight adds pressure on the back. (Image: Internet).
5. Lung Cancer
According to the American Cancer Society, lung cancer often does not cause symptoms in its early stages. However, common signs include chest pain, which tends to worsen with deep breathing or coughing.
If cancer spreads to other organs, it can cause bone pain in the back or hips, especially when coughing. Lung tumors may also press on nerves in the spine, affecting breathing rhythm and causing back pain when breathing.
In addition to chest pain and back pain when coughing, individuals with lung cancer may experience other symptoms such as chronic coughing, coughing up blood or blood in sputum, frequent or recurrent respiratory infections, shortness of breath, wheezing, hoarseness, difficulty swallowing, unexplained weight loss, and loss of appetite.
While we cannot completely prevent lung cancer, we can reduce risk through several measures such as:
- Avoid smoking and refrain from secondhand smoke exposure.
- Check radon levels in your home. Radon is a radioactive gas that can cause lung cancer.
- Avoid carcinogens in the workplace (if at risk).
- Eat a diet rich in fruits and vegetables and engage in regular exercise.
A common sign of lung cancer is chest pain when taking deep breaths, which may radiate to the back. (Image: Internet).
6. Pulmonary Embolism
Pulmonary embolism occurs when a blood clot forms in the arteries supplying blood to the lungs. This blocks blood flow to the lungs and can threaten the patient’s life. Therefore, if you suspect you have a pulmonary embolism, seek immediate medical assistance.
Individuals with pulmonary embolism often experience pain when taking deep breaths and pain in the upper back. Additionally, patients may feel chest pain, cough, and possibly cough up blood, have a rapid heartbeat, dizziness, and swelling in the legs.
Pulmonary embolism is often caused by the formation of blood clots. Thus, preventing blood clots is key to preventing pulmonary embolism. A healthy lifestyle can help minimize the risk of clot formation, such as: eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, avoiding smoking, and not staying up late…

Back pain when coughing can also be due to pulmonary embolism. (Image: Internet).
7. Pneumonia
Pneumonia can also be a condition that causes back pain when breathing. Additionally, patients may experience other symptoms such as fever and chills, coughing up phlegm, shortness of breath, loss of appetite, wheezing, and vomiting.
When suffering from pneumonia, patients need to follow the treatment plan as prescribed by their doctor.
While it may not be possible to completely prevent pneumonia, you can reduce your risk through measures such as:
- Getting vaccinated, especially children and the elderly
- Regularly washing hands with soap to prevent infections
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle to boost the immune system.
- If you smoke, consider quitting.
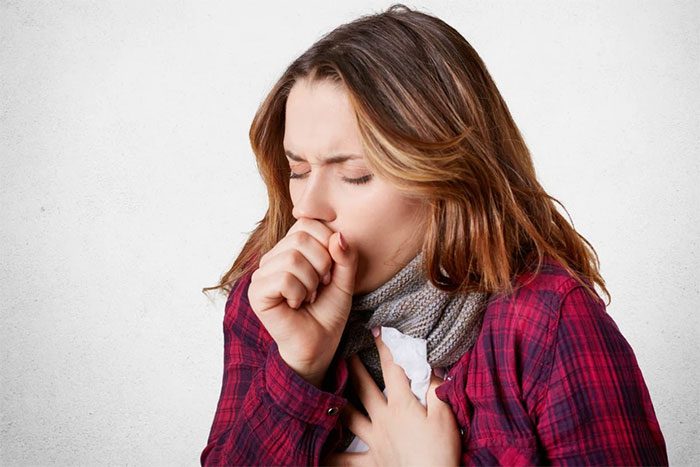

Coughing due to pneumonia can cause pain in the chest, abdomen, or back. (Image: Internet).
8. Herniated Disc
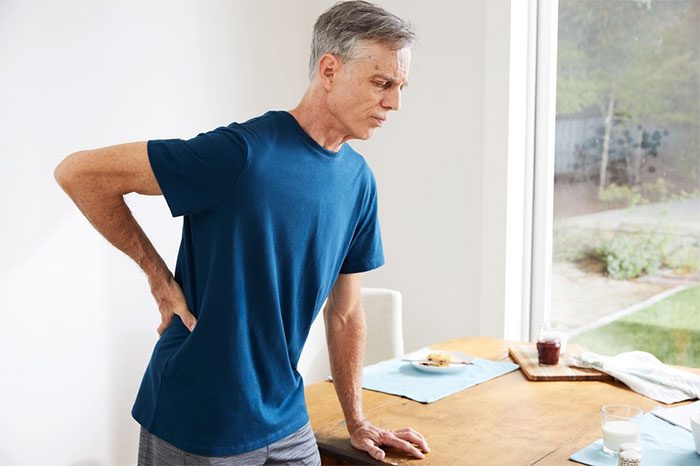
A herniated disc can occur at any location along the spine, but it is most commonly seen in the lower back, especially when the back pain worsens during breathing.
In addition to back pain when breathing, other symptoms of a herniated disc include: pain and numbness on one side of the body, tingling or burning sensations near the injury, muscle weakness, pain radiating down the arms or legs, and worsening pain after standing or sitting.
For most patients, lumbar herniated discs will gradually improve over a period of several days to weeks. Typically, most patients will see their symptoms resolve within 3 to 4 months. However, some patients may experience pain during the recovery process.
If non-surgical treatment is pursued, patients should rest more and engage in physical therapy exercises. In severe cases, a doctor may recommend surgery.
The above outlines 8 causes of back pain when breathing. While this is a warning sign of several potentially serious underlying conditions, most individuals experiencing this issue do so due to spinal problems. If this condition persists without improvement despite attempts at relief, it is advisable to visit a hospital for a thorough examination to determine the underlying cause.