The appearance of lumps behind the ear can signal health issues. However, in most cases, they are not serious.
Common Causes of Lumps Behind the Ear
Lumps behind the ear can occur in any location behind the ear and can be hard or soft, painful or painless, and range in size from small to medium. The appearance of these lumps can cause concern for patients, but fortunately, most conditions involving lumps behind the ear are benign and not serious. Below are common causes that may lead to lumps behind the ear:
1. Infection
Lumps behind the ear can occur due to infections. In this case, the lymph nodes behind the ear may swell to fight off the infection and protect the body. Some common infections that cause lumps behind the ear include streptococcal pharyngitis and mononucleosis.
Additionally, other infections can also cause swelling of the lymph nodes behind the ear, such as:
- Dental abscess
- Gum disease
- Flu or other upper respiratory infections
- Lyme disease (an illness caused by bacteria transmitted by ticks)
- Oral herpes (infection with the herpes simplex virus)
- Tonsillitis (inflammation of the tonsils at the back of the throat)
- Rubella
Depending on the cause of the infection, different treatment approaches will be necessary; for example, streptococcal pharyngitis requires treatment with antibiotics.
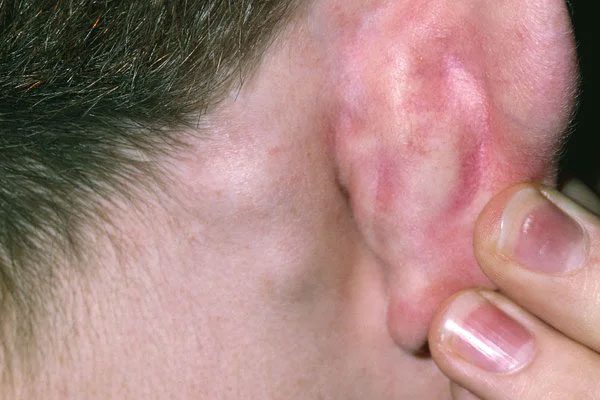
Lumps behind the ear can be due to infection. (Image: Internet).
2. Acne
Lumps behind the ear may sometimes simply be acne. Acne can manifest as pimples or other types of boils.
Acne is a common skin condition that often occurs due to hormonal changes and poor skin hygiene. It can appear in various areas of the body, but the face is the most common area, including behind the ears.
For some types of boils, if they become infected or if certain bacteria invade them, they can lead to more serious conditions forming lumps known as acne cysts, which can appear anywhere, including behind the ear.
To treat acne, individuals should maintain good skin hygiene, appropriate skincare, and may use acne creams. Importantly, avoid scratching or touching acne to reduce the risk of infection.
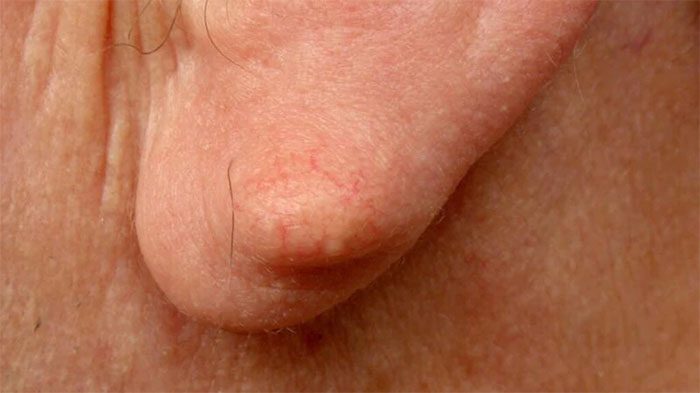
A lump behind the ear may simply be acne. (Image: Internet)
3. Cysts
A cyst is a fluid-filled sac, a benign condition that is not cancerous, which can appear anywhere on the skin, including behind the ear. Cysts are formed from dead skin cells and oil. When touched, a cyst feels soft and typically resolves on its own. Cysts are usually painless unless they become infected.
The lumps that appear behind the ear are often sebaceous cysts. This condition occurs when a sebaceous gland becomes blocked, causing a slow-growing swelling under the skin. Sebaceous cysts are usually soft and movable when touched. Typically, they are painless, but you may notice an unpleasant odor. Smaller cysts often resolve on their own, but doctors may need to drain or remove larger, swollen, or painful cysts.
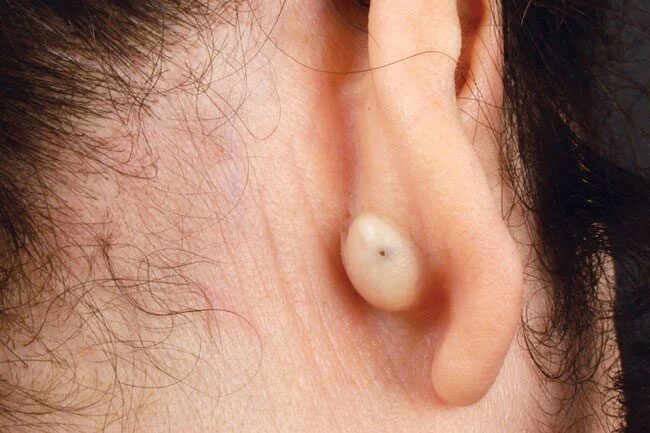
Sebaceous cysts behind the ear are benign. (Image: Internet).
