The Chinese company Betavolt Technology has announced the successful miniaturization of a nuclear battery measuring 15 x 15 x 5mm, smaller than a coin, ultra-durable, and safe.
This compact nuclear battery uses 63 nuclear isotopes to generate 100 microwatts at a voltage of 3V through the process of radioactive decay.
Unlimited Power Source
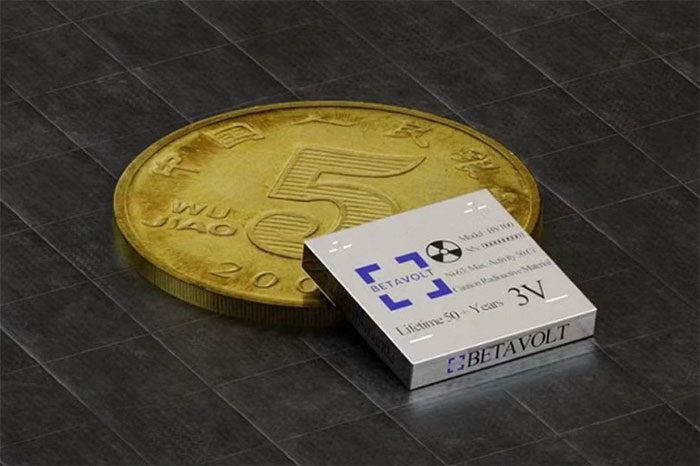

Nuclear battery smaller than a coin, lasts 50 years without charging – (Photo: BETAVOLT).
According to the British technology news site Techradar, the battery is currently in the testing phase and Betavolt plans to mass-produce it for use in commercial devices such as phones and drones.
Additionally, this nuclear battery could be used for aerospace devices, AI, medical equipment, sensors, and ultra-small robots, according to the company.
Betavolt claims to draw creative inspiration from devices that use nuclear batteries, such as pacemakers and satellites.
Betavolt is also planning to advance its technology to produce a 1-watt battery by 2025.
This technology could revolutionize electronic devices by completely eliminating the need for mobile chargers and creating devices that run continuously for 50 years without power degradation.
It also enhances user safety since the battery does not catch fire or explode in case of an accident.
How Does the Battery Work?
To create the nuclear battery, Betavolt scientists utilized nickel-63, a radioactive element, as the power source, and then used diamond semiconductors as energy converters.
The research team developed a single-crystal diamond semiconductor that is only 10 microns thick, then placed a 2-micron thick nickel-63 layer between two diamond semiconductor converters.
The energy released from the radioactive source is then converted into electrical current.
Betavolt claims that the advantages of atomic energy batteries include being lightweight, having a long lifespan, as well as high energy density, and the ability to operate normally under extreme temperatures ranging from -60 to 120°C.
Are Nuclear Batteries Harmful to Health?
Betavolt asserts that nuclear batteries are safe because they do not emit external radiation. Currently, medical devices implanted in the human body, such as pacemakers and cochlear implants, also use a type of nuclear battery.
Betavolt stated that after the battery degrades, the 63 nuclear isotopes will become copper, which is non-radioactive and poses no threat to health or the environment.