On June 13, the Sichuan Provincial Institute of Archaeology and Cultural Relics (China) announced an astonishing discovery of 13,000 artifacts excavated from six sacrificial pits at Sanxingdui (near Chengdu), an archaeological site that has previously shocked the world.
Sanxingdui is a very mysterious site for both archaeologists and historians. In fact, historians know relatively little about the Sanxingdui culture due to the lack of historical records or remaining human remains. Although many believe that Sanxingdui is part of the ancient Shu kingdom, there is still very little information available.
However, the new findings at this site may help archaeologists gain a better understanding of the kingdom that once ruled the western Sichuan Basin, along the upper reaches of the Yangtze River, until it was conquered in 316 BC.
According to the announcement from the Sichuan Provincial Institute of Archaeology and Cultural Relics, all sacrificial pits except for pits 5 and 6, which are dated later, are believed to date back to the late Shang Dynasty, approximately 3,000 to 3,200 years ago.
Moreover, experts also confirm that the Sanxingdui culture is considered an important part of Chinese civilization.
According to Xinhua, thanks to the excavation and the determination that the sacrificial pits are over 3,000 years old, archaeologists have resolved the decades-long debate over the dating mystery of Sanxingdui.
Unique Discoveries at Sanxingdui
Previously, a team of archaeologists from the Sichuan Provincial Institute of Cultural Heritage and Archaeology, Peking University, Sichuan University, and other research institutions began excavating six pits at the Sanxingdui site in 2020.
According to Xinhua, in the most recent excavation, archaeologists found 3,155 relatively intact artifacts, including over 2,000 bronze artifacts and statues.

Archaeologists discovered a bronze box containing a piece of jade at Sanxingdui. (Photo: Xinhua).
Notably, among the artifacts, archaeologists discovered a bronze box shaped like a turtle containing a piece of jade. This is one of the most remarkable discoveries at the Sanxingdui site, and archaeologists believe it is the first time they have uncovered such an object.
In an interview with Xinhua, Professor Li Haichao from Sichuan University remarked: “It would not be an exaggeration to say that this is a unique item due to its special shape, exquisite craftsmanship, and clever design. Although we do not know what this object was used for, we can speculate that ancient people regarded it as a treasure.”
In addition to the unique box, archaeologists also found a bronze altar about 0.9 meters tall in one of the burial pits at Sanxingdui. According to experts, the people of the ancient Shu kingdom may have used the altar to present offerings and sacrifices to ancestors, heaven, and earth. The traces of bamboo, reeds, soybeans, livestock, and wild boar found around the pits indicate that all these items were used as sacrificial offerings.

The bronze altar found in sacrificial pit number 8 at Sanxingdui. (Photo: Xinhua).
These new archaeological discoveries primarily come from sacrificial pits 7 and 8 at the Sanxingdui site.
In pit number 7, many artifacts and valuable items made of jade and bronze were found. Meanwhile, in sacrificial pit number 8, in addition to the bronze altar, archaeologists uncovered a variety of artifacts such as a gold mask, a sculpture with a human head and a snake body made of bronze, and more.
Associate Professor Zhao Hao from Peking University, who led the excavation at pit number 8, assessed: “These sculptures are very complex, rich in imagination, and reflect the world as envisioned by humans at that time. They also exhibit the diversity and richness of Chinese civilization.”
Mr. Ran Honglin, Director of the Sanxingdui Cultural Heritage and Archaeology Institute, mentioned that the diversity of artifacts at this site indicates cultural exchanges between ancient civilizations in China.
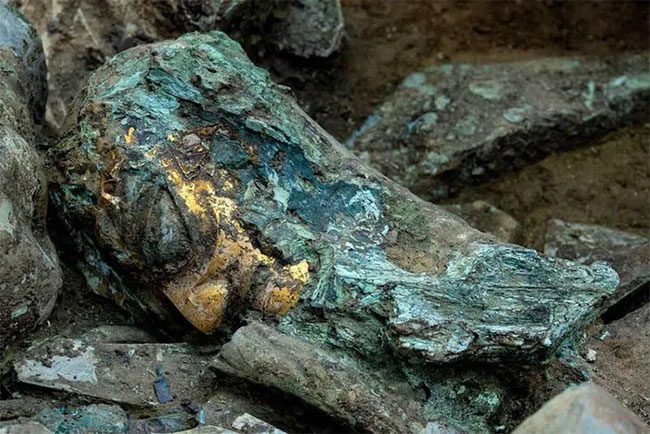

