In 2023, many groundbreaking treatment methods have been approved.
In 2023, several innovative treatment methods have been approved, including CRISPR gene-editing technology to treat genetic blood disorders and drugs that slow the progression of Alzheimer’s disease.
1. CRISPR-Based Gene Therapy
In November, the UK Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) approved the use of CRISPR therapy to treat two genetic blood disorders. This is the world’s first approved application of CRISPR gene-editing technology.
Named Casgevy, this CRISPR method treats sickle cell disease (SCD) and beta-thalassemia that requires blood transfusions. These are lifelong genetic disorders caused by mutations in the gene that encodes hemoglobin, a protein that red blood cells need to transport oxygen throughout the body.
Casgevy will correct the faulty BCL11A gene in the patient’s bone marrow stem cells so that they can produce normal functioning hemoglobin. To achieve this, hematopoietic stem cells are taken from the patient’s bone marrow, and the BCL11A gene is edited in the laboratory using Casgevy, then reintroduced back into the patient’s body. This method has the potential to cure patients for life with just a single treatment.
Currently, this is just the first method among dozens of potential treatments for other genetic disorders such as cancer and infertility.
2. Drug to Slow Alzheimer’s Disease
In 2023, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved Leqembi (lecanemab-irmb), the first drug to slow the progression of Alzheimer’s disease. This is the first fully approved Alzheimer’s treatment in the past 20 years. The FDA has deemed this drug “clinically meaningful” for Alzheimer’s, a disease that affects over 6.5 million Americans.
Research data indicates that the drug can slow the progression of Alzheimer’s disease by up to 27% over 18 months.
When amyloid protein abnormally accumulates in the brain, it forms sticky plaques, causing inflammation and damaging nerve connections. The buildup of amyloid plaques leads to memory loss in Alzheimer’s patients. Therefore, the mechanism of action of Leqembi is to remove amyloid plaques from the brain, thereby slowing the disease’s progression.
3. Paving the Way for Infertility Treatment
In March 2023, Japanese scientists announced a breakthrough in producing offspring from two male mice by creating eggs from male cells.
The scientists reprogrammed the skin cells of male mice into stem cell-like cells, then implanted them into a uterus placed in a cultured system mimicking the conditions inside a mouse’s uterus. The eggs can be fertilized by normal sperm. Subsequently, the fertilized eggs were transferred to a surrogate female mouse.
The scientists collected about 600 embryos, resulting in 7 healthy pups that had normal lifespans and could reproduce when mature.
From these results, experts predict that it may be possible to create viable human eggs from male skin cells within the next decade. This achievement could help treat many severe forms of infertility and provide hope for same-sex couples wishing to have children together in the future.
4. The First Complete Map of Insect Brains
After 12 years of meticulous work, in March 2023, a research team of 20 scientists from the UK, the USA, and Germany announced the completion of a detailed brain map of the fruit fly larva, showing all neurons and synapses. The map reveals how cells can send chemical messages to each other, activating electrical signals that travel along the pathways of the cells.
This result is quite impressive since previously, humans had only constructed brain maps of roundworms, octopuses, and sea worms, each containing only a few hundred connections. The fruit fly brain map is a comprehensive system of connections.
The neural pathways in the fruit fly brain resemble networks in machine learning. Understanding the similarities and complexities of the fruit fly brain’s connectivity could help decode how the human brain works and how neurological diseases develop. This brain research also opens up opportunities for many advancements in the future, especially in new technologies like machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI).
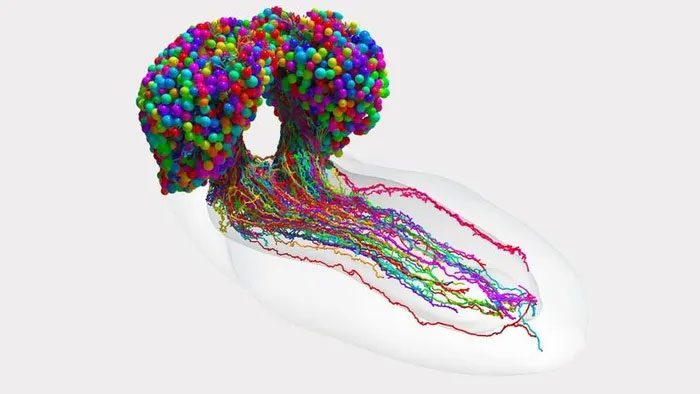
Map showing the assembly of neurons and synapses in the fruit fly larva brain.
5. AI Identifies Risk of Pancreatic Cancer
An artificial intelligence (AI) tool successfully identified individuals at the highest risk of developing pancreatic cancer up to three years before an actual diagnosis. This opens up many treatment opportunities and increases survival chances for individuals.
Currently, pancreatic cancer is among the deadliest types worldwide. It is often only diagnosed when it is in advanced stages, making treatment less effective, and most patients do not survive. The number of people diagnosed with this disease is expected to increase in the future.
However, the early symptoms of pancreatic cancer are easily misdiagnosed, but many patients can live longer if the cancer is detected early. Therefore, scientists have developed an AI algorithm based on the medical records of 6.2 million Danish individuals over 41 years to detect hidden patterns in the records of 24,000 patients who later developed pancreatic cancer.
The AI model analyzed the combination of these disease codes and their timing. By comparing specific condition sequences before a pancreatic cancer diagnosis, the AI model identified individuals at the highest risk. In fact, AI can accurately predict even when the disease codes, symptoms, and their timing are not directly related to the pancreas.
In this way, AI identifies individuals at the highest risk of pancreatic cancer. Doctors can then request diagnostic tests to detect the disease early and provide timely treatment. Common symptoms of pancreatic cancer include jaundice, mid-back pain, upper abdominal pain, weight loss, skin itching, and fatigue.

















































