In China, the issue of fake beef is not just about substituting low-quality meat; it’s also a burgeoning underground industry with alarming scale.
From Simple Tricks to High-Tech Processes
Since the 1980s, the concept of “fake beef” has emerged in China, initially involving simple tricks like injecting water into livestock to increase weight before slaughter. This practice not only diminishes meat quality but also deceives consumers. Over time, with the introduction of food additives and advanced technology, the production of fake beef has entered a new phase: larger scale, more professional, and harder to detect.
Currently, fake beef in the market is mainly divided into two types.
The first type is meat substitutes made from protein or low-quality meat: Dead pigs, ducks, or cheaper meats are used as the main ingredients. Producers add additives such as colorants, flavor enhancers, and meat extracts to transform them into fake beef. This type of meat not only has low nutritional value but also poses a risk of poisoning due to harmful chemicals.
The second type is synthetic beef made from gelatin and beef fat: Using scraps or beef fat, fraudsters mix in gelatin as a binder and press it into visually appealing beef-like pieces, mimicking real beef. Upscale restaurants often advertise this as “Japanese Wagyu”, selling it at exorbitant prices despite its low production cost.

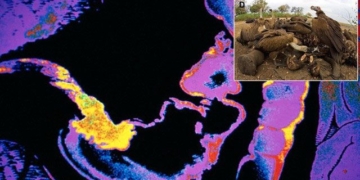
The production process of fake beef is becoming increasingly sophisticated. (Illustrative image).
Fake Beef: Technology So Fine It’s Hard to Distinguish
The production process of fake beef now relies on a combination of modern machinery and industrial chemicals. Equipment such as molding machines, cutters, mixers, and automated water pumps are used to create fake beef. Chemicals like colorants, flavor enhancers, preservatives, and meat tenderizers are added to improve the appearance, texture, and shelf life of the product.
Remarkably, thanks to these techniques, fake beef sometimes has a texture and smoothness that surpasses real meat, making it extremely difficult to detect, even when cooked.
A striking case announced in September this year in Sichuan Province, China revealed the scale of this issue – a gang produced and sold over 900 tons of fake beef from 2020 to 2022. However, when experts examined the products, they found no signs indicating any relation to livestock, leading to outrage among netizens in China. “Not even a trace of beef skin? This is outrageous!” – one social media user expressed.
The sophistication of these counterfeiting methods not only deceives ordinary consumers but also major restaurants. Synthetic beef, with a texture mimicking the snowflake-like marbling of Wagyu beef, is often sold at prices many times higher than the original cost.
Health Risks from Consuming Fake Beef
Consuming fake beef not only reduces nutritional value but also poses serious health risks. First, the chemicals and additives in fake beef can harm the liver and increase the risk of liver dysfunction with long-term consumption. Moreover, they can irritate the digestive system, leading to issues such as bloating, diarrhea, gastritis, or gastric ulcers.
The low protein content and nutritional value of fake beef can lead to malnutrition if consumed over an extended period. Additionally, fake beef made from spoiled meat or containing bacteria and heavy metals can cause food poisoning and severely impact consumers’ health.
The ingredients used for fake beef are often low-quality meat, even spoiled meat, containing bacteria and heavy metals. Consuming such food not only risks malnutrition but also poses the threat of food poisoning and chronic diseases.
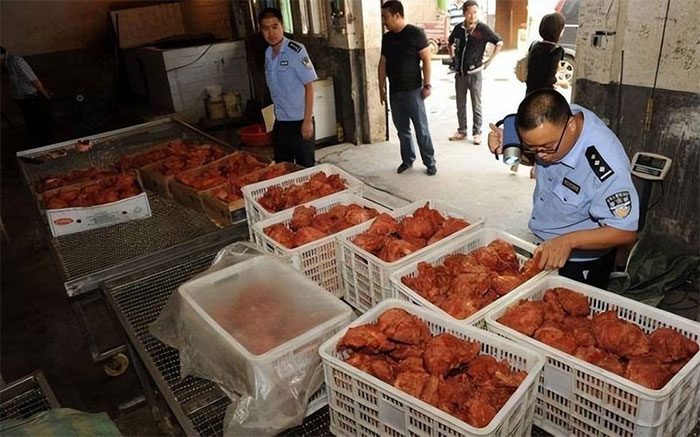

Consuming fake beef poses serious health risks.
How to Avoid Buying Fake Beef?
To protect health, consumers should choose beef from reliable brands and suppliers. Real beef typically has a bright red color, firm texture, and natural deliciousness. In contrast, fake beef appears dull, has a smooth texture, and lacks distinctive flavor.
Additionally, thoroughly checking product information and prioritizing purchases from reputable supermarkets or stores will minimize the risk of buying counterfeit products.
The counterfeiting of beef not only causes economic damage but also poses serious threats to public health. To combat this issue, cooperation between regulatory agencies, businesses, and consumers is essential. In particular, tightening food quality inspections and imposing strict penalties on individuals and organizations that violate regulations are crucial.
Beef – a beloved dish for many – has now become the focal point of food safety issues in China. Stories like these serve as warnings about the dangers of counterfeit food and urge us to be more cautious in our daily choices and consumption.