The bronze head with a gold mask found from sacrificial pit number 8 at Sanxingdui. (Photo: Xinhua)
Sanxingdui – An Archaeological Site That Shocked the World
The Sanxingdui site is located on the south bank of the Yazi River, in the northwest of Guanghan City, Sichuan Province, China. It is considered one of the most important archaeological discoveries of the 20th century, having shocked the world.
The reason Sanxingdui has achieved such groundbreaking discoveries in archaeology is due to the participation and cooperation of 39 scientific research organizations, universities, and numerous technology companies behind the excavation efforts. This large team of experts has made significant breakthroughs in excavation, preservation, and interdisciplinary research.
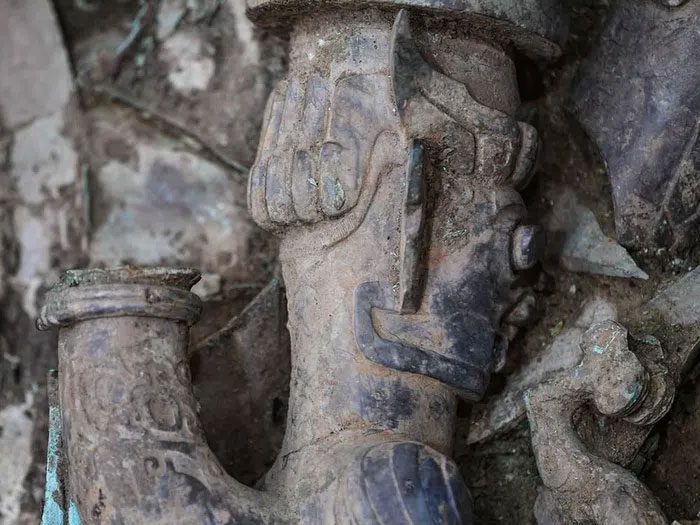

In sacrificial pit number 8, archaeologists found a bronze sculpture depicting a human head and a snake body. (Photo: Xinhua)
Sanxingdui covers an area of 12 km² and is believed to be the remnants of the Shu kingdom, dating from approximately 4,500 to 3,000 years ago.
This site was first discovered in the late 1920s when a farmer accidentally found over 400 jade artifacts.
In the 1980s, archaeologists unexpectedly discovered two sacrificial pits with over 1,700 artifacts. However, excavation work was halted until 2019. According to SCMP, from 2020 to 2022, experts uncovered six additional sacrificial pits at the Sanxingdui site. Therefore, a total of eight sacrificial pits have now been found at Sanxingdui.
Notably, in 2021, archaeologists were astonished to find a gold mask weighing about 100 grams, along with artifacts made of ivory and jade at this mysterious site. Additionally, in sacrificial pit number 5, experts also discovered many pieces of gold.
Over 90 years since the initial discovery, every excavation at Sanxingdui has become a topic of curiosity for many. A series of rare artifacts have been found at this archaeological site. Some bronze statues and masks remain intact with exquisite craftsmanship, leading many experts to believe they could not have come from a simple civilization. Consequently, people often joke that Sanxingdui may have connections to an extraterrestrial civilization.
According to researchers, the discovery of numerous bronze artifacts at Sanxingdui indicates that the bronzing technology and craftsmanship of the artisans in the ancient Shu kingdom were highly advanced.
In the future, archaeologists and experts will continue their research to uncover the mysteries of Sanxingdui, a place that holds one of humanity’s enigmatic civilizations.