4. Lipomas
A lipoma is another cause of lumps behind the ear. Lipomas are benign fatty tumors that can develop anywhere there are fat cells, commonly appearing on the neck, shoulders, back, abdomen, arms, and thighs but can also occur behind the ear.
Lipomas feel soft and doughy when touched and can be easily movable. They typically have a diameter of less than 5 cm, but they can grow larger. Lipomas can cause pain if they grow and press against nearby nerves or if the lump contains a lot of blood vessels.
Lipomas are harmless and do not require treatment, but they can be uncomfortable. Therefore, you may visit a hospital to have the lump removed if it affects your quality of life.
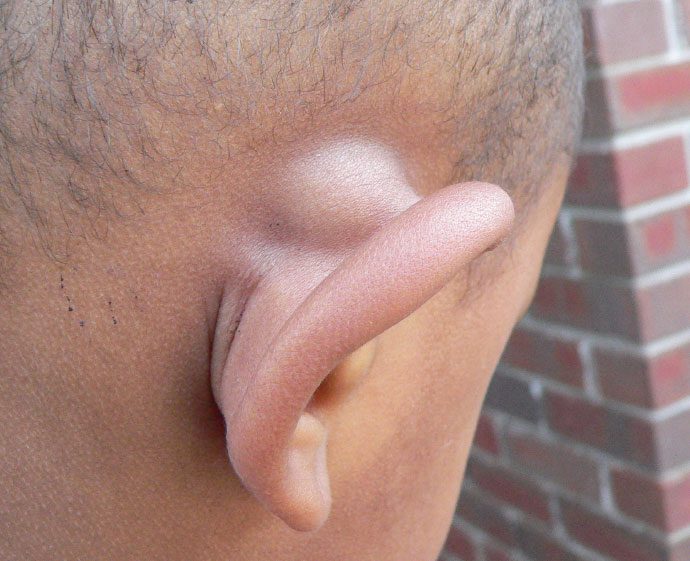
A lipoma behind the ear is soft and doughy to the touch. (Image: Internet).
5. Mastoiditis
Mastoiditis is a bacterial infection affecting the mastoid bone, which is part of the skull located behind the ear.
Mastoiditis is more common in children than adults. It is a serious infection that requires medical attention. The swelling behind the ear is often soft and may push the ear outward.
Other symptoms of mastoiditis that may accompany the lump include:
- Ear discharge
- Possible hearing loss
- Fever
- Fatigue
- Headache
A person is more likely to have mastoiditis if they have a severe ear infection or frequent ear infections.
To treat mastoiditis, a visit to the hospital is necessary. Doctors may prescribe antibiotics or perform surgery to drain and remove the infection.
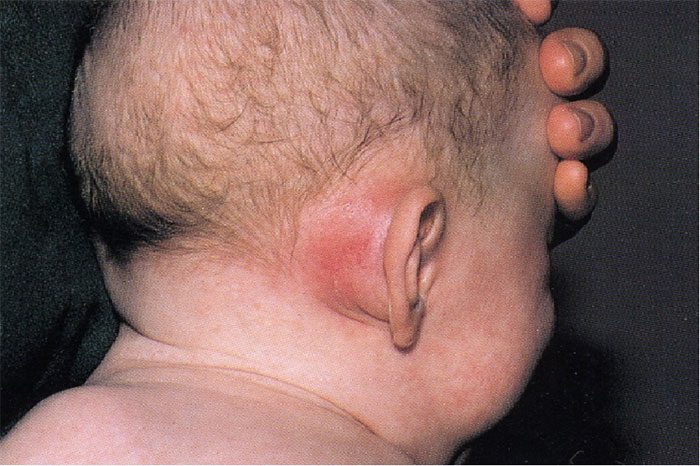
Lumps behind the ear due to mastoiditis often occur in children. (Image: Internet).
6. Cancer
Although uncommon, a lump behind the ear can be a sign of cancer. This includes salivary gland cancer.
Cancerous lumps often have the following characteristics:
- Fixed in place and difficult to move
- Irregular shape of the lump
- Feels firm
Pain and discomfort are not necessarily signs of a cancerous lump. Some benign lumps can cause pain, while some malignant tumors may not be painful.
When to See a Doctor?
Although most lumps behind the ear are benign, this does not mean that you won’t encounter a serious condition. Therefore, when noticing lumps behind the ear, you should visit a hospital for an examination.
In particular, if the lump shows any of the following signs, you should seek medical attention promptly:
- Causing pain, swelling, and redness.
- Fixed in place and immovable.
- Appearing suddenly.
- Larger or not reducing in size after a few weeks.
- Accompanied by symptoms such as fever, night sweats, or unexplained weight loss.
What does a lump on the right side of the neck indicate? Is it dangerous?



















































